Sample Solution from
Organic Chemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305080485
Chapter 1.SE
Problem 18VC
Try another sample solutionarrow_forward
Textbook Problem
Convert each of the following molecular models into a skeletal structure, and give the formula of each. Only the connections between atoms are shown; multiple bonds are not indicated (gray = C, red = O, blue = N, ivory = H).
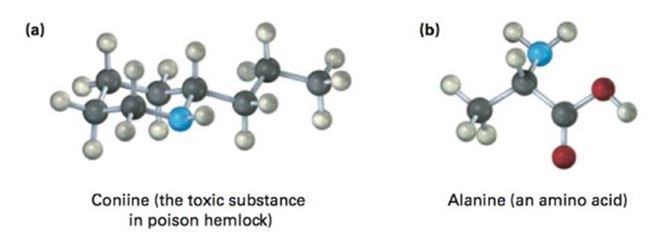
check_circle
Expert Solution
Interpretation Introduction
a) Coniine (the toxic substance in poison hemlock)
Interpretation:
The molecular orbital picture of Coniine (the toxic substance in poison hemlock) is given. It has to be converted into its skeletal structure, and its formula is to be stated.Concept introduction:
In skeletal structures the carbon atoms are not usually shown. Instead a carbon is assumed to be at each intersection of two lines and at the end of each line. The hydrogen atoms bonded to carbons are also not shown. The correct number of hydrogen atoms for each carbon atom is assigned keeping in mind that carbon has a valence of 4. The end of a line represents a carbon atom with three hydrogen atoms, CH3; a two-way intersection is a carbon atom with two hydrogen atoms, CH2; a three way intersection is a carbon with hydrogen, CH; a four way intersection is a carbon with no attached hydrogen. Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are shown. Molecular formula can be obtained by counting the number of atoms of each element present in a molecule of coniine.Answer
The skeletal structure of coniine (the toxic substance in poison hemlock) is
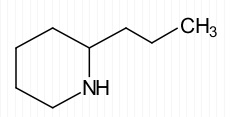
Conine
The molecular formula of conine is C8H17NExplanation of Solution
In skeletal structures the carbon atoms are not usually shown. Instead a carbon is assumed to be at each intersection of two lines and at the end of each line. The hydrogen atoms bonded to carbons are also not shown. The correct number of hydrogen atoms for each carbon atom is assigned keeping in mind that carbon has a valence of 4. The end of a line represents a carbon atom with three hydrogen atoms, CH3; a two-way intersection is a carbon atom with two hydrogen atoms, CH2; a three way intersection is a carbon with a hydrogen, CH; a four way intersection is a carbon with no attached hydrogen. Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are shown. Molecular formula can be obtained by counting the number of atoms of each element present in a molecule of coniine. Conine contains eight carbons, seventeen hydrogens and a nitrogen atom in a molecule. Hence its molecular formula is C8H17N.
Conclusion
The skeletal structure of coniine (the toxic substance in poison hemlock) is

Conine
The molecular formula of conine is C8H17N.check_circle
Expert Solution
Interpretation Introduction
b) Alanine (an amino acid)
Interpretation:
The molecular orbital picture of alanine (an amino acid) is given. It has to be converted into its skeletal structure, and its formula is to be stated.Concept introduction: :
In skeletal structures the carbon atoms are not usually shown. Instead a carbon is assumed to be at each intersection of two lines and at the end of each line. The hydrogen atoms bonded to carbons are also not shown. The correct number of hydrogen atoms for each carbon atom is assigned keeping in mind that carbon has a valence of 4. The end of a line represents a carbon atom with three hydrogen atoms, CH3; a two-way intersection is a carbon atom with two hydrogen atoms, CH2; a three way intersection is a carbon with hydrogen, CH; a four way intersection is a carbon with no attached hydrogen. Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are shown. Molecular formula can be obtained by counting the number of atoms of each element present in a molecule of coniine.Answer
The skeletal structure of alanine (an amino acid) is
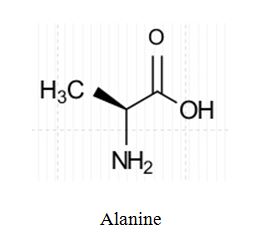
Explanation of Solution
In skeletal structures the carbon atoms are not usually shown. Instead a carbon is assumed to be at each intersection of two lines and at the end of each line. The hydrogen atoms bonded to carbons are also not shown. The correct number of hydrogen atoms for each carbon atom is assigned keeping in mind that carbon has a valence of 4. The end of a line represents a carbon atom with three hydrogen atoms, CH3; a two-way intersection is a carbon atom with two hydrogen atoms, CH2; a three way intersection is a carbon with hydrogen, CH; a four way intersection is a carbon with no attached hydrogen. Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are shown. Molecular formula can be obtained by counting the number of atoms of each element present in a molecule of coniine. Alanine contains three carbons, seven hydrogens, one nitrogen atom and two oxygen atoms in a molecule. Hence its molecular formula is C3H7NO2.
Conclusion
The skeletal structure of Alanine (an amino acid) is

Not sold yet?Try another sample solutionarrow_forward