1. Consider the following schematic of a power plant (operating in what is called a "Rankine Cycle') Tubine Stam gerenter Condenser Culing woter Ecomomiar The power plant control room reports that the plant is operating continuously at the following peak load conditions: a. Power to pump = 300KW b. Rate of steam flow = 25 kg/s c. Cooling water temperature at condenser inlet = 13 C d. Cooling water temperature at condenser outlet = 34 C Additionally, the following measurements were made at various points in the piping connecting the power plant components Data Pressure Temp. Quality enthalpy Specific Velocity (kJ/kg) point (kPa) (x) volume (m/s) (m³/kg) (C) 1 6200 2 6100 43 3 5900 177 4 5700 493 5 5500 482 6 103 0.94 183 7 96 43
1. Consider the following schematic of a power plant (operating in what is called a "Rankine Cycle') Tubine Stam gerenter Condenser Culing woter Ecomomiar The power plant control room reports that the plant is operating continuously at the following peak load conditions: a. Power to pump = 300KW b. Rate of steam flow = 25 kg/s c. Cooling water temperature at condenser inlet = 13 C d. Cooling water temperature at condenser outlet = 34 C Additionally, the following measurements were made at various points in the piping connecting the power plant components Data Pressure Temp. Quality enthalpy Specific Velocity (kJ/kg) point (kPa) (x) volume (m/s) (m³/kg) (C) 1 6200 2 6100 43 3 5900 177 4 5700 493 5 5500 482 6 103 0.94 183 7 96 43
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
ChapterMA: Math Assessment
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1MA
Related questions
Question
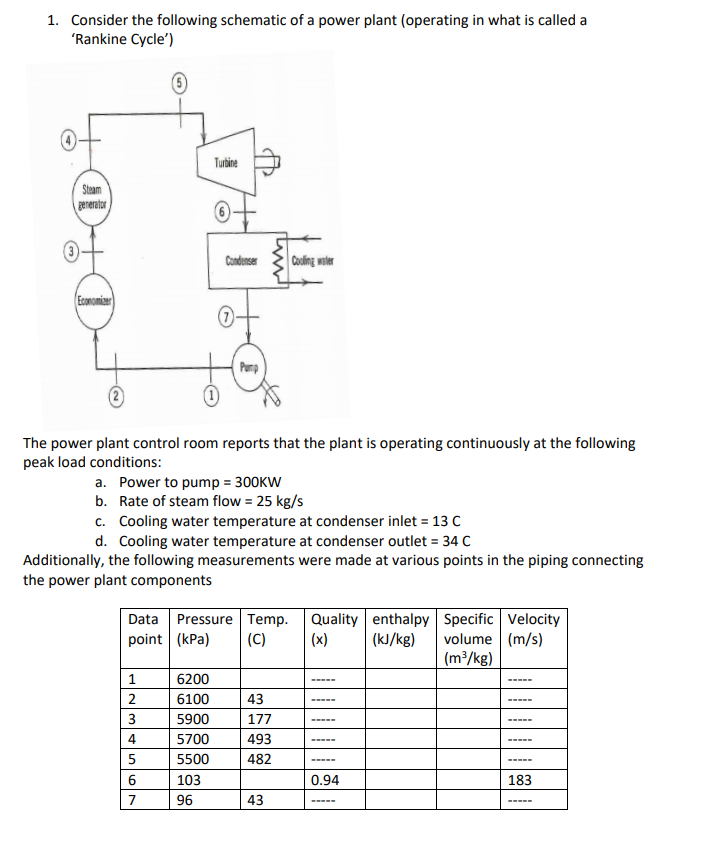
Transcribed Image Text:1. Consider the following schematic of a power plant (operating in what is called a
'Rankine Cycle')
Turbine
Steam
generator
Condenser
Coling water
Economiaer
The power plant control room reports that the plant is operating continuously at the following
peak load conditions:
a. Power to pump = 300KW
b. Rate of steam flow = 25 kg/s
c. Cooling water temperature at condenser inlet = 13 C
d. Cooling water temperature at condenser outlet = 34 C
Additionally, the following measurements were made at various points in the piping connecting
the power plant components
Data Pressure Temp. Quality enthalpy Specific Velocity
(kJ/kg)
point (kPa)
volume (m/s)
(m3/kg)
(C)
(x)
1
6200
2
6100
43
5900
177
----
4.
5700
493
-----
5
5500
482
-----
6
103
0.94
183
7
96
43
-----

Transcribed Image Text:a. What physical phenomena causes the pressure to drop from point 4-5 (and point 1-2)?
b. Define the following types of processes:
• an isothermal process is a constant
_process.
• an isobaric process is a constant
_process.
• An isenthalpic process is a constant
process.
• An isometric process is a constant
process.
• An isentropic process is a constant_
_process.
An adiabatic process does not transfer heat to the
c. Use the pump power and other information to calculate the pump inlet and outlet
conditions.
Step 1: Sketch the entire system (Given in this problem).
• Step 2: Draw the complete control volume (CV) for the component(s) of interest.
Step 3: Show state variables with units and other useful information on CV
sketch.
• Step 3: Write the governing equation.
• Step 4: State all assumptions including type of process and simplify equation(s).
• Step 5: Solve equation(s)
• Step 6: Does it make sense?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 8 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780190698614
Author:
Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:
Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9780134319650
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259822674
Author:
Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118170519
Author:
Norman S. Nise
Publisher:
WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093347
Author:
Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118807330
Author:
James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:
WILEY