1. Implement a Rational Number class with the following specifications. Data members a) numerator and denominator Functions a) Constructors: 1) default constructor 2) single parameter constructor to create numerator/1 3) dual parameter constructor to create numerator/denominator 4) Use constructor delegation across all constructors. b) Accessors and Mutators for both data members. c) Static recursive GCD function using Euclid's algorithm. d) Static LCM function for two numbers. e) Reduce function simplify a rational number. This function modifies its calling object. f) Your program should work with the supplied driver program. Notes LCM (Least Common Multiple) This function returns the smallest multiple of a and b. Step 1: Multiply a and b to find a common multiple. Step 2: Divide the common multiple by the GCD of a and b. Step 3: Return the result of Step 2. Reduce: This function reduces a fraction to simplest terms (i.e. 9/12 to 3/4). Step 1: Find the GCD of the numerator and denominator. Step 2: Divide the numerator by GCD and store as the new numerator. Step 3: Divide the denominator by GCD and store as the new denominator. Static Functions Recall that static functions are class functions and not associated with instances of the class (objects). In this class, the static functions GCD and LCM should accept inputs any input pair (a and b) and return an answer based upon that input pair. As such, these functions can be used by the programmer upon Rational Number objects or random values for a and b. Example Driver Program int main() { cout <« endl; // test constructors, accessors, mutators cout <« "Default Constructor: "; RatNum r1; cout « r1.getNum() <« "/" « r1.getDen() « endl; cout <« "Single Parameter Constructor: "; RatNum r2(2); cout « r2.getNum( ) << "/" « r2.getDen() « endl; cout <« "Dual Parameter Constructor: "; RatNum r3(1,3); cout <« r3.getNum() <« "/" « r3.getDen() « endl; cout <« "Accessors / Mutators: "; r3.setNum(3); r3.setDen(12); cout « r3.getNum( ) << "/" « r3.getDen() « endl; // test gcd cout <« "\NGCD of the last fraction: " « RatNum::gcd(r3.getNum(),r3.getDen()) <« endl; cout <« "GCD of 40 and 24: " « RatNum::gcd(40,24) « endl; // test lcm cout << "\NLCM of the last fraction: " « RatNum::lcm(r3.getNum(), r3.getDen()) « endl; cout <« "LCM of 3 and 5: " <« RatNum::lcm(3,5) <« endl; // test reduce cout << "\nReducing the last fraction: "; r3. reduce(); cout « r3.getNum( ) <« "/" « r3.getDen() « endl; cout « endl; return 0;
1. Implement a Rational Number class with the following specifications. Data members a) numerator and denominator Functions a) Constructors: 1) default constructor 2) single parameter constructor to create numerator/1 3) dual parameter constructor to create numerator/denominator 4) Use constructor delegation across all constructors. b) Accessors and Mutators for both data members. c) Static recursive GCD function using Euclid's algorithm. d) Static LCM function for two numbers. e) Reduce function simplify a rational number. This function modifies its calling object. f) Your program should work with the supplied driver program. Notes LCM (Least Common Multiple) This function returns the smallest multiple of a and b. Step 1: Multiply a and b to find a common multiple. Step 2: Divide the common multiple by the GCD of a and b. Step 3: Return the result of Step 2. Reduce: This function reduces a fraction to simplest terms (i.e. 9/12 to 3/4). Step 1: Find the GCD of the numerator and denominator. Step 2: Divide the numerator by GCD and store as the new numerator. Step 3: Divide the denominator by GCD and store as the new denominator. Static Functions Recall that static functions are class functions and not associated with instances of the class (objects). In this class, the static functions GCD and LCM should accept inputs any input pair (a and b) and return an answer based upon that input pair. As such, these functions can be used by the programmer upon Rational Number objects or random values for a and b. Example Driver Program int main() { cout <« endl; // test constructors, accessors, mutators cout <« "Default Constructor: "; RatNum r1; cout « r1.getNum() <« "/" « r1.getDen() « endl; cout <« "Single Parameter Constructor: "; RatNum r2(2); cout « r2.getNum( ) << "/" « r2.getDen() « endl; cout <« "Dual Parameter Constructor: "; RatNum r3(1,3); cout <« r3.getNum() <« "/" « r3.getDen() « endl; cout <« "Accessors / Mutators: "; r3.setNum(3); r3.setDen(12); cout « r3.getNum( ) << "/" « r3.getDen() « endl; // test gcd cout <« "\NGCD of the last fraction: " « RatNum::gcd(r3.getNum(),r3.getDen()) <« endl; cout <« "GCD of 40 and 24: " « RatNum::gcd(40,24) « endl; // test lcm cout << "\NLCM of the last fraction: " « RatNum::lcm(r3.getNum(), r3.getDen()) « endl; cout <« "LCM of 3 and 5: " <« RatNum::lcm(3,5) <« endl; // test reduce cout << "\nReducing the last fraction: "; r3. reduce(); cout « r3.getNum( ) <« "/" « r3.getDen() « endl; cout « endl; return 0;
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design
8th Edition
ISBN:9781337102087
Author:D. S. Malik
Publisher:D. S. Malik
Chapter10: Classes And Data Abstraction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7SA: Assume the definition of class foodType as given in Exercise 6. Answer the following questions? (1,...
Related questions
Question
100%
I'm stuck on this question and I don't know how I should be approaching this. What should I do?

Transcribed Image Text:1. Implement a Rational Number class with the following specifications.
Data members
a) numerator and denominator
Functions
a) Constructors:
1) default constructor
2) single parameter constructor to create numerator/1
3) dual parameter constructor to create numerator/denominator
4) Use constructor delegation across all constructors.
b) Accessors and Mutators for both data members.
c) Static recursive GCD function using Euclid's algorithm.
d) Static LCM function for two numbers.
e) Reduce function simplify a rational number.
This function modifies its calling object.
f) Your program should work with the supplied driver program.
Notes
LCM (Least Common Multiple)
This function returns the smallest multiple of a and b.
Step 1: Multiply a and b to find a common multiple.
Step 2: Divide the common multiple by the GCD of a and b.
Step 3: Return the result of Step 2.
Reduce:
This function reduces a fraction to simplest terms (i.e. 9/12 to 3/4).
Step 1: Find the GCD of the numerator and denominator.
Step 2: Divide the numerator by GCD and store as the new numerator.
Step 3: Divide the denominator by GCD and store as the new denominator.
Static Functions
Recall that static functions are class functions and not associated with
instances of the class (objects). In this class, the static functions GCD
and LCM should accept inputs any input pair (a and b) and return an answer
based upon that input pair. As such, these functions can be used by the
programmer upon Rational Number objects or random values for a and b.
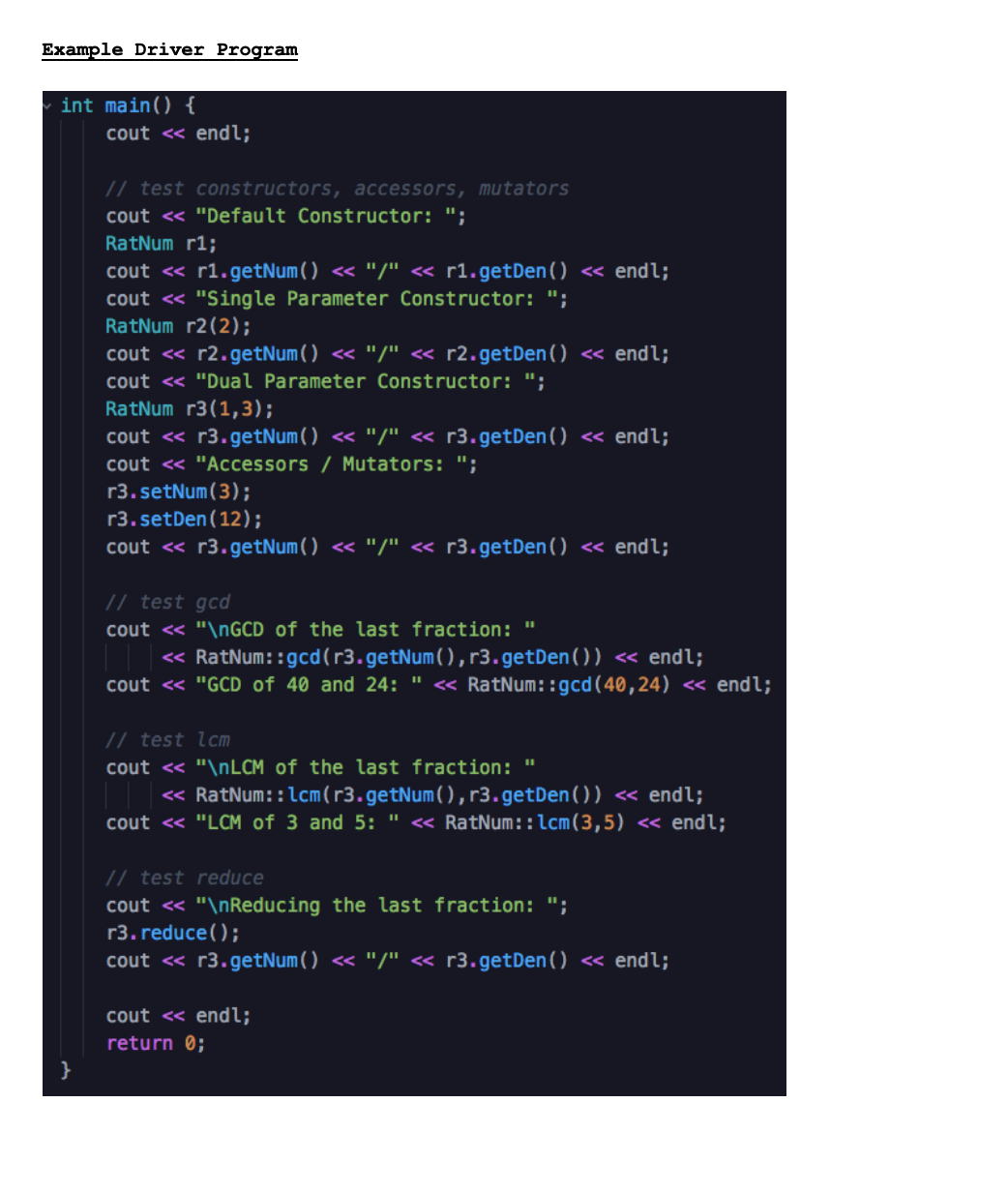
Transcribed Image Text:Example Driver Program
int main() {
cout <« endl;
// test constructors, accessors, mutators
cout <« "Default Constructor: ";
RatNum r1;
cout « r1.getNum() <« "/" « r1.getDen() « endl;
cout <« "Single Parameter Constructor: ";
RatNum r2(2);
cout « r2.getNum( ) << "/" « r2.getDen() « endl;
cout <« "Dual Parameter Constructor: ";
RatNum r3(1,3);
cout <« r3.getNum() <« "/" « r3.getDen() « endl;
cout <« "Accessors / Mutators: ";
r3.setNum(3);
r3.setDen(12);
cout « r3.getNum( ) << "/" « r3.getDen() « endl;
// test gcd
cout <« "\NGCD of the last fraction: "
« RatNum::gcd(r3.getNum(),r3.getDen()) <« endl;
cout <« "GCD of 40 and 24: " « RatNum::gcd(40,24) « endl;
// test lcm
cout << "\NLCM of the last fraction: "
« RatNum::lcm(r3.getNum(), r3.getDen()) « endl;
cout <« "LCM of 3 and 5: " <« RatNum::lcm(3,5) <« endl;
// test reduce
cout << "\nReducing the last fraction: ";
r3. reduce();
cout « r3.getNum( ) <« "/" « r3.getDen() « endl;
cout « endl;
return 0;
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781337102087
Author:
D. S. Malik
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781337102087
Author:
D. S. Malik
Publisher:
Cengage Learning