1. Individual Problems 19-1 In the late 1990s, car leasing was very popular in the United States. A customer would lease a car from the manufacturer for a set term, usually two years, and then have the option of keeping the car. If the customer decided to keep the car, the customer would pay a price to the manufacturer, the "residual value," computed as 60% of the new car price. The manufacturer would then sell the retumed cars at auction. In 1999, manufacturers lost an average of $480 on each returned car (the auction price was, on average, $480 less than the residual value). Suppose two customers have leased cars from a manufacturer. Their lease agreements are up, and they are considering whether to keep (and purchase at 60% of the new car price) their cars or return their cars. Two years ago, Shen leased a car valued new at $15,000. If he returns the car, the manufacturer could likely get $10,500 at auction for the car. Ana also leased a car, valued new at $15,500, two years ago. If she retums the car, the manufacturer could likely get $7,750 at auction for the car. Use the following table to indicate whether each buyer is more likely to purchase or return the car. Buyer Keep and Purchase Car Return Car Shen Ana The manufacturer will lose money (at auction, relative to the residual value of the car) if returns the car instead of keeping and purchasing it. True or False: Setting a more accurate residual price of each car would help attenuate the problems of adverse selection. O True O False
1. Individual Problems 19-1 In the late 1990s, car leasing was very popular in the United States. A customer would lease a car from the manufacturer for a set term, usually two years, and then have the option of keeping the car. If the customer decided to keep the car, the customer would pay a price to the manufacturer, the "residual value," computed as 60% of the new car price. The manufacturer would then sell the retumed cars at auction. In 1999, manufacturers lost an average of $480 on each returned car (the auction price was, on average, $480 less than the residual value). Suppose two customers have leased cars from a manufacturer. Their lease agreements are up, and they are considering whether to keep (and purchase at 60% of the new car price) their cars or return their cars. Two years ago, Shen leased a car valued new at $15,000. If he returns the car, the manufacturer could likely get $10,500 at auction for the car. Ana also leased a car, valued new at $15,500, two years ago. If she retums the car, the manufacturer could likely get $7,750 at auction for the car. Use the following table to indicate whether each buyer is more likely to purchase or return the car. Buyer Keep and Purchase Car Return Car Shen Ana The manufacturer will lose money (at auction, relative to the residual value of the car) if returns the car instead of keeping and purchasing it. True or False: Setting a more accurate residual price of each car would help attenuate the problems of adverse selection. O True O False
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
5th Edition
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Chapter19: The Problem Of Adverse Selection
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 19.1IP
Related questions
Question
Hey Expert, can you confirm correct answer "True" or "False" ?
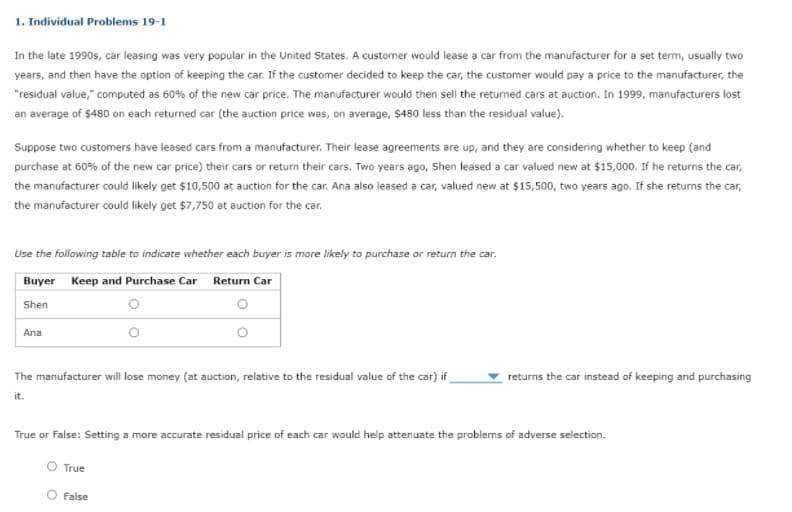
Transcribed Image Text:1. Individual Problems 19-1
In the late 1990s, car leasing was very popular in the United States. A customer would lease a car from the manufacturer for a set term, usually two
years, and then have the option of keeping the car. If the customer decided to keep the car, the customer would pay a price to the manufacturer, the
"residual value," computed as 60% of the new car price. The manufacturer would then sell the retumed cars at auction. In 1999, manufacturers lost
an average of $480 on each returned car (the auction price was, on average, $480 less than the residual value).
Suppose two customers have leased cars from a manufacturer. Their lease agreements are up, and they are considering whether to keep (and
purchase at 60% of the new car price) their cars or return their cars. Two years ago, Shen leased a car valued new at $15,000. If he returns the car,
the manufacturer could likely get $10,500 at auction for the car. Ana also leased a car, valued new at $15,500, two years ago. If she returns the car,
the manufacturer could likely get $7,750 at auction for the car.
Use the following table to indicate whether each buyer is more likely to purchase or return the car.
Buyer Keep and Purchase Car Return Car
Shen
Ana
The manufacturer will lose money (at auction, relative to the residual value of the car) if
returns the car instead of keeping and purchasing
it.
True or False: Setting a more accurate residual price of each car would help attenuate the problems of adverse selection.
O True
False
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou…
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165875
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781285165912
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning