(1). % of men in this study received only Vitamin E and developed prostate cancer. (2). % of men who took a placebo eventually developed prostate cancer. (3). % of men who did not develop prostate cancer took a placebo.
(1). % of men in this study received only Vitamin E and developed prostate cancer. (2). % of men who took a placebo eventually developed prostate cancer. (3). % of men who did not develop prostate cancer took a placebo.
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
1st Edition
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Chapter11: Data Analysis And Probability
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8CR
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
(1). % of men in this study received only Vitamin E and developed prostate cancer.
(2). % of men who took a placebo eventually developed prostate cancer.
(3). % of men who did not develop prostate cancer took a placebo.
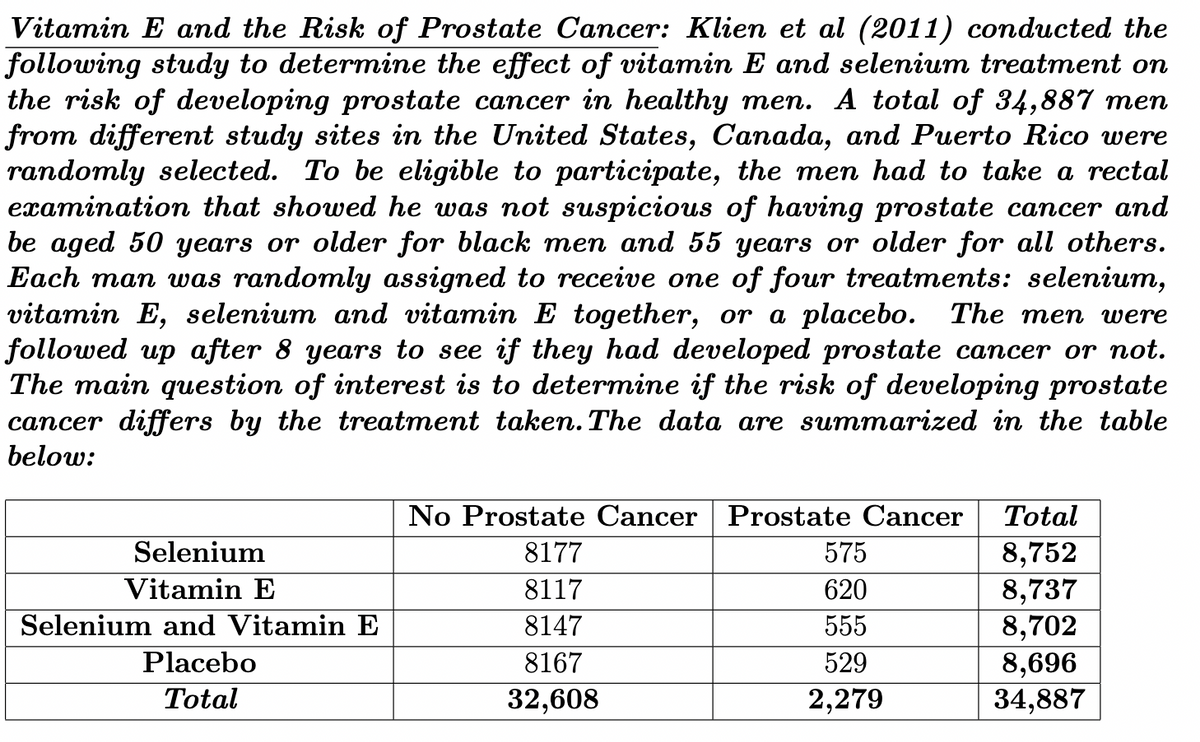
Transcribed Image Text:Vitamin E and the Risk of Prostate Cancer: Klien et al (2011) conducted the
following study to determine the effect of vitamin E and selenium treatment on
the risk of developing prostate cancer in healthy men. A total of 34,887 men
from different study sites in the United States, Canada, and Puerto Rico were
randomly selected. To be eligible to participate, the men had to take a rectal
examination that showed he was not suspicious of having prostate cancer and
be aged 50 years or older for black men and 55 years or older for all others.
Each man was randomly assigned to receive one of four treatments: selenium,
vitamin E, selenium and vitamin E together, or a placebo. The men were
followed up after 8 years to see if they had developed prostate cancer or not.
The main question of interest is to determine if the risk of developing prostate
cancer differs by the treatment taken. The data are summarized in the table
below:
No Prostate Cancer Prostate Cancer
Total
Selenium
8,752
8,737
8,702
8,696
34,887
8177
575
Vitamin E
8117
620
Selenium and Vitamin E
8147
555
Placebo
8167
529
Total
32,608
2,279
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
