1. Plate count data are used to calculate microbial population density as colony forming units (CFUs) per milliliter of culture. Culture density (CFU/mL) = number of colonies (dilution factor) x (volume plated, in mL) Use these data below to calculate the CFU/mL in this sample of bacteria after 1 hr of growth. **Important to know for these types of questions - only use colony counts that fall between 10 and 300. TNTC = too numerous to count, so many colonies that you can't distinguish them to count. Use the plates with numbers of colonies that can be counted, calculate the CFU on each one, and then calculate the average between all of them. Looking for more assistance? Read section 7.3 in the textbook. Time 1h Dilution (before plating) none 1:10 (1 x 10-¹) 1:100 (1 x 10-²) 1:1,000 (1 x 10-³) Volume spread on plate 0.1 mL 0.1 mL 0.1 mL 0.1 mL Number of colonies observed (replicate plates) TNTC 499 83 10 TNTC 518 87 8 TNTC indicates too numerous to count. *Cell density could not be calculated accurately because plates contained too many colonies to be counted, too many colonies to be counted accurately (>300), or too few colon to be meaningful (<10)
1. Plate count data are used to calculate microbial population density as colony forming units (CFUs) per milliliter of culture. Culture density (CFU/mL) = number of colonies (dilution factor) x (volume plated, in mL) Use these data below to calculate the CFU/mL in this sample of bacteria after 1 hr of growth. **Important to know for these types of questions - only use colony counts that fall between 10 and 300. TNTC = too numerous to count, so many colonies that you can't distinguish them to count. Use the plates with numbers of colonies that can be counted, calculate the CFU on each one, and then calculate the average between all of them. Looking for more assistance? Read section 7.3 in the textbook. Time 1h Dilution (before plating) none 1:10 (1 x 10-¹) 1:100 (1 x 10-²) 1:1,000 (1 x 10-³) Volume spread on plate 0.1 mL 0.1 mL 0.1 mL 0.1 mL Number of colonies observed (replicate plates) TNTC 499 83 10 TNTC 518 87 8 TNTC indicates too numerous to count. *Cell density could not be calculated accurately because plates contained too many colonies to be counted, too many colonies to be counted accurately (>300), or too few colon to be meaningful (<10)
Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative and Clinical Competencies (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN:9781305964792
Author:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy Correa
Publisher:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy Correa
Chapter42: Basic Microbiology
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 4CR
Related questions
Question
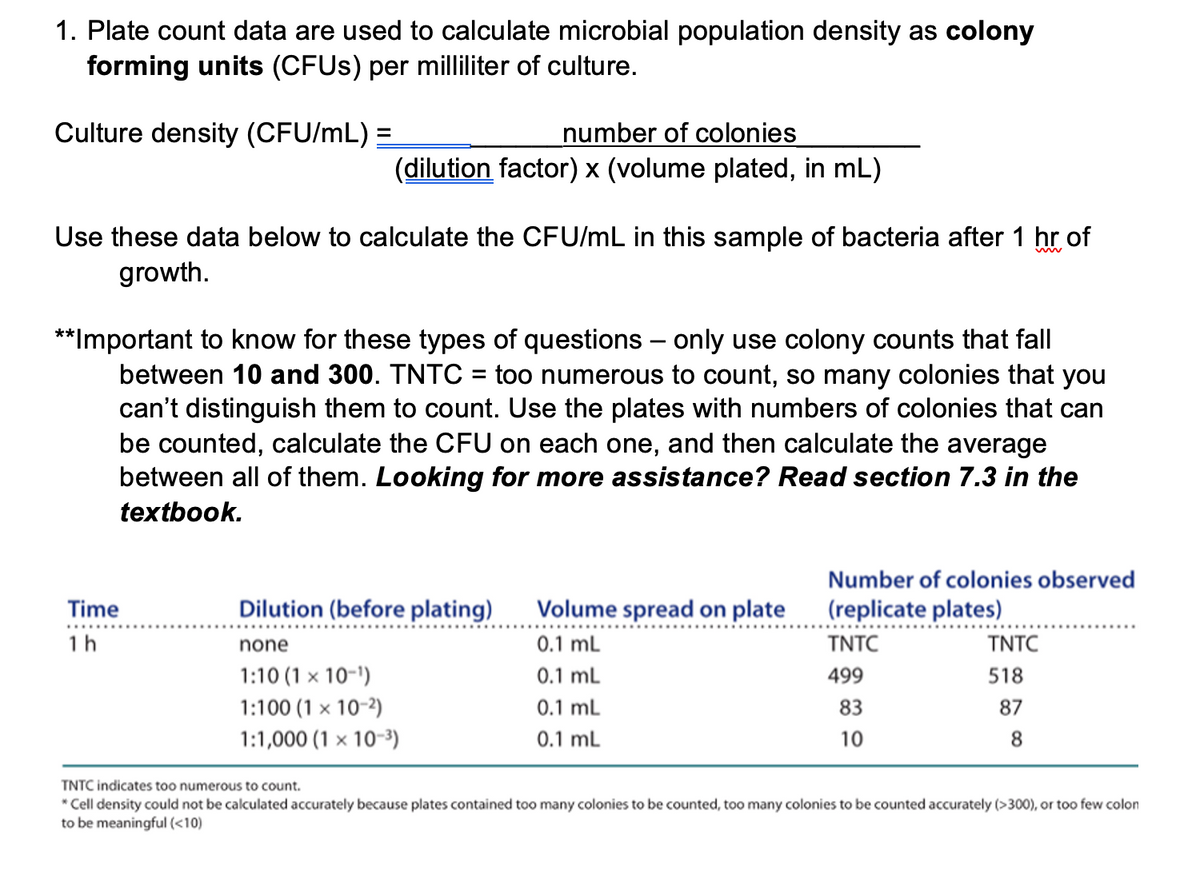
Transcribed Image Text:1. Plate count data are used to calculate microbial population density as colony
forming units (CFUs) per milliliter of culture.
Culture density (CFU/mL) =
number of colonies
(dilution factor) x (volume plated, in mL)
Use these data below to calculate the CFU/mL in this sample of bacteria after 1 hr of
growth.
**Important to know for these types of questions - only use colony counts that fall
between 10 and 300. TNTC = too numerous to count, so many colonies that you
can't distinguish them to count. Use the plates with numbers of colonies that can
be counted, calculate the CFU on each one, and then calculate the average
between all of them. Looking for more assistance? Read section 7.3 in the
textbook.
Time
1h
Dilution (before plating) Volume spread on plate
0.1 mL
0.1 mL
0.1 mL
0.1 mL
none
1:10 (1 x 10-¹)
1:100 (1 x 10-²)
1:1,000 (1 x 10-³)
Number of colonies observed
(replicate plates)
TNTC
499
83
10
TNTC
518
87
8
TNTC indicates too numerous to count.
*Cell density could not be calculated accurately because plates contained too many colonies to be counted, too many colonies to be counted accurately (>300), or too few colon
to be meaningful (<10)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a…
Nursing
ISBN:
9781305964792
Author:
Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy Correa
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a…
Nursing
ISBN:
9781305964792
Author:
Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy Correa
Publisher:
Cengage Learning