1. The electric field E is defined to be E = where F is the electrostatic force exerted on a small positive test charge q . E has units of N/C. 2. In uniform electric field the potential difference is AV = Ed, where E is electric field and d is the distance from A to B, or the distance between the plates. 3. A capacitor is a device used to store charge. The amount of charge q a capacitor can store depends on two major factors - the voltage applied and the capacitor's physical characteristics, such as its size. The capacitance C is the amount of charge stored per volt, or C = , units Farad (F). 4. Capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor Cc = td, where e, = 8.85 - 10-12 F/m is called the permittivity of free space, e is the dielectric constant of the material, A is area of plates and d is distance between plates. 5. Capacitors are used in a variety of devices, including defibrillators, microelectronics such as calculators, and flash lamps, to supply energy. The energy stored in a capacitor can be expressed in three ways: E = 94V capacitor(F). 6. Electric current I is the rate at which charge flows, given by / =, units Amperes (A). Here q is the amount of charge passing through an area in time t. 7. Current density is current per unit of cross sectional area / = , units A/m. 8. Ohm's law. One statement of Ohm's law gives the relationship between current I, voltage V , and resistance R in a simple circuit to be I = ". Here R is resistance in units of ohms ( 2 ). 9. Electric power. p=AV·1 = 1°R = 10. Heat effect of electrical current Q =AV 1·t = 1°R = 11. Resistors connections (a) in series R = R1 + R2 + Rą . + RN (b) in parallel = ; сдит where q is the charge (C), AV is the voltage (V), and C is the capacitance of the AV R. R. R. (a) R, RN here N total is number of the resistors. R2 Table 1 - Effects of Electrical Shock as a Function of Current Effect Effect Current Current (mA) |1 (mA) 50 Threshold of sensation Maximum harmless current Onset of pain Ventricular fibrillation possible; often fatal. 100-300 depending 300 Onset of burns on concentration of current Onset of sustained ventricular contraction and respiratory paralysis; both cease when shock ends; heartbeat may return to normal; used to defibrillate the heart Onset of sustained muscular contraction; cannot let go for duration of shock; contraction of chest muscles may stop breathing during shock |10-20 6000 PROBLEMS 1. Electrical currents through people can produce tremendously varied effects. The major factors upon which the effects of electrical shock depend are the amount of current I, the path taken by the current and the a person, for different current paths. (b) Using Table 1 make conclusion about physiological effect of these currents. (c) What was the power dissipated in his body? Table 2 Drd not shocked Cum Fow Current, A Person (SHOCKEDN Current path Resistance, Ohms 1000 Hgh Vatage and Load Hand-body-hand One hand-body-feet Hands-body-feet Foot-foot 650 1300
1. The electric field E is defined to be E = where F is the electrostatic force exerted on a small positive test charge q . E has units of N/C. 2. In uniform electric field the potential difference is AV = Ed, where E is electric field and d is the distance from A to B, or the distance between the plates. 3. A capacitor is a device used to store charge. The amount of charge q a capacitor can store depends on two major factors - the voltage applied and the capacitor's physical characteristics, such as its size. The capacitance C is the amount of charge stored per volt, or C = , units Farad (F). 4. Capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor Cc = td, where e, = 8.85 - 10-12 F/m is called the permittivity of free space, e is the dielectric constant of the material, A is area of plates and d is distance between plates. 5. Capacitors are used in a variety of devices, including defibrillators, microelectronics such as calculators, and flash lamps, to supply energy. The energy stored in a capacitor can be expressed in three ways: E = 94V capacitor(F). 6. Electric current I is the rate at which charge flows, given by / =, units Amperes (A). Here q is the amount of charge passing through an area in time t. 7. Current density is current per unit of cross sectional area / = , units A/m. 8. Ohm's law. One statement of Ohm's law gives the relationship between current I, voltage V , and resistance R in a simple circuit to be I = ". Here R is resistance in units of ohms ( 2 ). 9. Electric power. p=AV·1 = 1°R = 10. Heat effect of electrical current Q =AV 1·t = 1°R = 11. Resistors connections (a) in series R = R1 + R2 + Rą . + RN (b) in parallel = ; сдит where q is the charge (C), AV is the voltage (V), and C is the capacitance of the AV R. R. R. (a) R, RN here N total is number of the resistors. R2 Table 1 - Effects of Electrical Shock as a Function of Current Effect Effect Current Current (mA) |1 (mA) 50 Threshold of sensation Maximum harmless current Onset of pain Ventricular fibrillation possible; often fatal. 100-300 depending 300 Onset of burns on concentration of current Onset of sustained ventricular contraction and respiratory paralysis; both cease when shock ends; heartbeat may return to normal; used to defibrillate the heart Onset of sustained muscular contraction; cannot let go for duration of shock; contraction of chest muscles may stop breathing during shock |10-20 6000 PROBLEMS 1. Electrical currents through people can produce tremendously varied effects. The major factors upon which the effects of electrical shock depend are the amount of current I, the path taken by the current and the a person, for different current paths. (b) Using Table 1 make conclusion about physiological effect of these currents. (c) What was the power dissipated in his body? Table 2 Drd not shocked Cum Fow Current, A Person (SHOCKEDN Current path Resistance, Ohms 1000 Hgh Vatage and Load Hand-body-hand One hand-body-feet Hands-body-feet Foot-foot 650 1300
College Physics
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Chapter18: Electric Charge And Electric Field
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 54PE: Earth has a net charge that produces an electric field of approximately 150 N/C downward at its...
Related questions
Question
100%
Lower voltage and higher frequency are considered less dangerous for human health and life. In the United States of America the standard voltage is 120 V and the frequency is 60 Hz (European standard voltage is 220 V). Calculate the value of a current flowing through a person, for different current paths (Table 2). (b) What was the power dissipated in his body? (b) Using Table 1 make conclusion about physiological effect of these currents. (c) Estimate heat effect of the current if the impact duration was 5 msec? 3
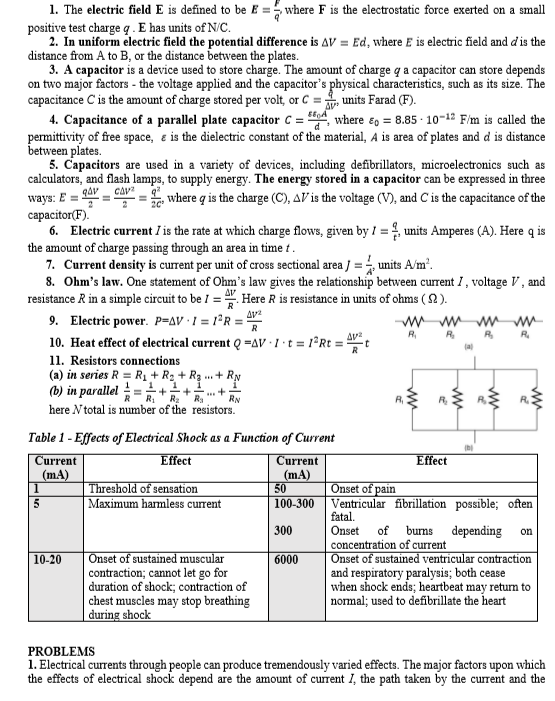
Transcribed Image Text:1. The electric field E is defined to be E = where F is the electrostatic force exerted on a small
positive test charge q . E has units of N/C.
2. In uniform electric field the potential difference is AV = Ed, where E is electric field and d is the
distance from A to B, or the distance between the plates.
3. A capacitor is a device used to store charge. The amount of charge q a capacitor can store depends
on two major factors - the voltage applied and the capacitor's physical characteristics, such as its size. The
capacitance C is the amount of charge stored per volt, or C = , units Farad (F).
4. Capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor Cc = td, where e, = 8.85 - 10-12 F/m is called the
permittivity of free space, e is the dielectric constant of the material, A is area of plates and d is distance
between plates.
5. Capacitors are used in a variety of devices, including defibrillators, microelectronics such as
calculators, and flash lamps, to supply energy. The energy stored in a capacitor can be expressed in three
ways: E = 94V
capacitor(F).
6. Electric current I is the rate at which charge flows, given by / =, units Amperes (A). Here q is
the amount of charge passing through an area in time t.
7. Current density is current per unit of cross sectional area / = , units A/m.
8. Ohm's law. One statement of Ohm's law gives the relationship between current I, voltage V , and
resistance R in a simple circuit to be I = ". Here R is resistance in units of ohms ( 2 ).
9. Electric power. p=AV·1 = 1°R =
10. Heat effect of electrical current Q =AV 1·t = 1°R =
11. Resistors connections
(a) in series R = R1 + R2 + Rą . + RN
(b) in parallel = ;
сдит
where q is the charge (C), AV is the voltage (V), and C is the capacitance of the
AV
R.
R.
R.
(a)
R,
RN
here N total is number of the resistors.
R2
Table 1 - Effects of Electrical Shock as a Function of Current
Effect
Effect
Current
Current
(mA)
|1
(mA)
50
Threshold of sensation
Maximum harmless current
Onset of pain
Ventricular fibrillation possible; often
fatal.
100-300
depending
300
Onset
of
burns
on
concentration of current
Onset of sustained ventricular contraction
and respiratory paralysis; both cease
when shock ends; heartbeat may return to
normal; used to defibrillate the heart
Onset of sustained muscular
contraction; cannot let go for
duration of shock; contraction of
chest muscles may stop breathing
during shock
|10-20
6000
PROBLEMS
1. Electrical currents through people can produce tremendously varied effects. The major factors upon which
the effects of electrical shock depend are the amount of current I, the path taken by the current and the
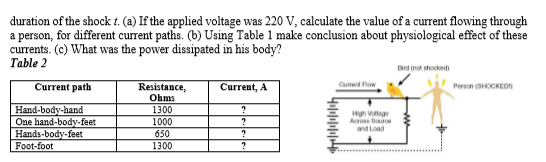
Transcribed Image Text:a person, for different current paths. (b) Using Table 1 make conclusion about physiological effect of these
currents. (c) What was the power dissipated in his body?
Table 2
Drd not shocked
Cum Fow
Current, A
Person (SHOCKEDN
Current path
Resistance,
Ohms
1000
Hgh Vatage
and Load
Hand-body-hand
One hand-body-feet
Hands-body-feet
Foot-foot
650
1300
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 8 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning