1. Two narrow slits separated by 1.5 mm are illuminated by light of wavelength 600 nm, and the interference pattern is viewed on a screen 1.2 m away. Calculate the number of bright fringes per centimeter on the screen. 2. A diffraction grating has 5, 400 lines per cm. (a) What range of angles do the visible wavelengths (400 – 700 nm) span in second order maxima? (b) What is the width (in cm) of the resulting second order spectrum on a screen placed 1.5 m away? 3. If you can read the bottom row of your doctor's eye chart, your eye has a resolving power of one arcminute, equal to degree. If this resolving power is diffraction limited, to what effective diameter of your eye's optical system does this correspond? Use Raleigh's criterion and assume A = 550 nm. 4. The direction of polarization of linearly polarized light is rotated through 90°, using two Polaroid filters. The first filter's polarization axis makes an angle of 20° with the incoming light's polarization direction. The second filter further rotates the light by 70º. By how much is the intensity reduced? 5. The polarizing angle for a certain substance is 63.4° (i.e., for a ray travelling from air into the substance) (a) What is the angle of refraction of light incident at this angle? (b) What is the index of refraction of this substance?
1. Two narrow slits separated by 1.5 mm are illuminated by light of wavelength 600 nm, and the interference pattern is viewed on a screen 1.2 m away. Calculate the number of bright fringes per centimeter on the screen. 2. A diffraction grating has 5, 400 lines per cm. (a) What range of angles do the visible wavelengths (400 – 700 nm) span in second order maxima? (b) What is the width (in cm) of the resulting second order spectrum on a screen placed 1.5 m away? 3. If you can read the bottom row of your doctor's eye chart, your eye has a resolving power of one arcminute, equal to degree. If this resolving power is diffraction limited, to what effective diameter of your eye's optical system does this correspond? Use Raleigh's criterion and assume A = 550 nm. 4. The direction of polarization of linearly polarized light is rotated through 90°, using two Polaroid filters. The first filter's polarization axis makes an angle of 20° with the incoming light's polarization direction. The second filter further rotates the light by 70º. By how much is the intensity reduced? 5. The polarizing angle for a certain substance is 63.4° (i.e., for a ray travelling from air into the substance) (a) What is the angle of refraction of light incident at this angle? (b) What is the index of refraction of this substance?
Related questions
Question
Please help with question #4. Thank you.

Transcribed Image Text:1. Two narrow slits separated by 1.5 mm are illuminated by light of wavelength 600 nm,
and the interference pattern is viewed on a screen 1.2 m away. Calculate the number of
bright fringes per centimeter on the screen.
2. A diffraction grating has 5, 400 lines per cm. (a) What range of angles do the visible
wavelengths (400 – 700 nm) span in second order maxima? (b) What is the width (in cm)
of the resulting second order spectrum on a screen placed 1.5 m away?
3. If you can read the bottom row of your doctor's eye chart, your eye has a resolving power
of one arcminute, equal to degree. If this resolving power is diffraction limited, to what
effective diameter of your eye's optical system does this correspond? Use Raleigh's criterion
and assume A = 550 nm.
4. The direction of polarization of linearly polarized light is rotated through 90°, using two
Polaroid filters. The first filter's polarization axis makes an angle of 20° with the incoming
light's polarization direction. The second filter further rotates the light by 70º. By how
much is the intensity reduced?
5. The polarizing angle for a certain substance is 63.4° (i.e., for a ray travelling from air
into the substance) (a) What is the angle of refraction of light incident at this angle? (b)
What is the index of refraction of this substance?
Expert Solution
Step 1
Let the intensity of incident polarized light is I0.
By Malus’s Law, the intensity of the light coming out of the first polarizer is
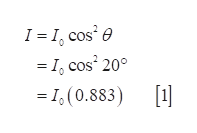
Step 2
The intensity of the light coming out of the second polarizer is
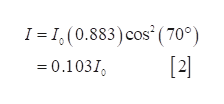
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images
