18. mmh An 0.80-kg object * (m) is attached to one end of a 0.080 spring, as in Figure 10.5, and the system is set into simple harmonic motion. The dis- 4.0 2.0 1.0 3.0 Time (s) placement x of the object as a function of time is shown in the drawing. With the aid of these data, determine (a) the amplitude A of the motion, (b) the angular frequency w, (c) the spring constant k, (d) the speed of the object at t = 1.0 s, and (e) the magnitude of the object's acceleration at 1 = 1.0 s. -0.080 %D
18. mmh An 0.80-kg object * (m) is attached to one end of a 0.080 spring, as in Figure 10.5, and the system is set into simple harmonic motion. The dis- 4.0 2.0 1.0 3.0 Time (s) placement x of the object as a function of time is shown in the drawing. With the aid of these data, determine (a) the amplitude A of the motion, (b) the angular frequency w, (c) the spring constant k, (d) the speed of the object at t = 1.0 s, and (e) the magnitude of the object's acceleration at 1 = 1.0 s. -0.080 %D
Related questions
Question
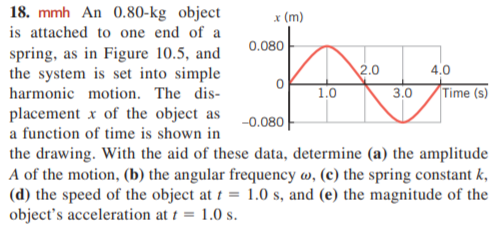
Transcribed Image Text:18. mmh An 0.80-kg object
* (m)
is attached to one end of a
0.080
spring, as in Figure 10.5, and
the system is set into simple
harmonic motion. The dis-
4.0
2.0
1.0
3.0
Time (s)
placement x of the object as
a function of time is shown in
the drawing. With the aid of these data, determine (a) the amplitude
A of the motion, (b) the angular frequency w, (c) the spring constant k,
(d) the speed of the object at t = 1.0 s, and (e) the magnitude of the
object's acceleration at 1 = 1.0 s.
-0.080
%D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 7 steps with 7 images
