2. Let us assume that a given hyperopic eye has a near point at 200 cm. The desired lens is to allow the eye to view objects at 25 cm. Find focal length and power of the lens required to fix this problem. OPTICS Defects of vision. Correction of vision 1. Correction lens for near-sightedness: Fmyopia fmyopia Pes Fmyopia - optical power of the lens, prescribed to correct near-sightedness or myopia (diopters), fmyopia – focal length of the lens, prescribed to correct near-sightedness or myopia (m), ps = 00 far point of a healthy eye (m), q – desired image distance (m). Lens too strong Eye too long (a) Myopia 2. Correction lens for far-sightedness: 1.1 -+- fnyperopia Po'a Fryperopia Fnyperopia - optical power of the lens, prescribed to correct far-sightedness or hyperopia (diopters), fnyperopia – focal length of the lens, prescribed to correct far-sightedness or hyperopia (m), Po = 25 cm is a far point of a healthy eye (m), q – desired image distance (m). Eye too short Lens too weak (b) Нурегорia 3. Lens equation: f- lens focal length (m); F – lens optical power (D); p – distance from the object to the lens or object distance (m); q – distance from the image to the lens or image distance (m). 4. Laser vision correction has progressed rapidly in the last few years. It is the latest and by far the most successful in a series of procedures that correct vision by reshaping the cornea. As noted at the beginning of this section, the cornea accounts for about two-thirds of the power of the eye. Thus, small adjustments of its curvature have the same effect as putting a lens in front of the eye. To a reasonable approximation, the power of multiple lenses placed close together equals the sum of their powers. For example, a concave spectacle lens (for nearsightedness) having P= -3.00 D has the same effect on vision as reducing the power of the eye itself by 3.00 D. So to correct the eye for nearsightedness, the cornea is flattened to reduce its power. Similarly, to correct for farsightedness, the curvature of the cornea is enhanced to increase the power of the eye - the same effect as the positive power spectacle lens used for farsightedness. Laser vision correction uses high intensity electromagnetic radiation to ablate (to remove material from the surface) and reshape the corneal surfaces. PROBLEMS 1. Let us assume that the farthest object a certain myopic eye can properly focus is 5 m from the eye. This is called the far point of the eye. Light from objects farther away than this is focused in front of the retina. Find focal length and power of the lens required to fix this problem.
2. Let us assume that a given hyperopic eye has a near point at 200 cm. The desired lens is to allow the eye to view objects at 25 cm. Find focal length and power of the lens required to fix this problem. OPTICS Defects of vision. Correction of vision 1. Correction lens for near-sightedness: Fmyopia fmyopia Pes Fmyopia - optical power of the lens, prescribed to correct near-sightedness or myopia (diopters), fmyopia – focal length of the lens, prescribed to correct near-sightedness or myopia (m), ps = 00 far point of a healthy eye (m), q – desired image distance (m). Lens too strong Eye too long (a) Myopia 2. Correction lens for far-sightedness: 1.1 -+- fnyperopia Po'a Fryperopia Fnyperopia - optical power of the lens, prescribed to correct far-sightedness or hyperopia (diopters), fnyperopia – focal length of the lens, prescribed to correct far-sightedness or hyperopia (m), Po = 25 cm is a far point of a healthy eye (m), q – desired image distance (m). Eye too short Lens too weak (b) Нурегорia 3. Lens equation: f- lens focal length (m); F – lens optical power (D); p – distance from the object to the lens or object distance (m); q – distance from the image to the lens or image distance (m). 4. Laser vision correction has progressed rapidly in the last few years. It is the latest and by far the most successful in a series of procedures that correct vision by reshaping the cornea. As noted at the beginning of this section, the cornea accounts for about two-thirds of the power of the eye. Thus, small adjustments of its curvature have the same effect as putting a lens in front of the eye. To a reasonable approximation, the power of multiple lenses placed close together equals the sum of their powers. For example, a concave spectacle lens (for nearsightedness) having P= -3.00 D has the same effect on vision as reducing the power of the eye itself by 3.00 D. So to correct the eye for nearsightedness, the cornea is flattened to reduce its power. Similarly, to correct for farsightedness, the curvature of the cornea is enhanced to increase the power of the eye - the same effect as the positive power spectacle lens used for farsightedness. Laser vision correction uses high intensity electromagnetic radiation to ablate (to remove material from the surface) and reshape the corneal surfaces. PROBLEMS 1. Let us assume that the farthest object a certain myopic eye can properly focus is 5 m from the eye. This is called the far point of the eye. Light from objects farther away than this is focused in front of the retina. Find focal length and power of the lens required to fix this problem.
College Physics
10th Edition
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Chapter25: Optical Instruments
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 32P
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:2. Let us assume that a given hyperopic eye has a near point at 200 cm. The desired lens is to
allow the eye to view objects at 25 cm. Find focal length and power of the lens required to fix this
problem.
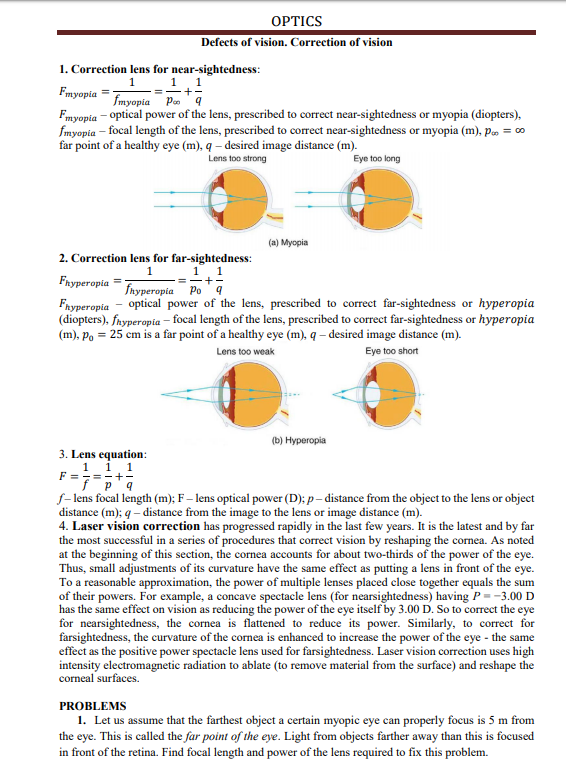
Transcribed Image Text:OPTICS
Defects of vision. Correction of vision
1. Correction lens for near-sightedness:
Fmyopia
fmyopia Pes
Fmyopia - optical power of the lens, prescribed to correct near-sightedness or myopia (diopters),
fmyopia – focal length of the lens, prescribed to correct near-sightedness or myopia (m), ps = 00
far point of a healthy eye (m), q – desired image distance (m).
Lens too strong
Eye too long
(a) Myopia
2. Correction lens for far-sightedness:
1.1
-+-
fnyperopia Po'a
Fryperopia
Fnyperopia - optical power of the lens, prescribed to correct far-sightedness or hyperopia
(diopters), fnyperopia – focal length of the lens, prescribed to correct far-sightedness or hyperopia
(m), Po = 25 cm is a far point of a healthy eye (m), q – desired image distance (m).
Eye too short
Lens too weak
(b) Нурегорia
3. Lens equation:
f- lens focal length (m); F – lens optical power (D); p – distance from the object to the lens or object
distance (m); q – distance from the image to the lens or image distance (m).
4. Laser vision correction has progressed rapidly in the last few years. It is the latest and by far
the most successful in a series of procedures that correct vision by reshaping the cornea. As noted
at the beginning of this section, the cornea accounts for about two-thirds of the power of the eye.
Thus, small adjustments of its curvature have the same effect as putting a lens in front of the eye.
To a reasonable approximation, the power of multiple lenses placed close together equals the sum
of their powers. For example, a concave spectacle lens (for nearsightedness) having P= -3.00 D
has the same effect on vision as reducing the power of the eye itself by 3.00 D. So to correct the eye
for nearsightedness, the cornea is flattened to reduce its power. Similarly, to correct for
farsightedness, the curvature of the cornea is enhanced to increase the power of the eye - the same
effect as the positive power spectacle lens used for farsightedness. Laser vision correction uses high
intensity electromagnetic radiation to ablate (to remove material from the surface) and reshape the
corneal surfaces.
PROBLEMS
1. Let us assume that the farthest object a certain myopic eye can properly focus is 5 m from
the eye. This is called the far point of the eye. Light from objects farther away than this is focused
in front of the retina. Find focal length and power of the lens required to fix this problem.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College


Horizons: Exploring the Universe (MindTap Course …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305960961
Author:
Michael A. Seeds, Dana Backman
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning