2. Note on the graph the temperature at which all of the ice has melted and the temperature at which the water starts to boil. 3. Are there any temperature plateaus (flat regions of the curve) on the temperature versus time graph? Name the physical property of water corresponding to each temperature plateau. 4. Was heat being added to the system during the times that the temperature remained rela- tively constant? Use the law of conservation of energy to describe what happened to the heat energy that was absorbed during this time. 5. Was heat being added to the system during the times that the temperature was rising? Use the law of conservation of energy to describe what happened to the heat energy that was absorbed during this time.
2. Note on the graph the temperature at which all of the ice has melted and the temperature at which the water starts to boil. 3. Are there any temperature plateaus (flat regions of the curve) on the temperature versus time graph? Name the physical property of water corresponding to each temperature plateau. 4. Was heat being added to the system during the times that the temperature remained rela- tively constant? Use the law of conservation of energy to describe what happened to the heat energy that was absorbed during this time. 5. Was heat being added to the system during the times that the temperature was rising? Use the law of conservation of energy to describe what happened to the heat energy that was absorbed during this time.
Chemistry: Matter and Change
1st Edition
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Chapter12: States Of Matter
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 81A
Related questions
Question
To ensure that you are not confused, I attached what the experiment was about. I highly recommend you read through it before going to the questions.
file:///Users/michaelzheng/Downloads/MeasuringEnergy%20(1).pdf
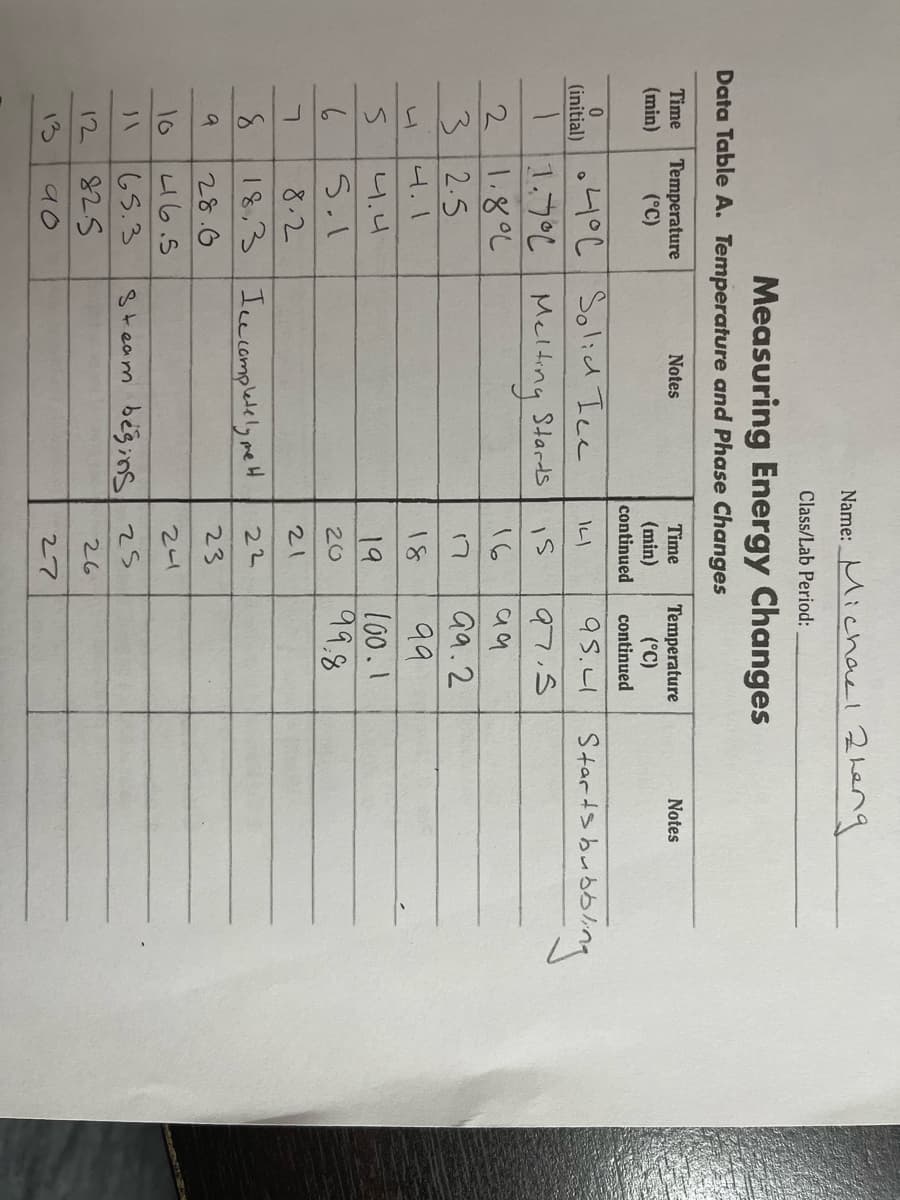
Transcribed Image Text:Name: Michae1 Zheng
Class/Lab Period:
Measuring Energy Changes
Data Table A. Temperature and Phase Changes
Time
Temperature
(°C)
Notes
Time
Temperature
(°C)
continued
Notes
(min)
(min)
continued
.4°C Solid Ice
1.7°C Melting Stards
|. ४°८
32.5
bubbling
95.1
Starts bub
(initial)
is
97.5
16
aa.2
4.1
18
99
니.니
19
100.1
20
8.2
21
8.
18,3 Ice complelely me H
22
28.6
23
10
u6.5
24
65.3
Steam begins 2s
12
26
13
90
27

Transcribed Image Text:Page 5-EA
Measuring Energy Changes- Page 6
Post-Lab Calculations and Analysis (Use a separate sheet of paper to ansuwer the following questions.)
Part A. Temperature and Phase Changes
1. Using your data, draw a graph of temperature (y-axis) versus time (x-axis). q
Excel
2. Note on the graph the temperature at which all of the ice has melted and the temperature
at which the water starts to boil.
3. Are there any temperature plateaus (flat regions of the curve) on the temperature versus
time graph? Name the physical property of water corresponding to each temperature
plateau.
4. Was heat being added to the system during the times that the temperature remained rela-
tively constant? Use the law of conservation of energy to describe what happened to the
heat energy that was absorbed during this time.
5. Was heat being added to the system during the times that the temperature was rising?
Use the law of conservation of energy to describe what happened to the heat energy that
was absorbed during this time.
Part B. Energy Needed to Melt Ice
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079250
Author:
Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078746376
Author:
Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079250
Author:
Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning