Sales Variable costs (50% of sales) Fixed costs Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) Interest (10% cost) Earnings before taxes (EBT) Tax (35%) Earnings after taxes (EAT) Shares of common stock Earnings per share The company is currently financed with 50 percent debt and 50 percent equity (common stock, par value of $10). In order to expand the facilities, Mr. Delsing estimates a need for $4.5 million in additional financing. His investment banker has laid out three plans for mim to consider: 1. Sell $4.5 million of debt at 9 percent. 2. Sell $4.5 million of common stock at $15 per share. 3. Sell $2.25 million of debt at 8 percent and $2.25 million of common stock at $20 per share. Before expansion After expansion Variable costs are expected to stay at 50 percent of sales, while fixed expenses will increase to $2,550,000 per year. Delsing is not sure how much this expansion will add to sales, but he estimates that sales will rise by $1 million per year for the next five years. Delsing is interested in a thorough analysis of his expansion plans and methods of financing.He would like you to analyze the Following: $ 7,500,000 3,750,000 2,050,000 $ 1,700,000 700,000 a. The break-even point for operating expenses before and after expansion (in sales dollars). Note: Enter your answers in dollars not in millions, I.e, $1,234,567. Before expansion After expansion $ 1,000,000 350,000 $ 650,000 Break-Even Point 450,000 $ 1.44 Degree of financial leverage b. The degree of operating leverage before and after expansion. Assume sales of $7.5 million before expansion and $8.5 million after expansion. Use the formula: DOL=(S-TVC)/(S-TVC-FC). Note: Round your answers to 2 decimal places. Degree of Operating Leverage -1. The degree of financial leverage before expansion. Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places.
Sales Variable costs (50% of sales) Fixed costs Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) Interest (10% cost) Earnings before taxes (EBT) Tax (35%) Earnings after taxes (EAT) Shares of common stock Earnings per share The company is currently financed with 50 percent debt and 50 percent equity (common stock, par value of $10). In order to expand the facilities, Mr. Delsing estimates a need for $4.5 million in additional financing. His investment banker has laid out three plans for mim to consider: 1. Sell $4.5 million of debt at 9 percent. 2. Sell $4.5 million of common stock at $15 per share. 3. Sell $2.25 million of debt at 8 percent and $2.25 million of common stock at $20 per share. Before expansion After expansion Variable costs are expected to stay at 50 percent of sales, while fixed expenses will increase to $2,550,000 per year. Delsing is not sure how much this expansion will add to sales, but he estimates that sales will rise by $1 million per year for the next five years. Delsing is interested in a thorough analysis of his expansion plans and methods of financing.He would like you to analyze the Following: $ 7,500,000 3,750,000 2,050,000 $ 1,700,000 700,000 a. The break-even point for operating expenses before and after expansion (in sales dollars). Note: Enter your answers in dollars not in millions, I.e, $1,234,567. Before expansion After expansion $ 1,000,000 350,000 $ 650,000 Break-Even Point 450,000 $ 1.44 Degree of financial leverage b. The degree of operating leverage before and after expansion. Assume sales of $7.5 million before expansion and $8.5 million after expansion. Use the formula: DOL=(S-TVC)/(S-TVC-FC). Note: Round your answers to 2 decimal places. Degree of Operating Leverage -1. The degree of financial leverage before expansion. Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places.
Chapter14: Capital Structure Management In Practice
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7P
Related questions
Question
100%
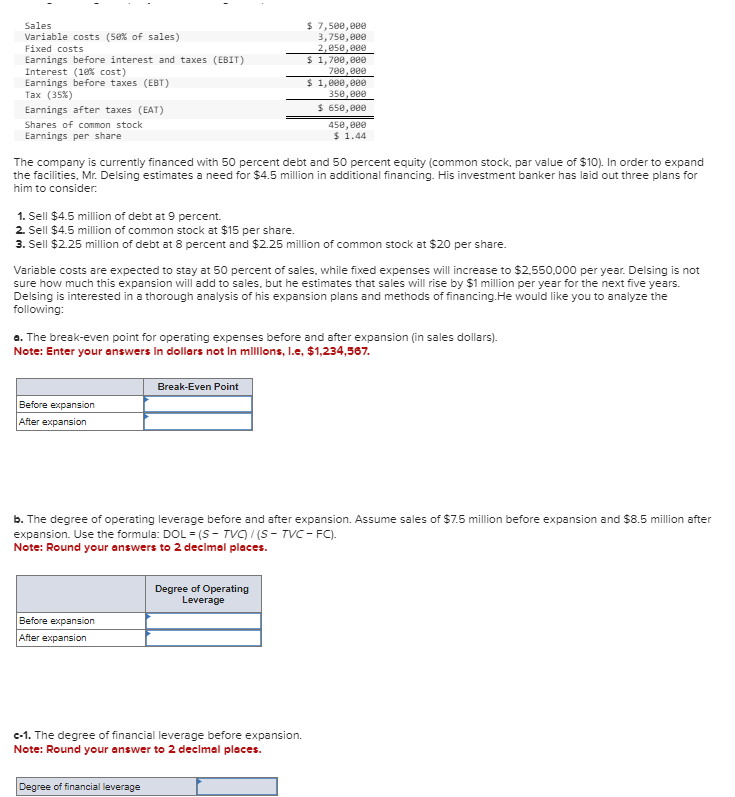
Transcribed Image Text:Sales
Variable costs (50% of sales)
Fixed costs
Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT)
Interest (18% cost)
Earnings before taxes (EBT)
Tax (35%)
Earnings after taxes (EAT)
Shares of common stock
Earnings per share.
The company is currently financed with 50 percent debt and 50 percent equity (common stock, par value of $10). In order to expand
the facilities, Mr. Delsing estimates a need for $4.5 million in additional financing. His investment banker has laid out three plans for
him to consider:
1. Sell $4.5 million of debt at 9 percent.
2. Sell $4.5 million of common stock at $15 per share.
3. Sell $2.25 million of debt at 8 percent and $2.25 million of common stock at $20 per share.
Variable costs are expected to stay at 50 percent of sales, while fixed expenses will increase to $2,550,000 per year. Delsing is not
sure how much this expansion will add to sales, but he estimates that sales will rise by $1 million per year for the next five years.
Delsing is interested in a thorough analysis of his expansion plans and methods of financing.He would like you to analyze the
following:
Before expansion
After expansion
a. The break-even point for operating expenses before and after expansion (in sales dollars).
Note: Enter your answers in dollars not in millions, I.e, $1,234,567.
$ 7,500,000
3,750,000
2,050,000
$ 1,700,000
700,000
1,000,000
350,000
$
$ 650,000
Before expansion
After expansion
450,000
$ 1.44
Break-Even Point
b. The degree of operating leverage before and after expansion. Assume sales of $7.5 million before expansion and $8.5 million after
expansion. Use the formula: DOL = (S-TVC)/(S-TVC - FC).
Note: Round your answers to 2 decimal places.
Degree of financial leverage
Degree of Operating
Leverage
c-1. The degree of financial leverage before expansion.
Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
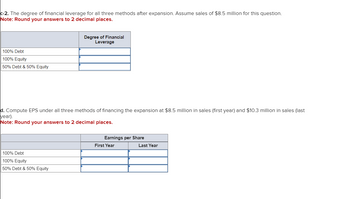
Transcribed Image Text:c-2. The degree of financial leverage for all three methods after expansion. Assume sales of $8.5 million for this question.
Note: Round your answers to 2 decimal places.
100% Debt
100% Equity
50% Debt & 50% Equity
Degree of Financial
Leverage
d. Compute EPS under all three methods of financing the expansion at $8.5 million in sales (first year) and $10.3 million in sales (last
year).
Note: Round your answers to 2 decimal places.
100% Debt
100% Equity
50% Debt & 50% Equity
Earnings per Share
First Year
Last Year
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:
9781337514835
Author:
MOYER
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course…
Finance
ISBN:
9781337395083
Author:
Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:
9781337514835
Author:
MOYER
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course…
Finance
ISBN:
9781337395083
Author:
Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
