2. Two small-sized objects are placed on a uniform 9.00 kg plastic beam 3.00 m long, as shown in Figure 2 8.00 kg 7.50 kg 9.00 kg k 60.0 cm> 3.00 m Figure 2 (a) Find the location of the center of mass of this system by setting at x = 0 at the left end of the beam. (b) Find the location of the center of mass of this system by setting at x = 0 the right end of the beam. (c) Do you get the same result both ways? Explain your results.
2. Two small-sized objects are placed on a uniform 9.00 kg plastic beam 3.00 m long, as shown in Figure 2 8.00 kg 7.50 kg 9.00 kg k 60.0 cm> 3.00 m Figure 2 (a) Find the location of the center of mass of this system by setting at x = 0 at the left end of the beam. (b) Find the location of the center of mass of this system by setting at x = 0 the right end of the beam. (c) Do you get the same result both ways? Explain your results.
University Physics Volume 1
18th Edition
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Chapter9: Linear Momentum And Collisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 37P: The figure below shows a bullet of mass 200 g traveling horizontally towards the east with speed 400...
Related questions
Question
I want this question's Answer in one hour.It's urgent.
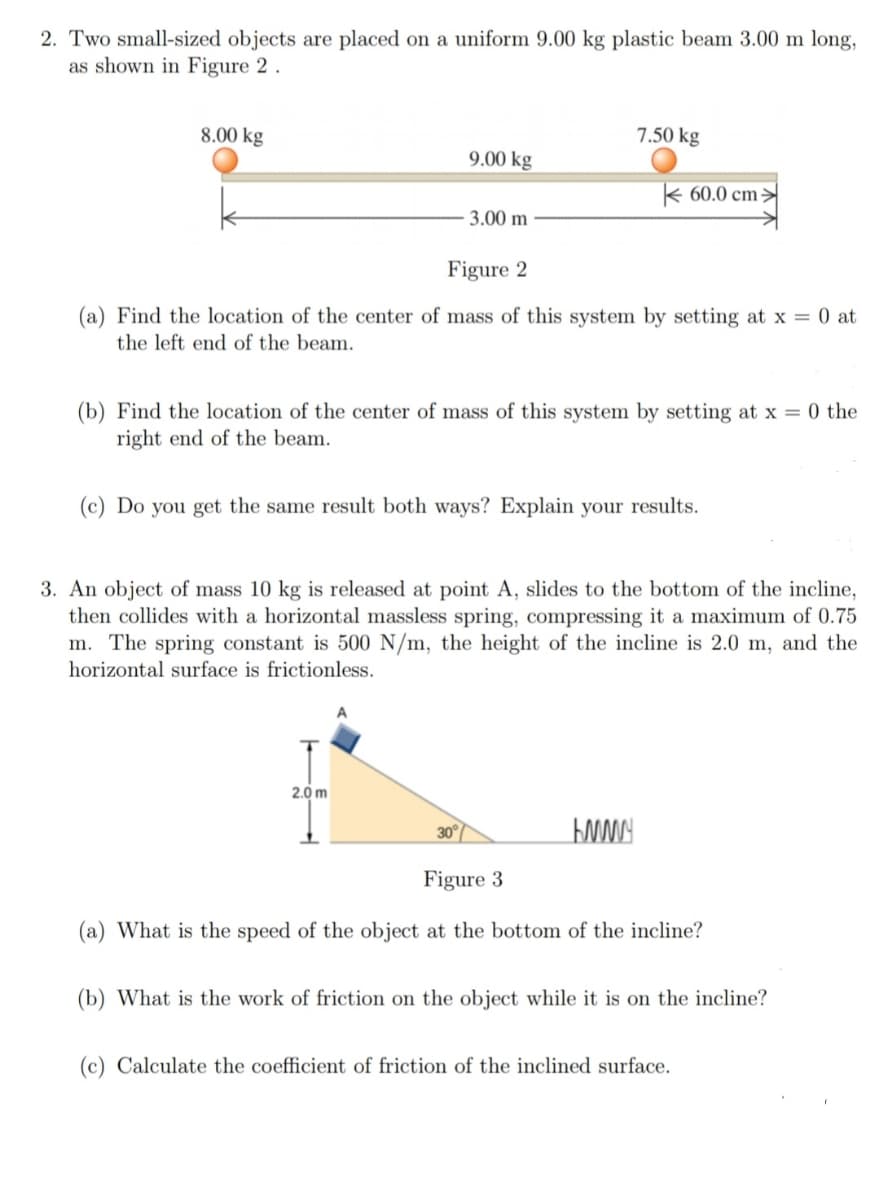
Transcribed Image Text:2. Two small-sized objects are placed on a uniform 9.00 kg plastic beam 3.00 m long,
as shown in Figure 2.
8.00 kg
7.50 kg
9.00 kg
k 60.0 cm>
3.00 m
Figure 2
(a) Find the location of the center of mass of this system by setting at x = 0 at
the left end of the beam.
(b) Find the location of the center of mass of this system by setting at x = 0 the
right end of the beam.
(c) Do you get the same result both ways? Explain your results.
3. An object of mass 10 kg is released at point A, slides to the bottom of the incline,
then collides with a horizontal massless spring, compressing it a maximum of 0.75
m. The spring constant is 500 N/m, the height of the incline is 2.0 m, and the
horizontal surface is frictionless.
2.0 m
30
Figure 3
(a) What is the speed of the object at the bottom of the incline?
(b) What is the work of friction on the object while it is on the incline?
(c) Calculate the coefficient of friction of the inclined surface.
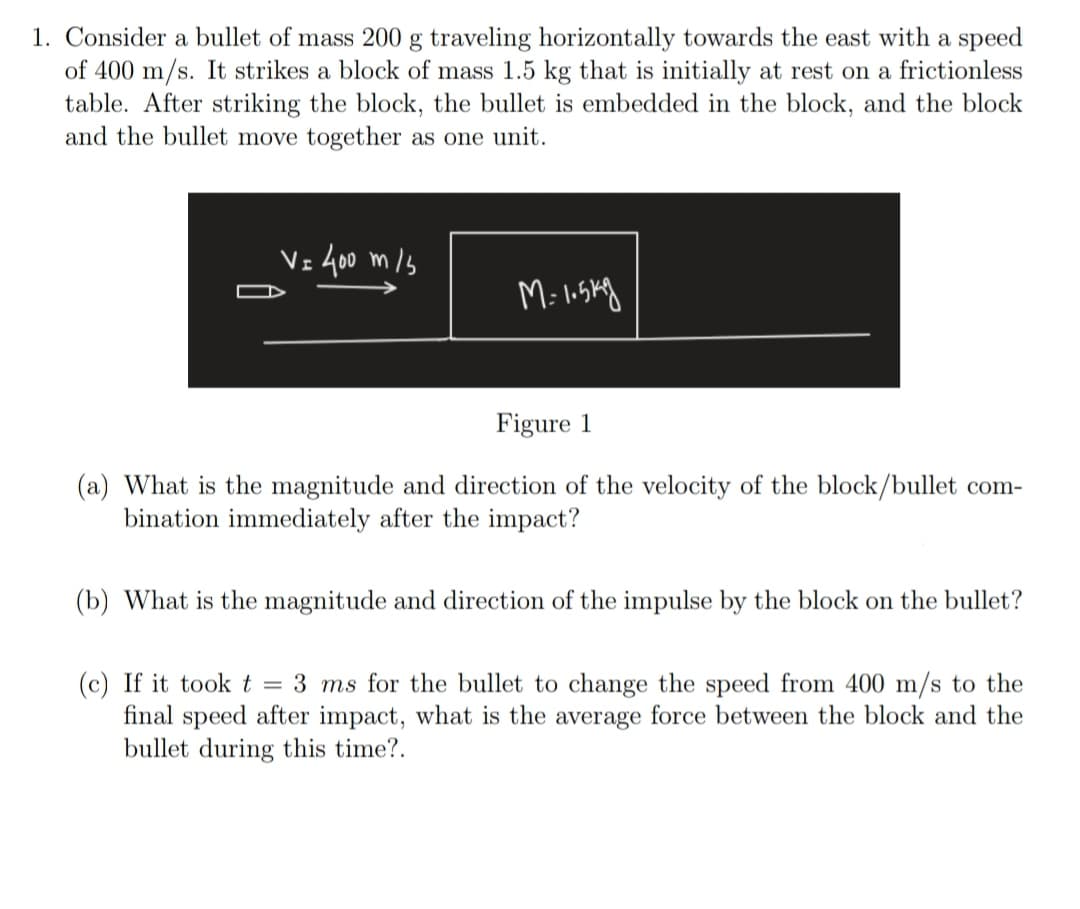
Transcribed Image Text:1. Consider a bullet of mass 200 g traveling horizontally towards the east with a speed
of 400 m/s. It strikes a block of mass 1.5 kg that is initially at rest on a frictionless
table. After striking the block, the bullet is embedded in the block, and the block
and the bullet move together as one unit.
Vz 400 m/s
Figure 1
(a) What is the magnitude and direction of the velocity of the block/bullet com-
bination immediately after the impact?
(b) What is the magnitude and direction of the impulse by the block on the bullet?
(c) If it tookt = 3 ms for the bullet to change the speed from 400 m/s to the
final speed after impact, what is the average force between the block and the
bullet during this time?.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning