2. Use the definition to prove that if (xn) is a sequence of real numbers which converges to -3, then the sequence (2In + 1) converges to -5.
2. Use the definition to prove that if (xn) is a sequence of real numbers which converges to -3, then the sequence (2In + 1) converges to -5.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter6: The Trigonometric Functions
Section6.4: Values Of The Trigonometric Functions
Problem 24E
Related questions
Question
Using Definition in 2nd photo, solve question 2
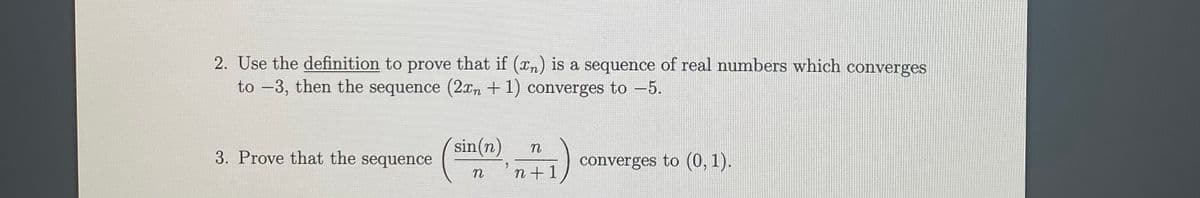
Transcribed Image Text:2. Use the definition to prove that if (xn) is a sequence of real numbers which converges
to -3, then the sequence (2xn + 1) converges to -5.
sin(n)
3. Prove that the sequence
converges to (0, 1).
n
n +1
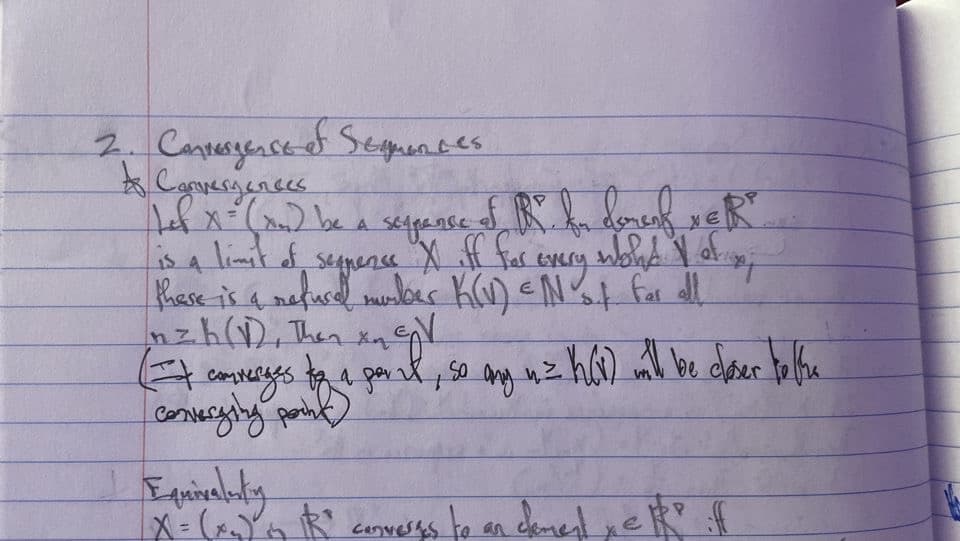
Transcribed Image Text:2. Cansesgenced Seguen. bes
Canvergences
%3D
is 4 limit of
Rhase is 4 nefucel munler K) EN%¢ for dll
nzh(D, Then xqe
converys.
segnense
a per
X=(YR' covess to an demel yek f
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage