= 2H*(aq) In each case indicate whether the reaction is homoge- neous or heterogeneous. (g) 2 H2O(1) 15.16 Write the expressions for K, for the following react 3 O2(8) = TICL4(1) (a) 2O3(g) = 302(g) (b) Ti(s) + 2 Cl2(8) (c) 2 C2H4(8) + 2 H20(8) (d) C(s) +2 H2(8) CH4(8) (e) 4 HCI(aq) + O2(g) = 2 H2O(1) + 2 Cl2(8) (f) 2 C3H18(1) + 25 O2(8) (g) 2 C3H18(1) + 25 O2(g) = 16 CO2(g) + 18 H2O(1) 2 C2H6(g) + O2(8) = 16 CO2(8) + 18 H2O(g) = 15.17 When the following reactions come to equilibrium, does the equilibrium mixture contain mostly reactants or mostly products? Kc = 1.5 × 10-10 (a) N2(g) + O2(8) = 2 NO(8) %3D (b) 2 SO2(g) + O2(8) = 2 SO3(8) K, = 2.5 × 10° 15.18 Which of the following reactions lies to the right, favor- ing the formation of products, and which lies to the left, favoring formation of reactants? %3D (a) 2 NO(8) + O2(8) = 2 NO2(g) K,= 5.0 × 1012 (b) 2 HBr(8) %3D mo( = H2(g) + Br2(g) 15.19 Which of the following statements are true and which are false? (a) The equilibrium constant can never be a negative number. (b) In reactions that we draw with a single-headed arrow, the equilibrium constant has a value that is very close to zero. (c) As the value of the equilibrium constant increases, the speed at which a reaction reaches equilibrium K = 5.8x 10-18 %3D increases. 5.20 Which of the following statements are true and which are false? (a) For the reaction 2 A(g) + B(g) = A,B(g) K and K, are numerically the same. (h) It i distinguish K fro
Lipids
The heterogeneous classes of organic compounds that are not water-soluble but are dissolved in organic solvents that are non-polar in nature are termed lipids. They are a long chain of fatty acids and esters of alcohols. Lipids are generally seen in several plants, microorganisms, and animals. They are utilized as insulation, components of the cell membrane, hormones, and molecules for the storage of energy.
Glycerophospholipid
Glycerophospholipid is the most abundantly occuring phospholipids found in the biological membranes. Lipids include a group of organic compounds like fats, hormones, oils, waxes, vitamins etc. They are non-polar molecules and are insoluble in water. Lipids play an important role in biological systems. They are the building blocks of our cell membranes, store energy and are involved in signaling.
Structure Of Camphor
A terpene with the molecular formula of C10H16O is a waxy, white color solid known as camphor. It is flammable. It also possesses a very pungent taste and a strong odor. There are various sources for extracting camphor from natural products such as the wood of the tree of camphor laurel. Sublimation of wood and steam distillation are some of the methods involved in obtaining camphor.
Glycolipid In Organic Chemistry
Glycolipids are lipids that are an important class of organic compounds in chemistry that have simple to complex applications. They contain carbohydrates, fatty acids, sphingolipids or a glycerol group. In other words, they are the modifications of lipids like acylglycerols, prenols and ceramides. They are all part of a wider group of compounds known as glycoconjugates.
Diterpenoid
The terpenoid class includes diterpenoids, which are chemical compounds with 20 carbon atoms. They are made up of four isoprene units and are derived from geranylgeraniol, a C20 precursor. They have a C20H32 basic structure. These characteristics distinguish diterpenoids from simple terpenes, which have just 10 carbon atoms.
see photo. Problem # 15.18
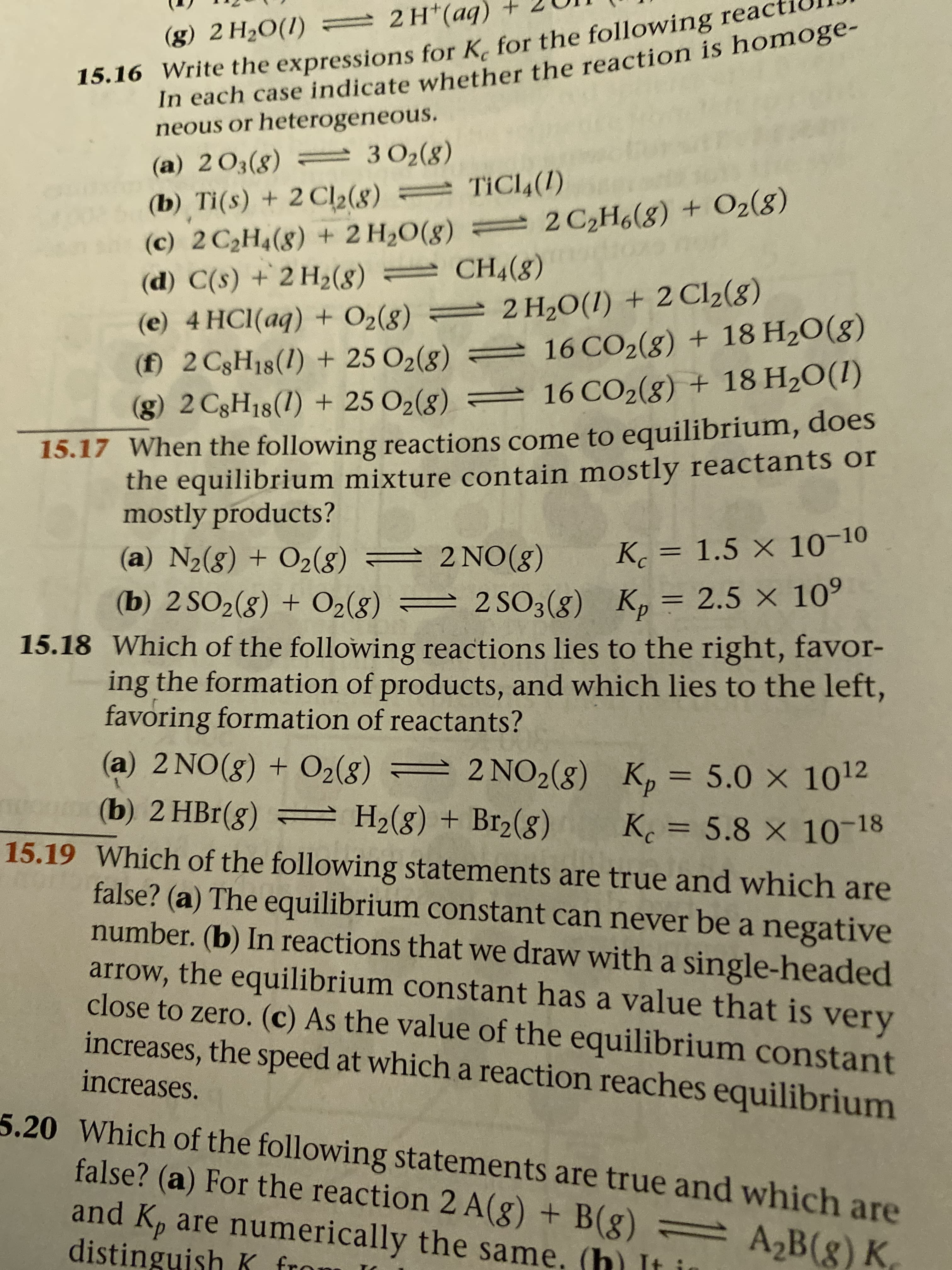
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images







