2v Tectors a, b, e, and d 8. Vectors w, x, y, and z
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter2: Systems Of Linear Equations
Section2.3: Spanning Sets And Linear Independence
Problem 21EQ
Related questions
Concept explainers
Equations and Inequations
Equations and inequalities describe the relationship between two mathematical expressions.
Linear Functions
A linear function can just be a constant, or it can be the constant multiplied with the variable like x or y. If the variables are of the form, x2, x1/2 or y2 it is not linear. The exponent over the variables should always be 1.
Question
solution for number 8
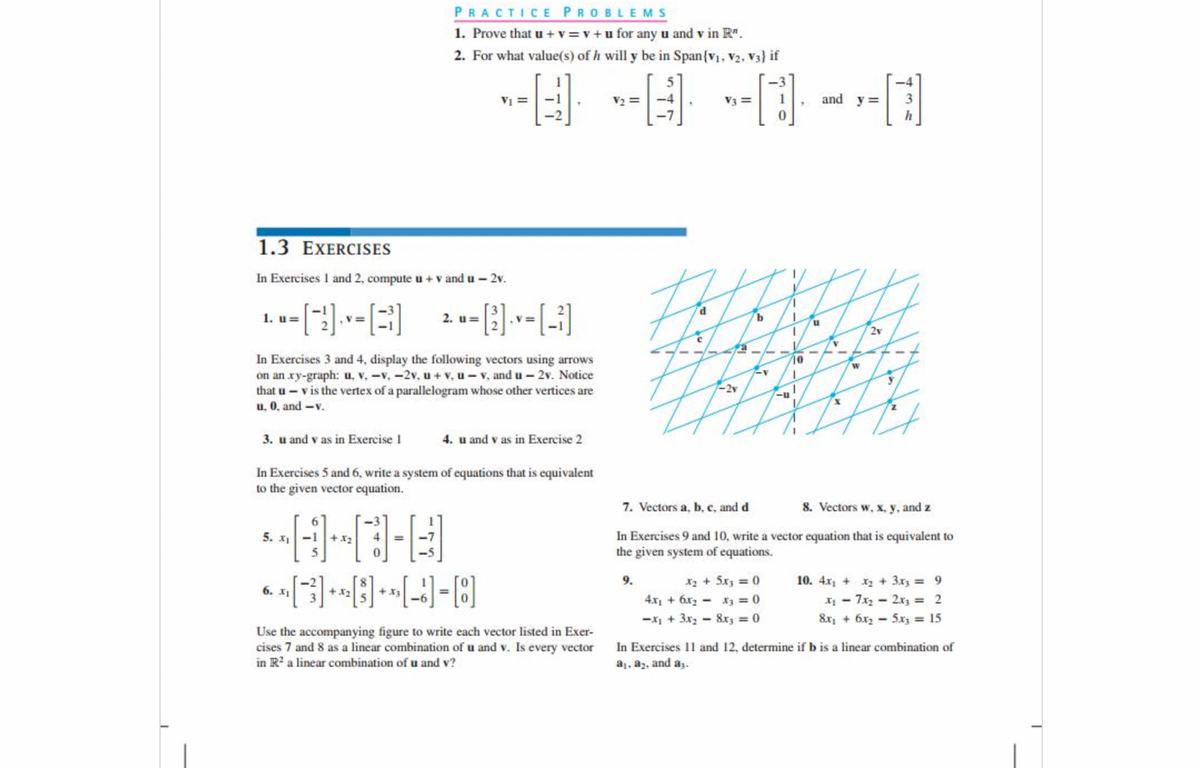
Transcribed Image Text:PRACTICE PROBLEMS
1. Prove that u + v =v + u for any u and v in R".
2. For what value(s) of h will y be in Span{v. V2. V3) if
-3
VI
V2 =
V3 =
and y =
1.3 EXERCISES
In Exercises 1 and 2, compute u + v and u - 2v.
1. u=
2. u=
2v
In Exercises 3 and 4, display the following vectors using arrows
on an xy-graph: u, v. -v,-2v, u+ v, u- v, and u - 2v. Notice
that u - v is the vertex of a parallelogram whose other vertices are
u, 0, and -v.
-2v
3. u and v as in Exercise I
4. u and v as in Exercise 2
In Exercises 5 and 6, write a system of equations that is equivalent
to the given vector equation.
7. Vectors a, b, c, and d
8. Vectors w, x, y. and z
In Exercises 9 and 10, write a vector equation that is equivalent to
the given system of equations.
5. x1
-1
+ x2
X2 + 5x3 = 0
4.x + 6x2 - x3 = 0
9.
10. 4x, + x2 + 3xrz = 9
6. x1
+x2
+ x3
I - 7x - 2x3 = 2
&x, + 6x2 - 5x3 = 15
-x + 3x2 - 8x3 = 0
Use the accompanying figure to write each vector listed in Exer-
cises 7 and 8 as a linear combination of u and v. Is every vector
in R? a linear combination of u and v?
In Exercises 11 and 12, determine if b is a linear combination of
a, az, and a;.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage