3.10 m/s when it makes contact with a light spring (Figure b) that has a force constant of 50.0 N/m. The object comes to rest after the A 1.50-kg object slides to the right on a surface having a coefficient of kinetic friction 0.250 (Figure a). The object has a speed of vi spring has been compressed a distance d (Figure c). The object is then forced toward the left by the spring (Figure d) and continues to move in that direction beyond the spring's unstretched position. Finally, the object comes to rest a distance D to the left of the unstretched spring (Figure e). a m (a) Find the distance of compression d. (b) Find the speed v at the unstretched position when the object is moving to the left (Figure d) m/s (c) Find the distance D where the object comes to rest
3.10 m/s when it makes contact with a light spring (Figure b) that has a force constant of 50.0 N/m. The object comes to rest after the A 1.50-kg object slides to the right on a surface having a coefficient of kinetic friction 0.250 (Figure a). The object has a speed of vi spring has been compressed a distance d (Figure c). The object is then forced toward the left by the spring (Figure d) and continues to move in that direction beyond the spring's unstretched position. Finally, the object comes to rest a distance D to the left of the unstretched spring (Figure e). a m (a) Find the distance of compression d. (b) Find the speed v at the unstretched position when the object is moving to the left (Figure d) m/s (c) Find the distance D where the object comes to rest
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter7: Conservation Of Energy
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 55P: A horizontal spring attached to a wall has a force constant of k = 850 N/m. A block of mass m = 1.00...
Related questions
Question
100%
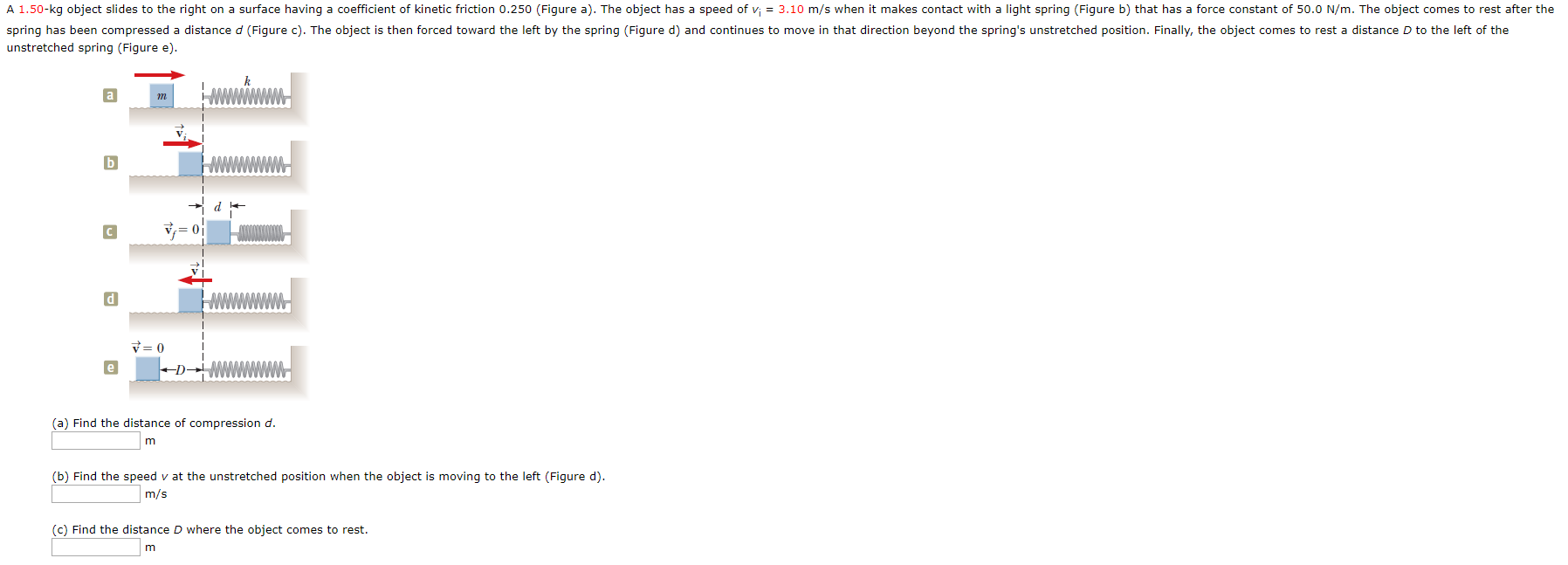
Transcribed Image Text:3.10 m/s when it makes contact with a light spring (Figure b) that has a force constant of 50.0 N/m. The object comes to rest after the
A 1.50-kg object slides to the right on a surface having a coefficient of kinetic friction 0.250 (Figure a). The object has a speed of vi
spring has been compressed a distance d (Figure c). The object is then forced toward the left by the spring (Figure d) and continues to move in that direction beyond the spring's unstretched position. Finally, the object comes to rest a distance D to the left of the
unstretched spring (Figure e).
a
m
(a) Find the distance of compression d.
(b) Find the speed v at the unstretched position when the object is moving to the left (Figure d)
m/s
(c) Find the distance D where the object comes to rest
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:
9781305079137
Author:
James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:
Cengage Learning