7. For compound A in acid, it is the hydroxyl that is protonated to a greater extent than the carbonyl oxygen. However, for compound B in acid, it is the carbonyl oxygen that is protonated to a greater extent than the hydroxyl oxygen. Explain this difference. H2SO4 ОН ОН2 ОН H2SO4 ОН ОН
7. For compound A in acid, it is the hydroxyl that is protonated to a greater extent than the carbonyl oxygen. However, for compound B in acid, it is the carbonyl oxygen that is protonated to a greater extent than the hydroxyl oxygen. Explain this difference. H2SO4 ОН ОН2 ОН H2SO4 ОН ОН
Chapter18: Ethers And Epoxides; Thiols And Sulfides
Section18.SE: Something Extra
Problem 69GP
Related questions
Question
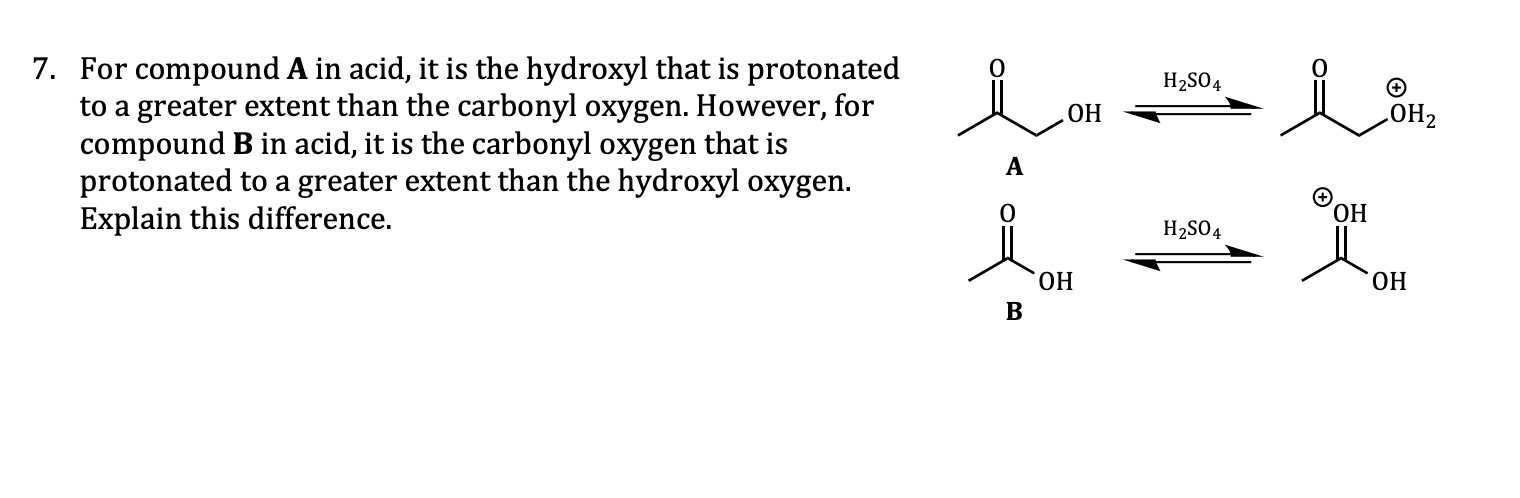
Transcribed Image Text:7. For compound A in acid, it is the hydroxyl that is protonated
to a greater extent than the carbonyl oxygen. However, for
compound B in acid, it is the carbonyl oxygen that is
protonated to a greater extent than the hydroxyl oxygen.
Explain this difference.
H2SO4
ОН
ОН2
ОН
H2SO4
ОН
ОН
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you


Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780618974122
Author:
Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580350
Author:
William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:
Cengage Learning