OPTICS Wave optics. Interference. Diffraction. Polarization 1. Young's Double Slit Experiment Constructive interference: 8 = x; n, - x; n; Screen 8 = k) = 2k Destructive interference: 8 = (2k +1) Coordinates of bright and dark fringes on the screen: (*.+) Ymax =± Ymin =± Ay = Here d is path difference (m), 1 is wavelength of light (m), I is distance from the slits to the screen (m), k = 0, 1, 2, 3 ... is minimum or maximum order number, d is distance between the slits (m), Ymax are coordinates of bright fringes on the screen (m), ymin are coordinates of dark fringes on the screen (m), Ay is width of the fridges (m). 2. Interference in thin films: Air Constructive interference: Film 21 /n² – sin² a : (2k + 1) B Destructive interference: Air 21 Vn² – sin² a = k) Here n is refractive index of the film, a is angle of light incidence, k = 0, 1, 2, 3 ... is minimum or maximum order number, 1 is wavelength of light (m), l is thickness of the film (m). 3. Single-Slit Diffraction Constructive: sin- 2/a sine/a a sin© = ±(2k + 1) : 2 sine0 Destructive: sine/ * sine --2 a sin© = ±kl a is the slit width, k = 0, 1, 2, 3 ... is minimum or maximum order number, 1 is wavelength of light (m), 0 is the angle on corresponding minimum or maximum. 4. Diffraction grating: Viewing sereen d sin o ±kA d = /N is period of diffraction grating and N is number of lines per unit length, ø is angle on corresponding minimum or maximum, k = 0, 1, 2... is minimum or maximum order number, 1 is wavelength of light (m). 5. Resolution of the optical instruments Limiting angle of resolution 0min: 1.222 Өmin Omin = D Minimum separation distance d: d = L0min 1 is wavelength of light (m), D is aperture diameter, for human eye pupil diameter (m). 9. For the human eye, with a pupil diameter of about 2 mm and using a wavelength of 500 nm, calculate the minimum angle separating two just resolvable points. Then find the actual minimum distance between such just resolvable points as well as the distance between their images on the retina.
OPTICS Wave optics. Interference. Diffraction. Polarization 1. Young's Double Slit Experiment Constructive interference: 8 = x; n, - x; n; Screen 8 = k) = 2k Destructive interference: 8 = (2k +1) Coordinates of bright and dark fringes on the screen: (*.+) Ymax =± Ymin =± Ay = Here d is path difference (m), 1 is wavelength of light (m), I is distance from the slits to the screen (m), k = 0, 1, 2, 3 ... is minimum or maximum order number, d is distance between the slits (m), Ymax are coordinates of bright fringes on the screen (m), ymin are coordinates of dark fringes on the screen (m), Ay is width of the fridges (m). 2. Interference in thin films: Air Constructive interference: Film 21 /n² – sin² a : (2k + 1) B Destructive interference: Air 21 Vn² – sin² a = k) Here n is refractive index of the film, a is angle of light incidence, k = 0, 1, 2, 3 ... is minimum or maximum order number, 1 is wavelength of light (m), l is thickness of the film (m). 3. Single-Slit Diffraction Constructive: sin- 2/a sine/a a sin© = ±(2k + 1) : 2 sine0 Destructive: sine/ * sine --2 a sin© = ±kl a is the slit width, k = 0, 1, 2, 3 ... is minimum or maximum order number, 1 is wavelength of light (m), 0 is the angle on corresponding minimum or maximum. 4. Diffraction grating: Viewing sereen d sin o ±kA d = /N is period of diffraction grating and N is number of lines per unit length, ø is angle on corresponding minimum or maximum, k = 0, 1, 2... is minimum or maximum order number, 1 is wavelength of light (m). 5. Resolution of the optical instruments Limiting angle of resolution 0min: 1.222 Өmin Omin = D Minimum separation distance d: d = L0min 1 is wavelength of light (m), D is aperture diameter, for human eye pupil diameter (m). 9. For the human eye, with a pupil diameter of about 2 mm and using a wavelength of 500 nm, calculate the minimum angle separating two just resolvable points. Then find the actual minimum distance between such just resolvable points as well as the distance between their images on the retina.
College Physics
1st Edition
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Chapter27: Wave Optics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 41PE: Unreasonable Results (a) What visible wavelength has its fourth-order maximum at an angle of 25.0°...
Related questions
Question
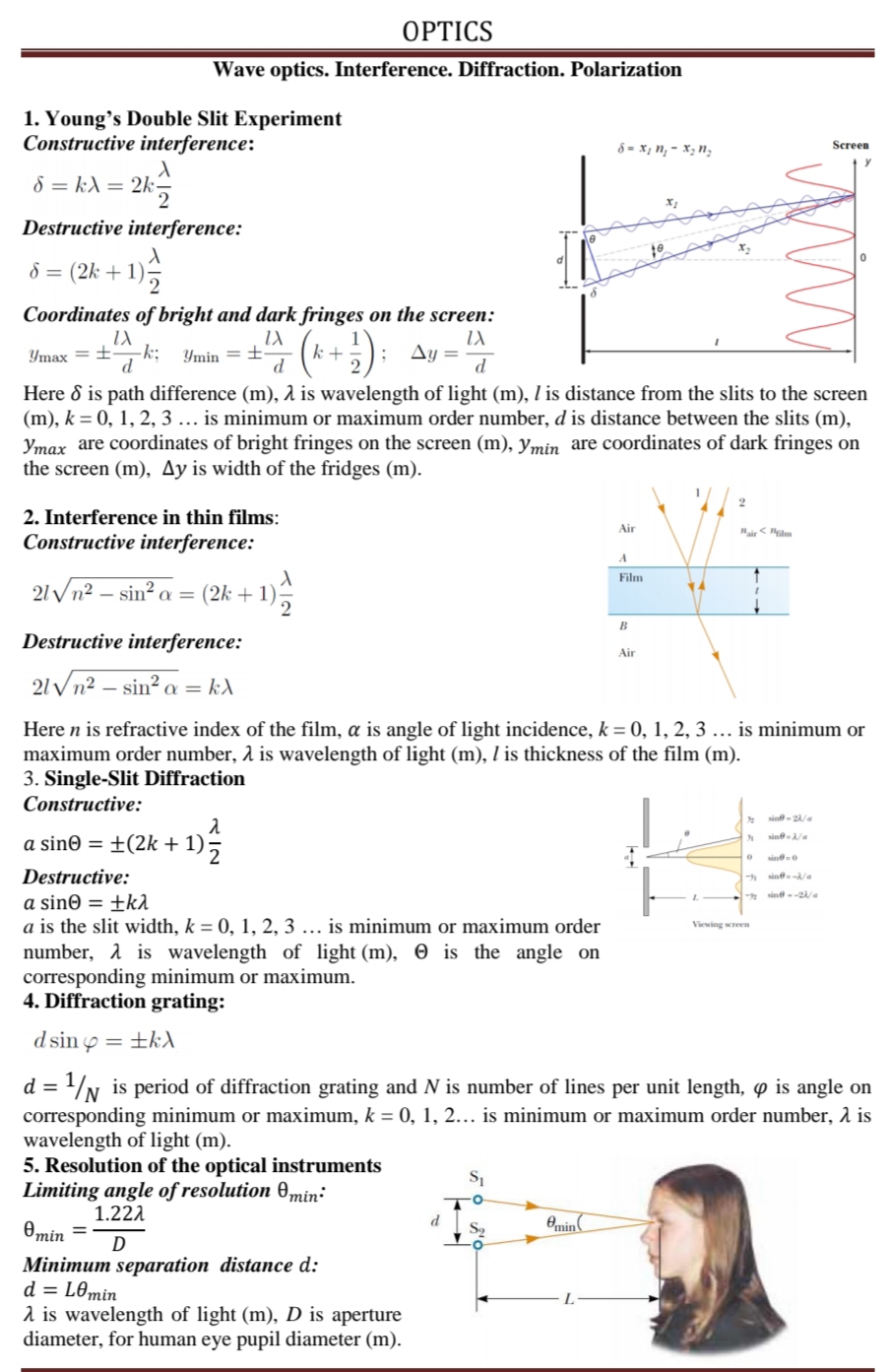
Transcribed Image Text:OPTICS
Wave optics. Interference. Diffraction. Polarization
1. Young's Double Slit Experiment
Constructive interference:
8 = x; n, - x; n;
Screen
8 = k) = 2k
Destructive interference:
8 = (2k +1)
Coordinates of bright and dark fringes on the screen:
(*.+)
Ymax =±
Ymin =±
Ay =
Here d is path difference (m), 1 is wavelength of light (m), I is distance from the slits to the screen
(m), k = 0, 1, 2, 3 ... is minimum or maximum order number, d is distance between the slits (m),
Ymax are coordinates of bright fringes on the screen (m), ymin are coordinates of dark fringes on
the screen (m), Ay is width of the fridges (m).
2. Interference in thin films:
Air
Constructive interference:
Film
21 /n² – sin² a :
(2k + 1)
B
Destructive interference:
Air
21 Vn² – sin² a = k)
Here n is refractive index of the film, a is angle of light incidence, k = 0, 1, 2, 3 ... is minimum or
maximum order number, 1 is wavelength of light (m), l is thickness of the film (m).
3. Single-Slit Diffraction
Constructive:
sin- 2/a
sine/a
a sin© = ±(2k + 1) :
2
sine0
Destructive:
sine/
* sine --2
a sin© = ±kl
a is the slit width, k = 0, 1, 2, 3 ... is minimum or maximum order
number, 1 is wavelength of light (m), 0 is the angle on
corresponding minimum or maximum.
4. Diffraction grating:
Viewing sereen
d sin o
±kA
d = /N is period of diffraction grating and N is number of lines per unit length, ø is angle on
corresponding minimum or maximum, k = 0, 1, 2... is minimum or maximum order number, 1 is
wavelength of light (m).
5. Resolution of the optical instruments
Limiting angle of resolution 0min:
1.222
Өmin
Omin =
D
Minimum separation distance d:
d = L0min
1 is wavelength of light (m), D is aperture
diameter, for human eye pupil diameter (m).

Transcribed Image Text:9. For the human eye, with a pupil diameter of about 2 mm and using a wavelength of 500 nm,
calculate the minimum angle separating two just resolvable points. Then find the actual minimum
distance between such just resolvable points as well as the distance between their images on the
retina.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:
9781133104261
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168185
Author:
William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax