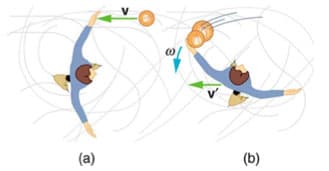
A ball of mass 0.280 kilograms is thrown at 24.5 meters per second to a skater standing on ice with arms outstretched. The skater has mass 60.5 kilograms and moment of inertia 1.37 kilogram·meters squared. After catching the ball, at a distance of 0.607 meters from the skater's center, the skater both recoils and rotates as shown in part b of the figure below. a. What is the skater's final linear speed? Include units in your answer. b. What is the skater's final angular speed? Include units in your answer. More information. Hint: Solve this using the rotational equivalent of the concept you used for solving part a. Granted, it seems like initially the ball is moving only translationally. But at the instant the skater catches the ball, the ball has a velocity perpendicular to a radius of rotation. Thus, we can think of its motion as rotational also. c. How much kinetic energy is lost in the collision? Include units in your answer.
Rigid Body
A rigid body is an object which does not change its shape or undergo any significant deformation due to an external force or movement. Mathematically speaking, the distance between any two points inside the body doesn't change in any situation.
Rigid Body Dynamics
Rigid bodies are defined as inelastic shapes with negligible deformation, giving them an unchanging center of mass. It is also generally assumed that the mass of a rigid body is uniformly distributed. This property of rigid bodies comes in handy when we deal with concepts like momentum, angular momentum, force and torque. The study of these properties – viz., force, torque, momentum, and angular momentum – of a rigid body, is collectively known as rigid body dynamics (RBD).
A ball of mass 0.280 kilograms is thrown at 24.5 meters per second to a skater standing on ice with arms outstretched. The skater has mass 60.5 kilograms and moment of inertia 1.37 kilogram·meters squared. After catching the ball, at a distance of 0.607 meters from the skater's center, the skater both recoils and rotates as shown in part b of the figure below.
a. What is the skater's final linear speed? Include units in your answer.
b. What is the skater's final angular speed? Include units in your answer. More information. Hint: Solve this using the rotational equivalent of the concept you used for solving part a. Granted, it seems like initially the ball is moving only translationally. But at the instant the skater catches the ball, the ball has a velocity perpendicular to a radius of rotation. Thus, we can think of its motion as rotational also.
c. How much kinetic energy is lost in the collision? Include units in your answer.
PLEASE ANSWER IN HANDWRITING
a)
Apply the momentum conservation equation and substitute the corresponding values to calculate the final linear speed of the skater.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps


