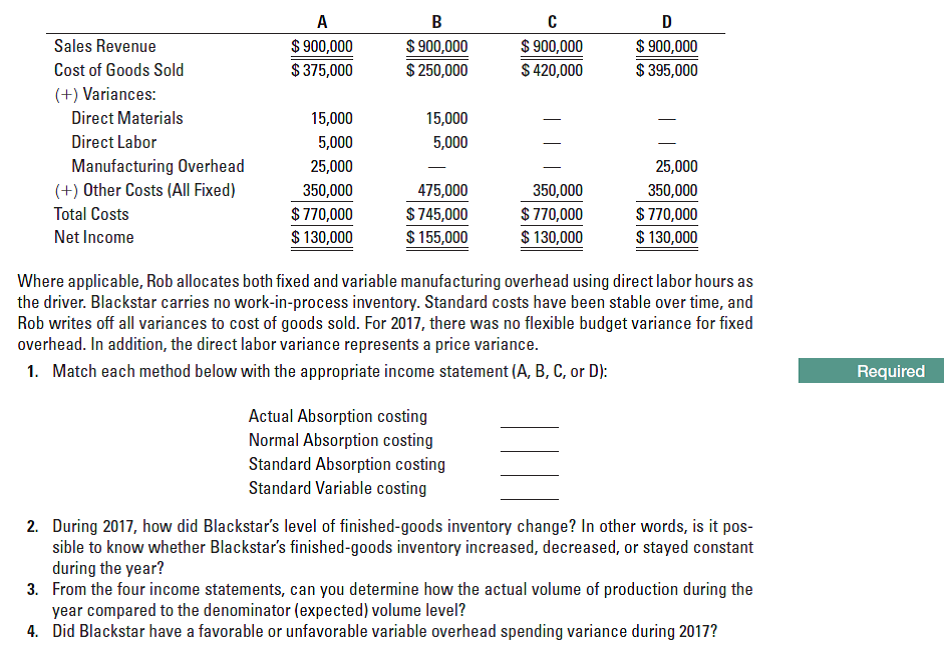
A D $ 900,000 $ 375,000 $ 900,000 $ 250,000 $ 900,000 $ 420,000 $ 900,000 $ 395,000 Sales Revenue Cost of Goods Sold (+) Variances: Direct Materials 15,000 15,000 Direct Labor 5,000 5,000 Manufacturing Overhead (+) Other Costs (All Fixed) 25,000 25,000 350,000 475,000 350,000 350,000 $ 770,000 $ 130,000 $ 770,000 $ 130,000 $ 770,000 $ 130,000 Total Costs $745,000 Net Income $ 155,000 Where applicable, Rob allocates both fixed and variable manufacturing overhead using direct labor hours as the driver. Blackstar carries no work-in-process inventory. Standard costs have been stable over time, and Rob writes off all variances to cost of goods sold. For 2017, there was no flexible budget variance for fixed overhead. In addition, the direct labor variance represents a price variance. 1. Match each method below with the appropriate income statement (A, B, C, or D): Required Actual Absorption costing Normal Absorption costing Standard Absorption costing Standard Variable costing 2. During 2017, how did Blackstar's level of finished-goods inventory change? In other words, is it pos- sible to know whether Blackstar's finished-goods inventory increased, decreased, or stayed constant during the year? 3. From the four income statements, can you determine how the actual volume of production during the year compared to the denominator (expected) volume level? 4. Did Blackstar have a favorable or unfavorable variable overhead spending variance during 2017?
Variance Analysis
In layman's terms, variance analysis is an analysis of a difference between planned and actual behavior. Variance analysis is mainly used by the companies to maintain a control over a business. After analyzing differences, companies find the reasons for the variance so that the necessary steps should be taken to correct that variance.
Standard Costing
The standard cost system is the expected cost per unit product manufactured and it helps in estimating the deviations and controlling them as well as fixing the selling price of the product. For example, it helps to plan the cost for the coming year on the various expenses.
Costing methods and variances, comprehensive. Rob Kapito, the controller of Blackstar Paint Supply Company, has been exploring a variety of internal accounting systems. Rob hopes to get the input of Blackstar’s board of directors in choosing one. To prepare for his presentation to the board, Rob applies four different cost accounting methods to the rm’s operating data for 2017. The four methods are actual absorption costing, normal absorption
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps


