A florist wants to determine if a new additive would Using this dotplot and the difference in proportions from the samples, is there convincing evidence that help extend the life of cut flowers longer than the original additive. The florist randomly selects 20 carnations and randomly assigns 10 to the new additive and 10 to the original additive. After three weeks, 6 carnations placed in the new additive still looked healthy and 2 carnations placed in the original additive still looked healthy. The difference in proportions (new- original) for the carnations that still looked healthy after three weeks was 0.4. Assuming there is no difference in the additives, 200 simulated differences in sample proportions are displayed in the dotplot. the new additive was more effective? O Yes, because a difference in proportions of 0.4 or more occurred 7 out of 200 times, meaning the difference is statistically significant and the new additive is more effective. O Yes, because a difference in proportions of 0.4 or less occurred 193 out of 200 times, meaning the difference is statistically significant and the new additive is more effective. No, because a difference in proportions of 0.4 or more occurred 7 out of 200 times, meaning the difference is not statistically significant and the new Simulation for Difference in Proportions of Carnation Health additive is not more effective. O No, because a difference in proportions of 0.4 or less occurred 193 out of 200 times, meaning the difference is not statistically significant and the new
A florist wants to determine if a new additive would Using this dotplot and the difference in proportions from the samples, is there convincing evidence that help extend the life of cut flowers longer than the original additive. The florist randomly selects 20 carnations and randomly assigns 10 to the new additive and 10 to the original additive. After three weeks, 6 carnations placed in the new additive still looked healthy and 2 carnations placed in the original additive still looked healthy. The difference in proportions (new- original) for the carnations that still looked healthy after three weeks was 0.4. Assuming there is no difference in the additives, 200 simulated differences in sample proportions are displayed in the dotplot. the new additive was more effective? O Yes, because a difference in proportions of 0.4 or more occurred 7 out of 200 times, meaning the difference is statistically significant and the new additive is more effective. O Yes, because a difference in proportions of 0.4 or less occurred 193 out of 200 times, meaning the difference is statistically significant and the new additive is more effective. No, because a difference in proportions of 0.4 or more occurred 7 out of 200 times, meaning the difference is not statistically significant and the new Simulation for Difference in Proportions of Carnation Health additive is not more effective. O No, because a difference in proportions of 0.4 or less occurred 193 out of 200 times, meaning the difference is not statistically significant and the new
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter10: Sequences, Series, And Probability
Section10.8: Probability
Problem 32E
Related questions
Concept explainers
Contingency Table
A contingency table can be defined as the visual representation of the relationship between two or more categorical variables that can be evaluated and registered. It is a categorical version of the scatterplot, which is used to investigate the linear relationship between two variables. A contingency table is indeed a type of frequency distribution table that displays two variables at the same time.
Binomial Distribution
Binomial is an algebraic expression of the sum or the difference of two terms. Before knowing about binomial distribution, we must know about the binomial theorem.
Topic Video
Question

Transcribed Image Text:A florist wants to determine if a new additive would
Using this dotplot and the difference in proportions
from the samples, is there convincing evidence that
help extend the life of cut flowers longer than the
original additive. The florist randomly selects 20
carnations and randomly assigns 10 to the new
additive and 10 to the original additive. After three
weeks, 6 carnations placed in the new additive still
looked healthy and 2 carnations placed in the original
additive still looked healthy. The difference in
proportions (new- original) for the carnations that still
looked healthy after three weeks was 0.4. Assuming
there is no difference in the additives, 200 simulated
differences in sample proportions are displayed in the
dotplot.
the new additive was more effective?
O Yes, because a difference in proportions of 0.4 or
more occurred 7 out of 200 times, meaning the
difference is statistically significant and the new
additive is more effective.
O Yes, because a difference in proportions of 0.4 or
less occurred 193 out of 200 times, meaning the
difference is statistically significant and the new
additive is more effective.
O No, because a difference in proportions of 0.4 or
more occurred 7 out of 200 times, meaning the
difference is not statistically significant and the new
additive is not more effective.
Simulation for Difference in
Proportions of Carnation Health
O No, because a difference in proportions of 0.4 or
less occurred 193 out of 200 times, meaning the
difference is not statistically significant and the new
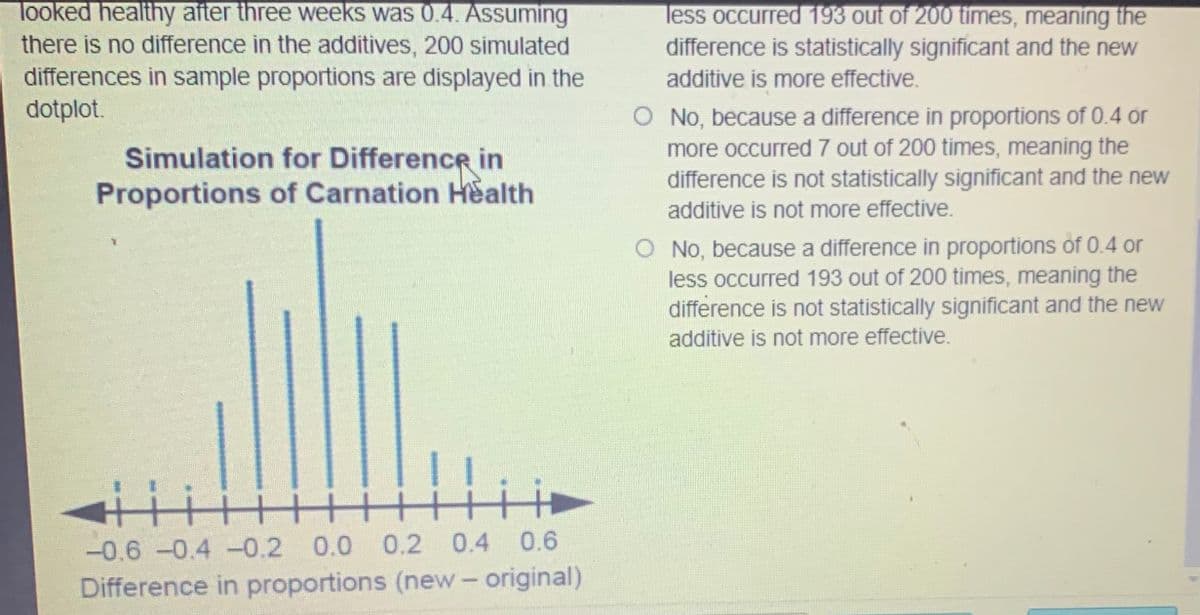
Transcribed Image Text:looked healthy after three weeks was 0.4. Assuming
less occurred 193 out of 200 times, meaning the
difference is statistically significant and the new
there is no difference in the additives, 200 simulated
differences in sample proportions are displayed in the
dotplot.
additive is more effective.
Simulation for Difference in
Proportions of Carnation Health
O No, because a difference in proportions of 0.4 or
more occurred 7 out of 200 times, meaning the
difference is not statistically significant and the new
additive is not more effective.
O No, because a difference in proportions of 0.4 or
less occurred 193 out of 200 times, meaning the
difference is not statistically significant and the new
additive is not more effective.
-0.6 -0.4 -0.2
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6
Difference in proportions (new- original)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, probability and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage
