A manufacturing plant has a potential production capacity of 1,000 units per month (capacity can be increased by 10% if subcontractors are employed). The plant is normally operated at about 80% of capacity. Operating the plant above this level significantly increases variable costs per unit because of the need to pay the skilled workers higher overtime wage rates. For output levels up to 80% of capacity, variable cost per unit is $100. Above 80% and up to 90%, variable costs on this additional output increase by 10%. When output is above 90% and up to 100% of capacity, the additional units cost an additional 25% over the unit variable costs for outputs up to 80% of capacity. For production above 100% and up to 110% of capacity, extensive subcontracting work is used and the unit variable costs of these additional units are 50% above those at output levels up to 80% of capacity. At 80% of capacity, the plant's fixed costs per unit are $50. Total fixed costs are not expected to change within the production range under consideration. Based on the preceding information, complete the following table. (Hint: If necessary, round to two decimal places.) AVC MC ATC (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars) 500 600 700 800 900 1,000 1,100 TTC (Dollars) TFC (Dollars) TVC (Dollars) AFC (Dollars)
A manufacturing plant has a potential production capacity of 1,000 units per month (capacity can be increased by 10% if subcontractors are employed). The plant is normally operated at about 80% of capacity. Operating the plant above this level significantly increases variable costs per unit because of the need to pay the skilled workers higher overtime wage rates. For output levels up to 80% of capacity, variable cost per unit is $100. Above 80% and up to 90%, variable costs on this additional output increase by 10%. When output is above 90% and up to 100% of capacity, the additional units cost an additional 25% over the unit variable costs for outputs up to 80% of capacity. For production above 100% and up to 110% of capacity, extensive subcontracting work is used and the unit variable costs of these additional units are 50% above those at output levels up to 80% of capacity. At 80% of capacity, the plant's fixed costs per unit are $50. Total fixed costs are not expected to change within the production range under consideration. Based on the preceding information, complete the following table. (Hint: If necessary, round to two decimal places.) AVC MC ATC (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars) 500 600 700 800 900 1,000 1,100 TTC (Dollars) TFC (Dollars) TVC (Dollars) AFC (Dollars)
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
5th Edition
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Chapter7: Economies Of Scale And Scope
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7.5IP
Related questions
Question
100%
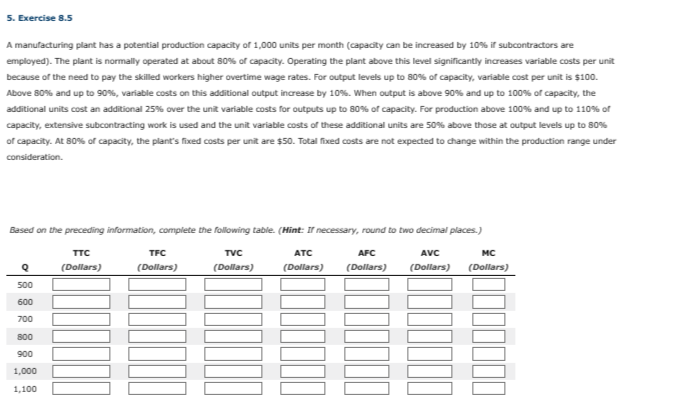
Transcribed Image Text:5. Exercise 8.5
A manufacturing plant has a potential production capacity of 1,000 units per month (capacity can be increased by 10% if subcontractors are
employed). The plant is normally operated at about 80% of capacity. Operating the plant above this level significantly increases variable costs per unit
because of the need to pay the skilled workers higher overtime wage rates. For output levels up to 80% of capacity, variable cost per unit is $100.
Above 80% and up to 90%, variable costs on this additional output increase by 10%. When output is above 90% and up to 100% of capacity, the
additional units cost an additional 25% over the unit variable costs for outputs up to 80% of capacity. For production above 100% and up to 110% of
capacity, extensive subcontracting work is used and the unit variable costs of these additional units are 50% above those at output levels up to 80%
of capacity. At 80% of capacity, the plant's fixed costs per unit are $50. Total fixed costs are not expected to change within the production range under
consideration.
Based on the preceding information, complete the following table. (Hint: If necessary, round to two decimal places.)
TTC
TVC
ATC
AFC
AVC
MC
(Dollars)
(Dollars)
(Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars)
Q
500
600
700
800
900
1,000
1,100
TFC
(Dollars)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:
9781337106665
Author:
Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an…
Economics
ISBN:
9781305506381
Author:
James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning