A student constructs a voltaic cell to study the reaction between M(s) and X(s) and their ions. A diagram of the cell is shown above. The student uses 1.0 M solutions of M2+ and X3+ as well as solid electrodes of M(s) and X(s). The reduction reactions of M2+ and X3+ are shown below. The student connects the voltaic cell and measures the voltage produced.
A student constructs a voltaic cell to study the reaction between M(s) and X(s) and their ions. A diagram of the cell is shown above. The student uses 1.0 M solutions of M2+ and X3+ as well as solid electrodes of M(s) and X(s). The reduction reactions of M2+ and X3+ are shown below. The student connects the voltaic cell and measures the voltage produced.
Chapter18: Electrochemistry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 83E: Consider a concentration cell that has both electrodes made of some metal M. Solution A in one...
Related questions
Question
A student constructs a voltaic cell to study the reaction between M(s) and X(s) and their ions. A diagram of the cell is shown above. The student uses 1.0 M solutions of M2+ and X3+ as well as solid electrodes of M(s) and X(s). The reduction reactions of M2+ and X3+ are shown below.
The student connects the voltaic cell and measures the voltage produced.
- As the reaction proceeds would you expect the mass of the electrode used as the cathode to increase, decrease, or remain the same. Justify your answer.
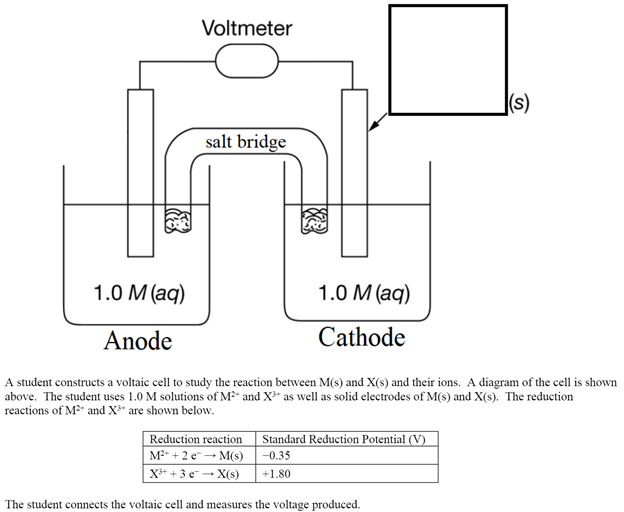
Transcribed Image Text:Voltmeter
|(s)
salt bridge
1.0 M (aq)
1.0 M (aq)
Anode
Cathode
A student constructs a voltaic cell to study the reaction between M(s) and X(s) and their ions. A diagram of the cell is shown
above. The student uses 1.0 M solutions of MF* and X** as well as solid electrodes of M(s) and X(s). The reduction
reactions of M* and X* are shown below.
Reduction reaction
Standard Reduction Potential (V)
M + 2 e - M(s)
-0.35
X* + 3 e - X(s)
+1.80
The student connects the voltaic cell and measures the voltage produced.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285199047
Author:
John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399074
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning