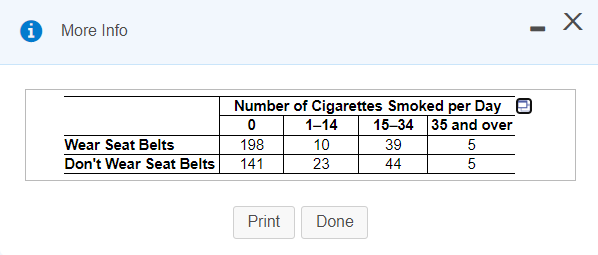
A study of seat belt users and nonusers yielded the randomly selected sample data summarized in the accompanying table. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that the amount of smoking is independent of seat use. A plausible theory is that people who smoke are less concerned about their health and safety and are therefore less inclined to wear seat belts. Is this theory supported by the sample data? E Click the icon to view the data table. Determine the null and alternative hypotheses. O A. Ho: Heavy smokers are less likely than non-smokers to wear a seat belt. H4: Heavy smokers are not less likely than non-smokers to wear a seat belt. VB. Ho: The amount of smoking is independent of seat belt use. H,: The amount of smoking is not independent of seat belt use. O C. Họ: The amount of smoking is dependent upon seat belt use. H: The amount of smoking is not dependent upon seat belt use. O D. Ho: Heavy smokers are not less likely than non-smokers to wear a seat belt. H: Heavy smokers are less likely than non-smokers to wear a seat belt. Determine the test statistic. 2 = (Round to three decimal places as needed.)
A study of seat belt users and nonusers yielded the randomly selected sample data summarized in the accompanying table. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that the amount of smoking is independent of seat use. A plausible theory is that people who smoke are less concerned about their health and safety and are therefore less inclined to wear seat belts. Is this theory supported by the sample data? E Click the icon to view the data table. Determine the null and alternative hypotheses. O A. Ho: Heavy smokers are less likely than non-smokers to wear a seat belt. H4: Heavy smokers are not less likely than non-smokers to wear a seat belt. VB. Ho: The amount of smoking is independent of seat belt use. H,: The amount of smoking is not independent of seat belt use. O C. Họ: The amount of smoking is dependent upon seat belt use. H: The amount of smoking is not dependent upon seat belt use. O D. Ho: Heavy smokers are not less likely than non-smokers to wear a seat belt. H: Heavy smokers are less likely than non-smokers to wear a seat belt. Determine the test statistic. 2 = (Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
(REV)00th Edition
ISBN:9780395977224
Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Chapter3: Solving Equation And Problems
Section3.6: Problem Solving: Using Charts
Problem 5P
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
Transcribed Image Text:More Info
Number of Cigarettes Smoked per Day O
15-34 35 and over
39
1-14
Wear Seat Belts
198
10
5
Don't Wear Seat Belts
141
23
44
5
Print
Done
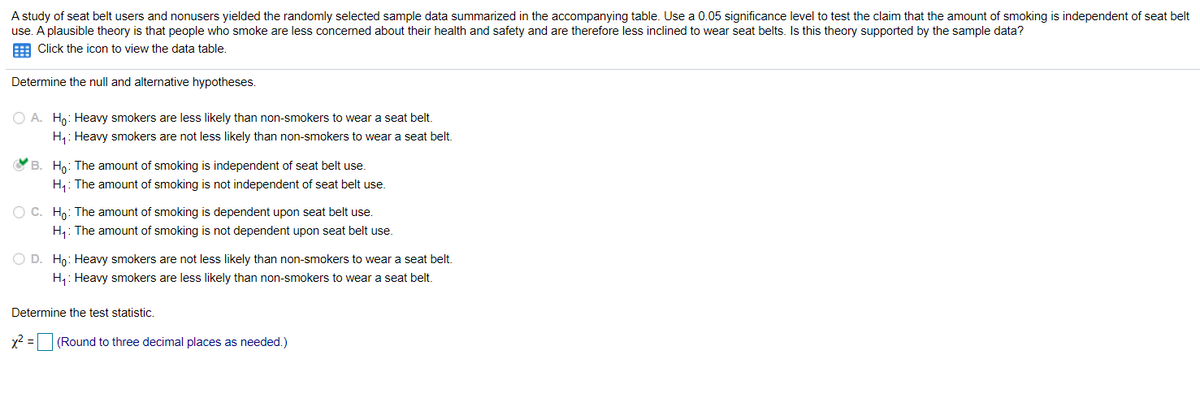
Transcribed Image Text:A study of seat belt users and nonusers yielded the randomly selected sample data summarized in the accompanying table. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that the amount of smoking is independent of seat belt
use. A plausible theory is that people who smoke are less concerned about their health and safety and are therefore less inclined to wear seat belts. Is this theory supported by the sample data?
E Click the icon to view the data table.
Determine the null and alternative hypotheses.
O A. Ho: Heavy smokers are less likely than non-smokers to wear a seat belt.
H: Heavy smokers are not less likely than non-smokers to wear a seat belt.
O B. Ho: The amount of smoking is independent of seat belt use.
H4: The amount of smoking is not independent of seat belt use.
OC. Ho: The amount of smoking is dependent upon seat belt use.
H: The amount of smoking is not dependent upon seat belt use.
O D. Ho: Heavy smokers are not less likely than non-smokers to wear a seat belt.
H: Heavy smokers are less likely than non-smokers to wear a seat belt.
Determine the test statistic.
x2 =
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:
9780395977224
Author:
Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:
McDougal Littell


Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:
9780395977224
Author:
Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:
McDougal Littell


Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780079039897
Author:
Carter
Publisher:
McGraw Hill

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781680331141
Author:
HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

Elementary Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9780998625713
Author:
Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-Smith
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University