A trucking company owns two types of trucks. Type A has 10 cubic metres of refrigerated space and 10 cubic metres of non-refrigerated space. Type B has 20 cubic metres of refrigerated space and 30 cubic metres of non-refrigerated space. A customer wants to haul some produce a certain distance and will require 180 cubic metres of refrigerated space and 240 cubic metres of non-refrigerated space. The trucking company figures that it will take 150 litres of fuel for the type A truck to make the trip and 400 litres of fuel for the type B truck. Find the number of trucks of each type that the company should allow for the job in order to minimise fuel consumption. (a) What can the manager assign directly to this job? Number of B trucks Amount of refrigerated space Number of A trucks Amount of non-refrigerated space Amount of fuel needed The manager wants trucks of type A and y trucks of type B. (b) Enter the constraint imposed by the required refrigerated space. It will be an inequality involving and y, you can enter less than or equal to, and greater than or equal to, as <= and >= respectively. (c) Enter the constraint imposed by the required non-refrigerated space. (d) Enter the total fuel required as a function of x and y. (e) Plot the inequalities on a graph. Enter the coordinates of the corners of the feasible region (the feasible basic solutions). Enter them in increasing order of their x-coordinate. For example, if one feasible basic solution is a = 1, y = 2; another is x = 5, y = 0 and a third is x = 2, y = 3, you would enter (1,2), (2,3), (5,0) If two feasible basic solutions have the same x-value, enter them in increasing order of y-value. Enter them exactly, with fractions if necessary (they will just produce smaller bags) (f) How many A trucks Number and B trucks Number should the company use to minimise fuel consumption?
A trucking company owns two types of trucks. Type A has 10 cubic metres of refrigerated space and 10 cubic metres of non-refrigerated space. Type B has 20 cubic metres of refrigerated space and 30 cubic metres of non-refrigerated space. A customer wants to haul some produce a certain distance and will require 180 cubic metres of refrigerated space and 240 cubic metres of non-refrigerated space. The trucking company figures that it will take 150 litres of fuel for the type A truck to make the trip and 400 litres of fuel for the type B truck. Find the number of trucks of each type that the company should allow for the job in order to minimise fuel consumption. (a) What can the manager assign directly to this job? Number of B trucks Amount of refrigerated space Number of A trucks Amount of non-refrigerated space Amount of fuel needed The manager wants trucks of type A and y trucks of type B. (b) Enter the constraint imposed by the required refrigerated space. It will be an inequality involving and y, you can enter less than or equal to, and greater than or equal to, as <= and >= respectively. (c) Enter the constraint imposed by the required non-refrigerated space. (d) Enter the total fuel required as a function of x and y. (e) Plot the inequalities on a graph. Enter the coordinates of the corners of the feasible region (the feasible basic solutions). Enter them in increasing order of their x-coordinate. For example, if one feasible basic solution is a = 1, y = 2; another is x = 5, y = 0 and a third is x = 2, y = 3, you would enter (1,2), (2,3), (5,0) If two feasible basic solutions have the same x-value, enter them in increasing order of y-value. Enter them exactly, with fractions if necessary (they will just produce smaller bags) (f) How many A trucks Number and B trucks Number should the company use to minimise fuel consumption?
Practical Management Science
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337406659
Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:WINSTON, Wayne L.
Chapter4: Linear Programming Models
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 107P
Related questions
Question
pleaser answer parts A,B and C
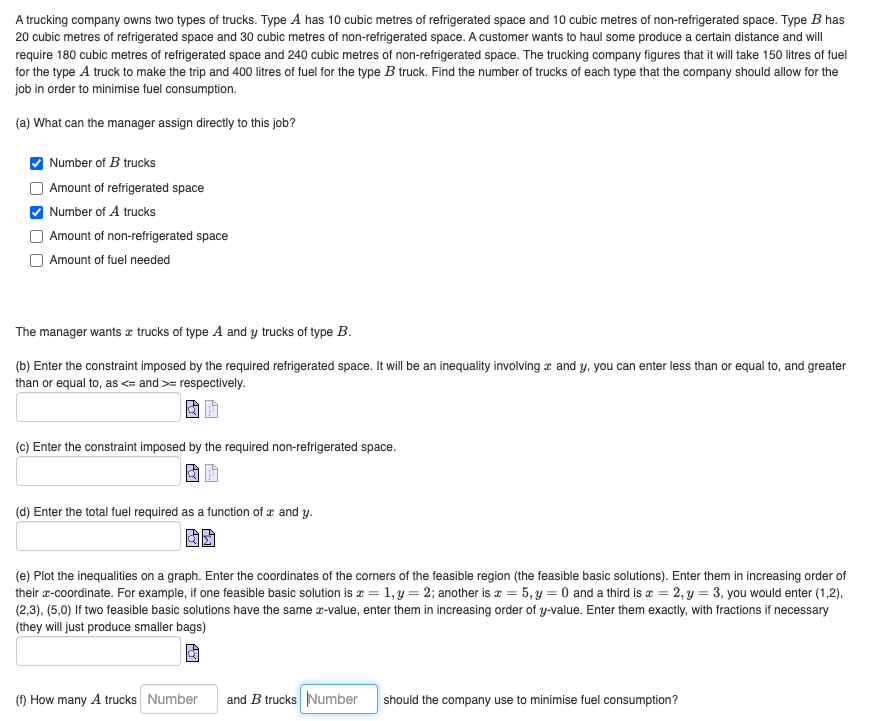
Transcribed Image Text:A trucking company owns two types of trucks. Type A has 10 cubic metres of refrigerated space and 10 cubic metres of non-refrigerated space. Type B has
20 cubic metres of refrigerated space and 30 cubic metres of non-refrigerated space. A customer wants to haul some produce a certain distance and will
require 180 cubic metres of refrigerated space and 240 cubic metres of non-refrigerated space. The trucking company figures that it will take 150 litres of fuel
for the type A truck to make the trip and 400 litres of fuel for the type B truck. Find the number of trucks of each type that the company should allow for the
job in order to minimise fuel consumption.
(a) What can the manager assign directly to this job?
Number of B trucks
Amount of refrigerated space
Number of A trucks
Amount of non-refrigerated space
Amount of fuel needed
The manager wants trucks of type A and y trucks of type B.
(b) Enter the constraint imposed by the required refrigerated space. It will be an inequality involving and y, you can enter less than or equal to, and greater
than or equal to, as <= and >= respectively.
(c) Enter the constraint imposed by the required non-refrigerated space.
(d) Enter the total fuel required as a function of x and y.
(e) Plot the inequalities on a graph. Enter the coordinates of the corners of the feasible region (the feasible basic solutions). Enter them in increasing order of
their x-coordinate. For example, if one feasible basic solution is a = 1, y = 2; another is x = 5, y = 0 and a third is x = 2, y = 3, you would enter (1,2),
(2,3), (5,0) If two feasible basic solutions have the same x-value, enter them in increasing order of y-value. Enter them exactly, with fractions if necessary
(they will just produce smaller bags)
(f) How many A trucks Number
and B trucks Number
should the company use to minimise fuel consumption?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Recommended textbooks for you

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Practical Management Science
Operations Management
ISBN:
9781337406659
Author:
WINSTON, Wayne L.
Publisher:
Cengage,