a. Determine the probability distribution of the random variable Y. y 4 5 6 7 P(Y = y) (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.) b. Use random-variable notation to describe the events that Y takes on the value 6, a value The event that Y takes on the value 6 can be represented as The event that Y takes on a value less than 6 can be represented as The event that Y takes on a value of at least 6 can be represented as c. Find P(Y = 6), P(Y<6), and P(Y>6). P(Y = 6) = (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.) P(Y < 6) = (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.)
a. Determine the probability distribution of the random variable Y. y 4 5 6 7 P(Y = y) (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.) b. Use random-variable notation to describe the events that Y takes on the value 6, a value The event that Y takes on the value 6 can be represented as The event that Y takes on a value less than 6 can be represented as The event that Y takes on a value of at least 6 can be represented as c. Find P(Y = 6), P(Y<6), and P(Y>6). P(Y = 6) = (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.) P(Y < 6) = (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.)
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305071742
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Chapter14: Counting And Probability
Section14.2: Probability
Problem 3E: The conditional probability of E given that F occurs is P(EF)=___________. So in rolling a die the...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
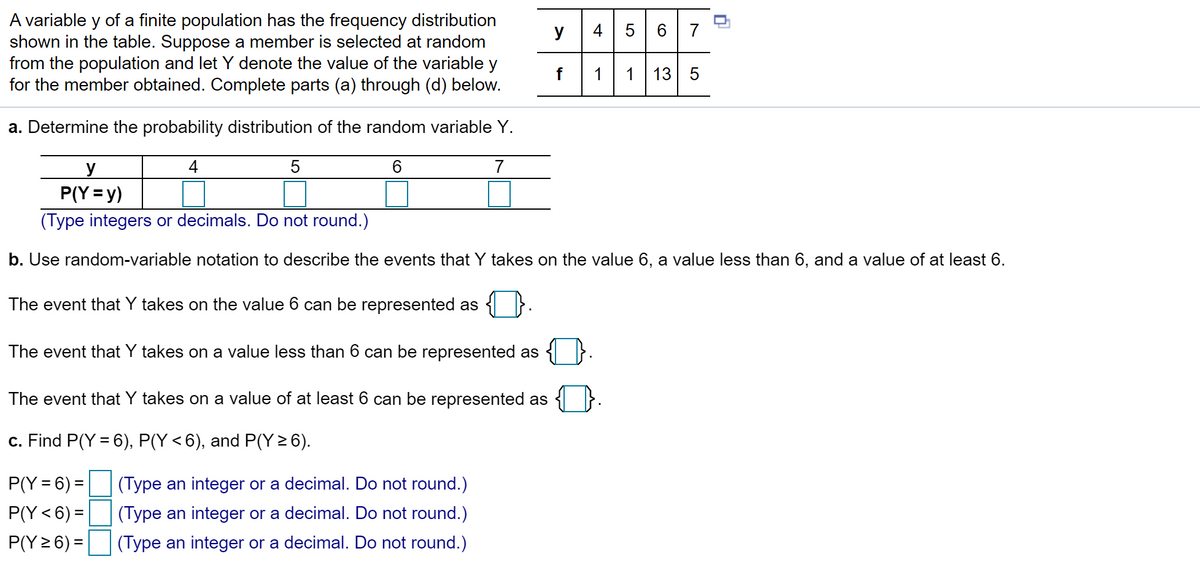
Transcribed Image Text:A variable y of a finite population has the frequency distribution
shown in the table. Suppose a member is selected at random
from the population and let Y denote the value of the variable y
for the member obtained. Complete parts (a) through (d) below.
y
4
5 6 7
1
1
13 5
a. Determine the probability distribution of the random variable Y.
4
6.
7
y
P(Y = y)
(Type integers or decimals. Do not round.)
b. Use random-variable notation to describe the events that Y takes on the value 6, a value less than 6, and a value of at least 6.
The event that Y takes on the value 6 can be represented as
The event that Y takes on a value less than 6 can be represented as
The event that Y takes on a value of at least 6 can be represented as
c. Find P(Y = 6), P(Y < 6), and P(Y > 6).
P(Y = 6) =
(Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.)
P(Y<6) =
(Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.)
P(Y 2 6) =
(Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305652231
Author:
R. David Gustafson, Jeff Hughes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage