Chapter31: Introduction To Analytical Separations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 31.19QAP
Related questions
Question
100%
Analyze the figure below and describe what happens to the colligative properties when solute is added to the solution.
Transcribed Image Text:Answer:
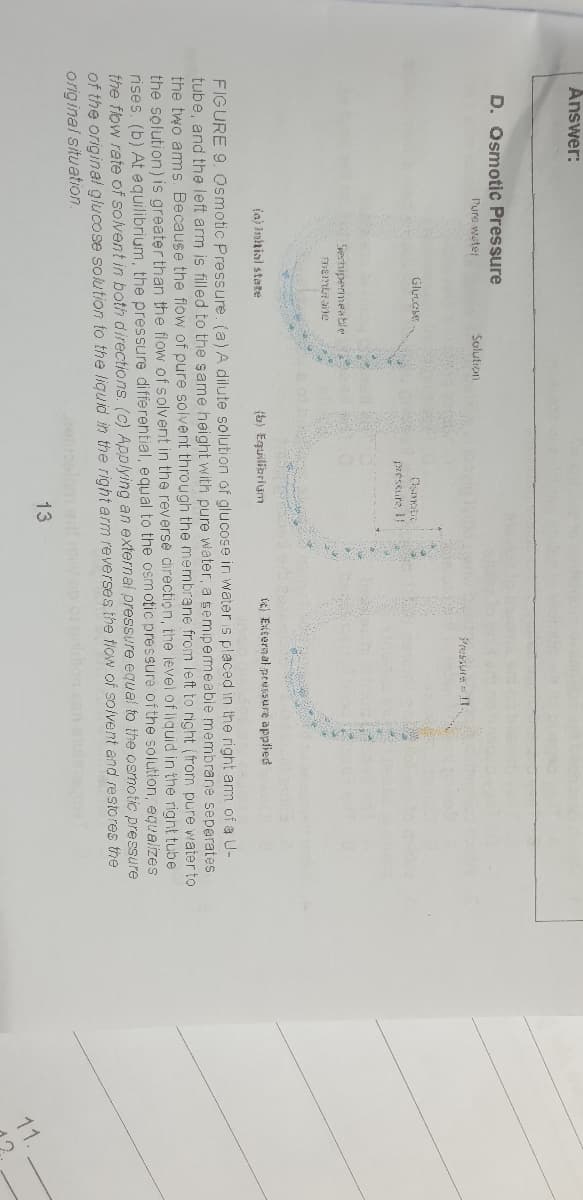
D. Osmotic Pressure
Pure water
Solution
Pressure f1.
pressure if
Spertipermeable
(a) Imhnial state
(b) Equiliarium
ig Enternal peusSure applied
FIGURE 9. Osmotic Pressure. (a)A dilute solution of glucose in wateris placed in the right am of a U-
tube, and the left arm is filled to the same height with pure water, a semipermeable membrane seperates
the two ams Because the flow of pure solvent through the membrane from left to right (from pure water to
the solution) is greater than the flow of solvent in the reverse direction, the level of liquid in the right tube
rises. (b) At equilibrium, the pressure differential, equal to the osmotic pressure of the solution, equalizes
the flow rete of solvent in both directions. (c) Applying an external pressure equal to the osmotic pressure
of the original glucose solution to the liguid in the right arm reverses the tlow of solvent and restores the
original situation.
ob non
13
11.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC L
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305446021
Author:
Lampman
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT



EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC L
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305446021
Author:
Lampman
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT



Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning