Assume that females have pulse rates that are normally distributed with a mean of u = 74.0 beats per minute and a standard deviation of o = 12.5 beats per minute. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. a. If 1 adult female is randomly selected, find the probability that her pulse rate is between 68 beats per minute and 80 beats per minute. The probability isO (Round to four decimal places as needed.) b. If 25 adult females are randomly selected, find the probability that they have pulse rates with a mean between 68 beats per minute and 80 beats per minute. The probability is (Round to four decimal places as needed.) c. Why can the normal distribution be used in part (b), even though the sample size does not exceed 30? O A. Since the original population has a normal distribution, the distribution of sample means is a normal distribution for any sample size. O B. Since the mean pulse rate exceeds 30, the distribution of sample means is a normal distribution for any sample size. O C. Since the distribution is of sample means, not individuals, the distribution is a normal distribution for any sample size. O D. Since the distribution is of individuals, not sample means, the distribution is a normal distribution for any sample size.
Assume that females have pulse rates that are normally distributed with a mean of u = 74.0 beats per minute and a standard deviation of o = 12.5 beats per minute. Complete parts (a) through (c) below. a. If 1 adult female is randomly selected, find the probability that her pulse rate is between 68 beats per minute and 80 beats per minute. The probability isO (Round to four decimal places as needed.) b. If 25 adult females are randomly selected, find the probability that they have pulse rates with a mean between 68 beats per minute and 80 beats per minute. The probability is (Round to four decimal places as needed.) c. Why can the normal distribution be used in part (b), even though the sample size does not exceed 30? O A. Since the original population has a normal distribution, the distribution of sample means is a normal distribution for any sample size. O B. Since the mean pulse rate exceeds 30, the distribution of sample means is a normal distribution for any sample size. O C. Since the distribution is of sample means, not individuals, the distribution is a normal distribution for any sample size. O D. Since the distribution is of individuals, not sample means, the distribution is a normal distribution for any sample size.
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Assume that females have pulse rates that are normally distributed with a mean of p = 74.0 beats per minute and a standard deviation of o = 12.5 beats per minute. Complete parts (a) through (c) below.
a. If 1 adult female is randomly selected, find the probability that her pulse rate is between 68 beats per minute and 80 beats per minute.
The probability is N
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
b. If 25 adult females are randomly selected, find the probability that they have pulse rates with a mean between 68 beats per minute and 80 beats per minute.
The probability is
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
c. Why can the normal distribution be used in part (b), even though the sample size does not exceed 30?
O A. Since the original population has
normal distribution, the distribution of sample means is a normal distribution for any sample size.
O B. Since the mean pulse rate exceeds 30, the distribution of sample means is a normal distribution for any sample size.
O C. Since the distribution is of sample means, not individuals, the distribution is a normal distribution for any sample size.
O D. Since the distribution is of individuals, not sample means, the distribution is a normal distribution for any sample size.
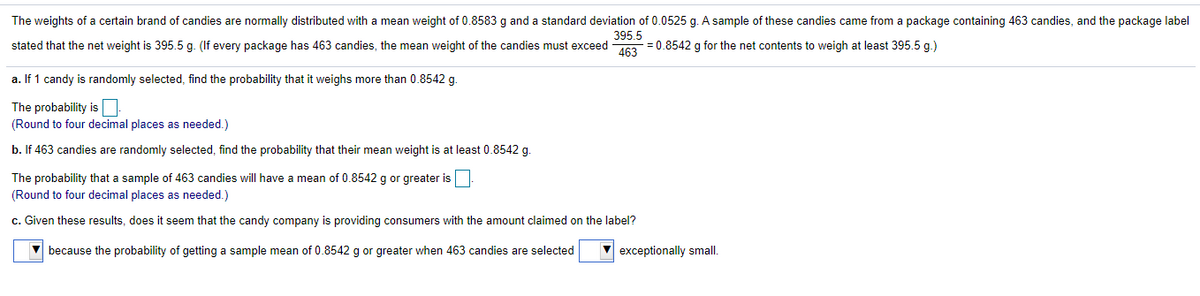
Transcribed Image Text:The weights of a certain brand of candies are normally distributed with a mean weight of 0.8583 g and a standard deviation of 0.0525 g. A sample of these candies came from a package containing 463 candies, and the package label
395.5
stated that the net weight is 395.5 g. (If every package has 463 candies, the mean weight of the candies must exceed a = 0.8542 g for the net contents to weigh at least 395.5 g.)
a. If 1 candy is randomly selected, find the probability that it weighs more than 0.8542 g.
The probability is
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
b. If 463 candies are randomly selected, find the probability that their mean weight is at least 0.8542 g.
mean of 0.8542 g or greater is
The probability that a sample of 463 candies will have
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
c. Given these results, does it seem that the candy company is providing consumers with the amount claimed on the label?
V because the probability of getting a sample mean of 0.8542 g or greater when 463 candies are selected
V exceptionally small.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman