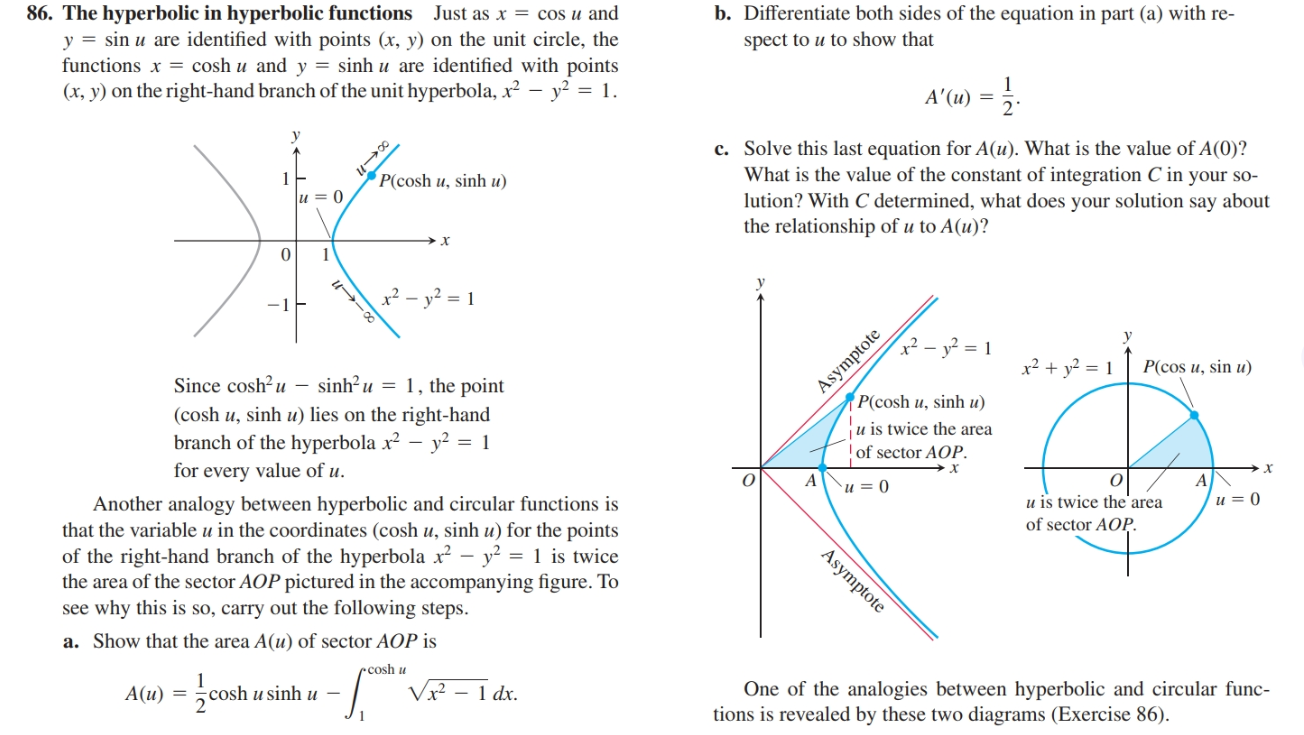
b. Differentiate both sides of the equation in part (a) with re- 86. The hyperbolic in hyperbolic functions Just as x = cos u and y = sin u are identified with points (x, y) on the unit circle, the functions x = cosh u and y = sinh u are identified with points (x, y) on the right-hand branch of the unit hyperbola, x² – y² = 1. spect to u to show that A'(u) = 2. c. Solve this last equation for A(u). What is the value of A(0)? What is the value of the constant of integration C in your so- P(cosh u, sinh u) lution? With C determined, what does your solution say about the relationship of u to A(u)? u = 0 · y² = 1 1 x² + v² = 1 P(cos u, sin u) Since cosh²u – sinh²u = 1, the point P(cosh u, sinh u) (cosh u, sinh u) lies on the right-hand u is twice the area branch of the hyperbola x² – y² = 1 of sector AOP. for every value of u. и 3D 0 и 3 0 u is twice the'area Another analogy between hyperbolic and circular functions is that the variable u in the coordinates (cosh u, sinh u) for the points of the right-hand branch of the hyperbola x – y? = 1 is twice the area of the sector AOP pictured in the accompanying figure. To see why this is so, carry out the following steps. of sector AOP. Asymptote a. Show that the area A(u) of sector AOP is One of the analogies between hyperbolic and circular func- tions is revealed by these two diagrams (Exercise 86). rcosh u Vx² – 1 dx. A(u) = cosh u sinh u – U -00 Asymptote
b. Differentiate both sides of the equation in part (a) with re- 86. The hyperbolic in hyperbolic functions Just as x = cos u and y = sin u are identified with points (x, y) on the unit circle, the functions x = cosh u and y = sinh u are identified with points (x, y) on the right-hand branch of the unit hyperbola, x² – y² = 1. spect to u to show that A'(u) = 2. c. Solve this last equation for A(u). What is the value of A(0)? What is the value of the constant of integration C in your so- P(cosh u, sinh u) lution? With C determined, what does your solution say about the relationship of u to A(u)? u = 0 · y² = 1 1 x² + v² = 1 P(cos u, sin u) Since cosh²u – sinh²u = 1, the point P(cosh u, sinh u) (cosh u, sinh u) lies on the right-hand u is twice the area branch of the hyperbola x² – y² = 1 of sector AOP. for every value of u. и 3D 0 и 3 0 u is twice the'area Another analogy between hyperbolic and circular functions is that the variable u in the coordinates (cosh u, sinh u) for the points of the right-hand branch of the hyperbola x – y? = 1 is twice the area of the sector AOP pictured in the accompanying figure. To see why this is so, carry out the following steps. of sector AOP. Asymptote a. Show that the area A(u) of sector AOP is One of the analogies between hyperbolic and circular func- tions is revealed by these two diagrams (Exercise 86). rcosh u Vx² – 1 dx. A(u) = cosh u sinh u – U -00 Asymptote
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter11: Topics From Analytic Geometry
Section11.4: Plane Curves And Parametric Equations
Problem 31E
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:b. Differentiate both sides of the equation in part (a) with re-
86. The hyperbolic in hyperbolic functions Just as x = cos u and
y = sin u are identified with points (x, y) on the unit circle, the
functions x = cosh u and y = sinh u are identified with points
(x, y) on the right-hand branch of the unit hyperbola, x² – y² = 1.
spect to u to show that
A'(u) = 2.
c. Solve this last equation for A(u). What is the value of A(0)?
What is the value of the constant of integration C in your so-
P(cosh u, sinh u)
lution? With C determined, what does your solution say about
the relationship of u to A(u)?
u = 0
· y² = 1
1
x² + v² = 1
P(cos u, sin u)
Since cosh²u – sinh²u = 1, the point
P(cosh u, sinh u)
(cosh u, sinh u) lies on the right-hand
u is twice the area
branch of the hyperbola x² – y² = 1
of sector AOP.
for every value of u.
и 3D 0
и 3 0
u is twice the'area
Another analogy between hyperbolic and circular functions is
that the variable u in the coordinates (cosh u, sinh u) for the points
of the right-hand branch of the hyperbola x – y? = 1 is twice
the area of the sector AOP pictured in the accompanying figure. To
see why this is so, carry out the following steps.
of sector AOP.
Asymptote
a. Show that the area A(u) of sector AOP is
One of the analogies between hyperbolic and circular func-
tions is revealed by these two diagrams (Exercise 86).
rcosh u
Vx² – 1 dx.
A(u) = cosh u sinh u –
U -00
Asymptote
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning