b1. F Pe, which assumes continuous compounding, says that the Future value (F) of an amount (P) invested today at an annual rate (), expressed as a decimal for the time (), in years is given by the function. Thus if you invested $100 now at the annual rate of 5 1/2% for 6 years and 3 months you would get back (at the end of the time), FS1005 $100 0055y625) $100$100(1.4102) S141.02. Suppose you put $2000 in a savings account when your son was born for 18 years and 6 months to help pay for his college education. If you can earn 3% annually on it, what should you have in his education savings account in 18 years and 6 months?
b1. F Pe, which assumes continuous compounding, says that the Future value (F) of an amount (P) invested today at an annual rate (), expressed as a decimal for the time (), in years is given by the function. Thus if you invested $100 now at the annual rate of 5 1/2% for 6 years and 3 months you would get back (at the end of the time), FS1005 $100 0055y625) $100$100(1.4102) S141.02. Suppose you put $2000 in a savings account when your son was born for 18 years and 6 months to help pay for his college education. If you can earn 3% annually on it, what should you have in his education savings account in 18 years and 6 months?
Chapter11: Capital Budgeting Decisions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5PB: Mason, Inc., is considering the purchase of a patent that has a cost of $85000 and an estimated...
Related questions
Question
1. (See image), which assumes continuous compounding, says that the Future value (F) of an amount (P) invested today at an annual rate (r), expressed as a decimal for the time (t), in years is given by the function. Thus if you invested $100 now at the annual rate of 5 1/2% for 6 years and 3 months you would get back (at the end of the time), F = $100e^(0.055)^(6.25) = $100e^(0.3438) = $100(1.4102) = $141.02. Suppose you put $2000 in a savings account when your son was born for 18 years and 6 months to help pay for his college education. If you can earn 3% annually on it, what should you have in his education savings account in 18 years and 6 months?
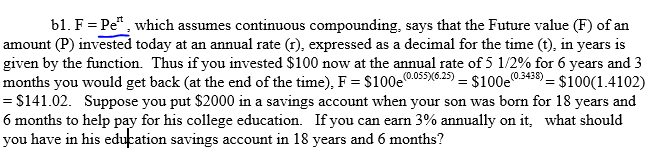
Transcribed Image Text:b1. F
Pe, which assumes continuous compounding, says that the Future value (F) of an
amount (P) invested today at an annual rate (), expressed as a decimal for the time (), in years is
given by the function. Thus if you invested $100 now at the annual rate of 5 1/2% for 6 years and 3
months you would get back (at the end of the time), FS1005 $100
0055y625) $100$100(1.4102)
S141.02. Suppose you put $2000 in a savings account when your son was born for 18 years and
6 months to help pay for his college education. If you can earn 3% annually on it, what should
you have in his education savings account in 18 years and 6 months?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College



Principles of Accounting Volume 2
Accounting
ISBN:
9781947172609
Author:
OpenStax
Publisher:
OpenStax College




Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course …
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305627734
Author:
Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. Anderson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning