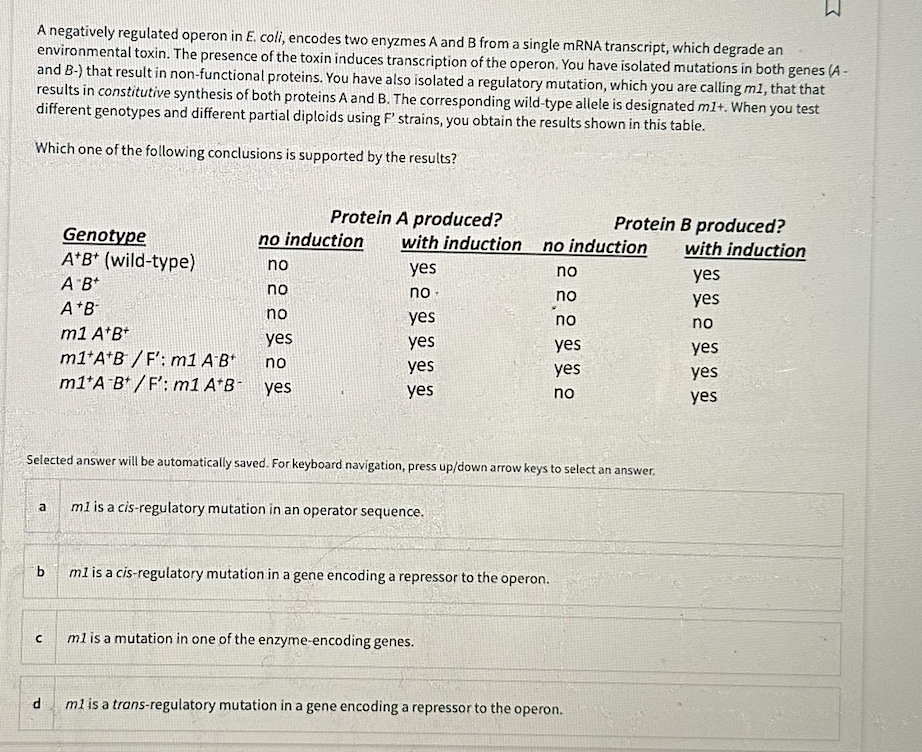
A negatively regulated operon in E. coli, encodes two enyzmes A and B from a single mRNA transcript, which degrade an environmental toxin. The presence of the toxin induces transcription of the operon. You have isolated mutations in both genes (A - and B-) that result in non-functional proteins. You have also isolated a regulatory mutation, which you are calling m1, that that results in constitutive synthesis of both proteins A and B. The corresponding wild-type allele is designated m1+. When you test different genotypes and different partial diploids using F' strains, you obtain the results shown in this table. Which one of the following conclusions is supported by the results? a b с Genotype A+B+ (wild-type) AB+ A+B m1 A*B* m1+A+B/F': m1 AB* m1 A B+/F': m1 A*B- d Protein A produced? no induction no no no yes no yes with induction yes no T yes yes yes yes Selected answer will be automatically saved. For keyboard navigation, press up/down arrow keys to select an answer. m1 is a cis-regulatory mutation in an operator sequence. no induction m1 is a cis-regulatory mutation in a gene encoding a repressor to the operon. m1 is a mutation in one of the enzyme-encoding genes. no no no yes yes no Protein B produced? with induction yes yes no m1 is a trans-regulatory mutation in a gene encoding a repressor to the operon. yes yes yes
Gene Interactions
When the expression of a single trait is influenced by two or more different non-allelic genes, it is termed as genetic interaction. According to Mendel's law of inheritance, each gene functions in its own way and does not depend on the function of another gene, i.e., a single gene controls each of seven characteristics considered, but the complex contribution of many different genes determine many traits of an organism.
Gene Expression
Gene expression is a process by which the instructions present in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) are converted into useful molecules such as proteins, and functional messenger ribonucleic (mRNA) molecules in the case of non-protein-coding genes.
2. please answer this asap
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps









