Case A: araldal ase Data Sheet: Vector Addition - Static Equilibrium polar coordinates magnitude direction (degrees) 155 Cartesian coordinates y-comp (grams) x-comp (grams) 20 (grams) F1 - 18. I 8.5 F2 40 38.6 10.4 106 210 -91.8 - 53 resultant 79 ఇ0క - 71.3 - 34.1 79 75 78 from calculation 205 equilibrant from graph 25 28 from force table Case B: Cartesian coordinates polar coordinates magnitude (grams) 80 y-comp (grams) - 56.6 direction x-comp (degrees) (grams) F1 315 56.6 F2 135 192 - 132.0 -28.1 F3 140 90.0 107.2 resultant 26.8 57 14.6 22.5 237 232 from calculation 26.8 24 32 equilibrant from graph from force table HS polar coordinates magnitude direction x-comp (grams) 85 Cartesian coordinates Case C: y-comp (degrees) (grams) -37.3 76.4 -19.9 44.6 12.6 (grams) 116 F1 175 1.74 -40.1 38 F2 60 318 Fs resultant 40 108 40 28,8 from calculation 41 297 from graph equilibrant from force table 400 105°
Case A: araldal ase Data Sheet: Vector Addition - Static Equilibrium polar coordinates magnitude direction (degrees) 155 Cartesian coordinates y-comp (grams) x-comp (grams) 20 (grams) F1 - 18. I 8.5 F2 40 38.6 10.4 106 210 -91.8 - 53 resultant 79 ఇ0క - 71.3 - 34.1 79 75 78 from calculation 205 equilibrant from graph 25 28 from force table Case B: Cartesian coordinates polar coordinates magnitude (grams) 80 y-comp (grams) - 56.6 direction x-comp (degrees) (grams) F1 315 56.6 F2 135 192 - 132.0 -28.1 F3 140 90.0 107.2 resultant 26.8 57 14.6 22.5 237 232 from calculation 26.8 24 32 equilibrant from graph from force table HS polar coordinates magnitude direction x-comp (grams) 85 Cartesian coordinates Case C: y-comp (degrees) (grams) -37.3 76.4 -19.9 44.6 12.6 (grams) 116 F1 175 1.74 -40.1 38 F2 60 318 Fs resultant 40 108 40 28,8 from calculation 41 297 from graph equilibrant from force table 400 105°
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
1st Edition
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Chapter5: Displacement And Force In Two Dimensions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6STP
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
Explain in words why the equilibrant vector is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the vector which represents the resultant of the first three forces in each case, in other words why Ex = -Rx and Ey = -Ry
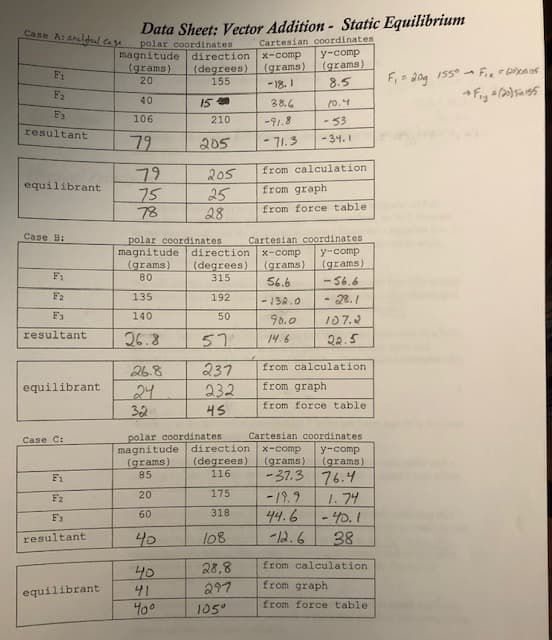
Transcribed Image Text:Case A: araldal ase
Data Sheet: Vector Addition - Static Equilibrium
polar coordinates
magnitude direction
(degrees)
155
Cartesian coordinates
y-comp
(grams)
x-comp
(grams)
20
(grams)
F1
- 18. I
8.5
F2
40
38.6
10.4
106
210
-91.8
- 53
resultant
79
ఇ0క
- 71.3
- 34.1
79
75
78
from calculation
205
equilibrant
from graph
25
28
from force table
Case B:
Cartesian coordinates
polar coordinates
magnitude
(grams)
80
y-comp
(grams)
- 56.6
direction
x-comp
(degrees)
(grams)
F1
315
56.6
F2
135
192
- 132.0
-28.1
F3
140
90.0
107.2
resultant
26.8
57
14.6
22.5
237
232
from calculation
26.8
24
32
equilibrant
from graph
from force table
HS
polar coordinates
magnitude direction x-comp
(grams)
85
Cartesian coordinates
Case C:
y-comp
(degrees)
(grams)
-37.3 76.4
-19.9
44.6
12.6
(grams)
116
F1
175
1.74
-40.1
38
F2
60
318
Fs
resultant
40
108
40
28,8
from calculation
41
297
from graph
equilibrant
from force table
400
105°
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student…
Physics
ISBN:
9780078807213
Author:
Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University