Classify the conditions given as indicating that a reaction is at equilibrium, is not at equilibrium, or that the conditions may occur in either state. At equilibrium Not at equilibrium May or may not be at equilibrium Answer Bank The products and reactants have equal concentrations. The concentration of products is greater than the concentration of reactants. The concentrations of products and reactants are constant. The forward reaction is occurring at a very slow rate. The concentration of reactants is slowly increasing. The forward and reverse reactions occur at equal rates.
Classify the conditions given as indicating that a reaction is at equilibrium, is not at equilibrium, or that the conditions may occur in either state. At equilibrium Not at equilibrium May or may not be at equilibrium Answer Bank The products and reactants have equal concentrations. The concentration of products is greater than the concentration of reactants. The concentrations of products and reactants are constant. The forward reaction is occurring at a very slow rate. The concentration of reactants is slowly increasing. The forward and reverse reactions occur at equal rates.
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
7th Edition
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:H. Stephen Stoker
Chapter9: Chemical Reactions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9.88EP: For the generalized chemical reaction A(g)+B(g)C(g)+D(g) determine whether the concentration of D in...
Related questions
Question
100%
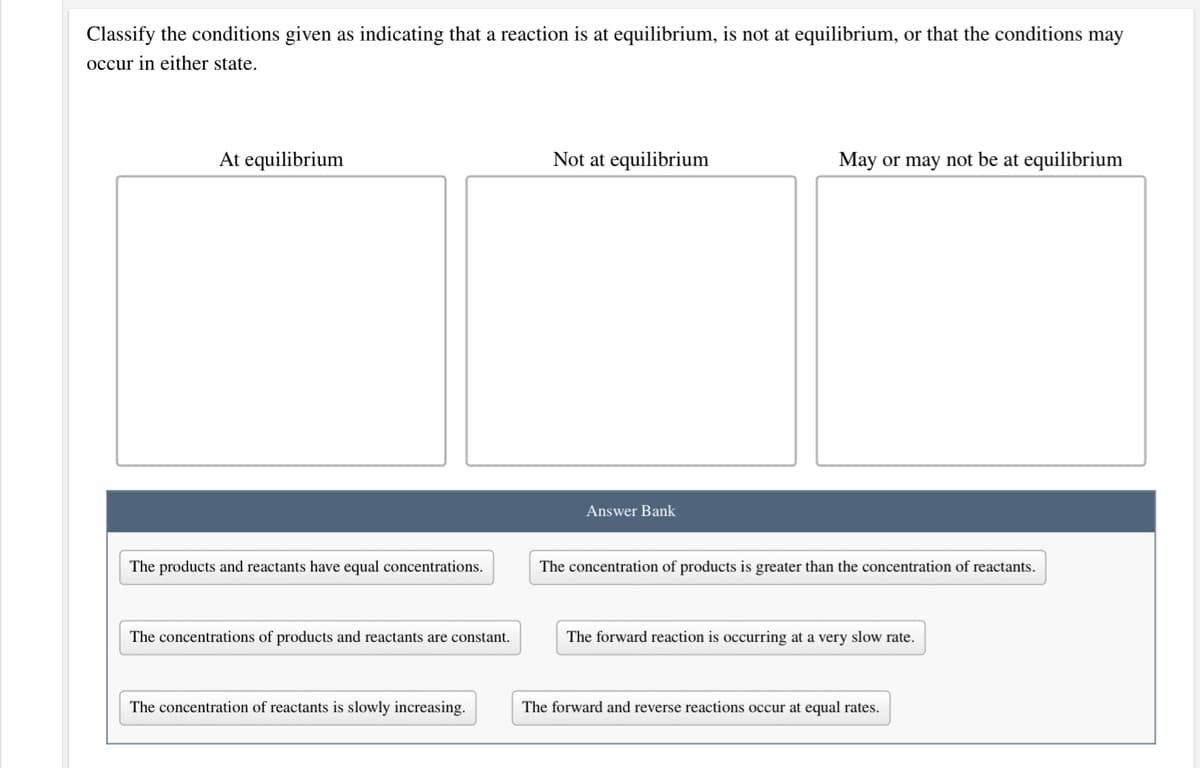
Transcribed Image Text:Classify the conditions given as indicating that a reaction is at equilibrium, is not at equilibrium, or that the conditions may
occur in either state.
At equilibrium
Not at equilibrium
May or may not be at equilibrium
Answer Bank
The products and reactants have equal concentrations.
The concentration of products is greater than the concentration of reactants.
The concentrations of products and reactants are constant.
The forward reaction is occurring at a very slow rate.
The concentration of reactants is slowly increasing.
The forward and reverse reactions occur at equal rates.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285853918
Author:
H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781559539418
Author:
Angelica Stacy
Publisher:
MAC HIGHER

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133109655
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781285853918
Author:
H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Living By Chemistry: First Edition Textbook
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781559539418
Author:
Angelica Stacy
Publisher:
MAC HIGHER

World of Chemistry, 3rd edition
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133109655
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337399425
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079250
Author:
Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
