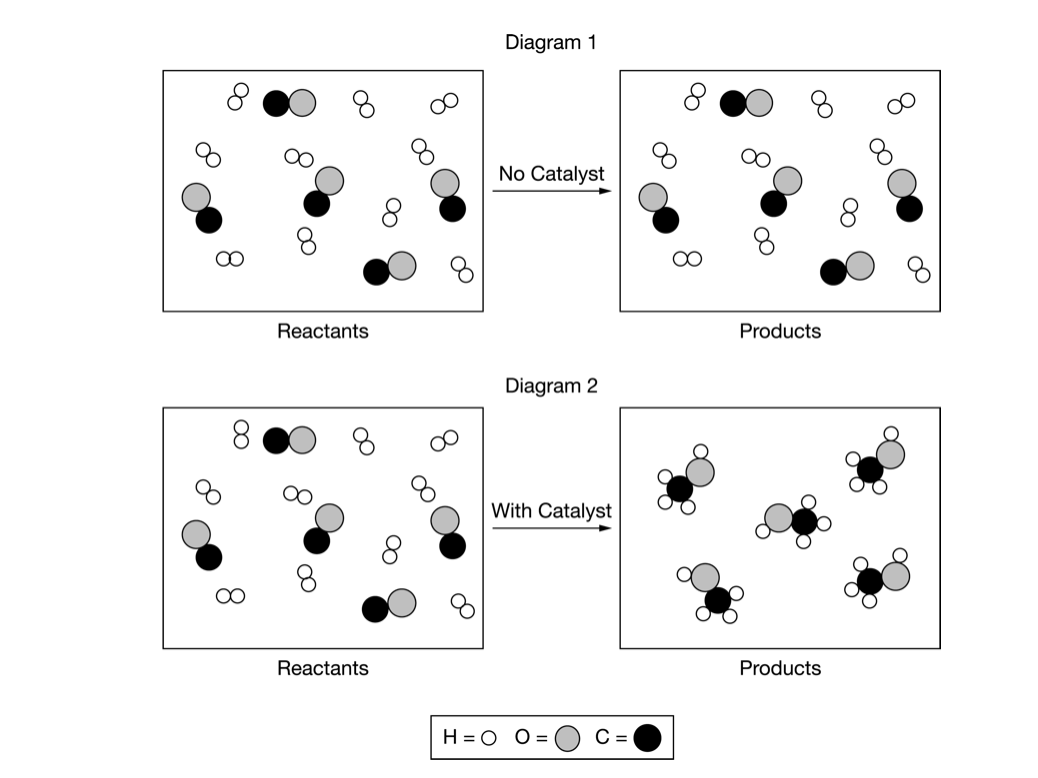
CO(g)+2H2(g)⇄CH3OH(g)K=2.2×104at298K A stoichiometric mixture of CO(g) and H2(g) was allowed to react in two different 2.0L rigid containers at a constant temperature of 298K. The reaction is represented by the equation above. Diagram 1 represents the uncatalyzed reaction and diagram 2 represents the catalyzed reaction one hour after the reactants were mixed. Which of the following correctly explains the experimental results represented in the particle diagrams? A Although the reaction is thermodynamically favorable because ΔG°<0 based on the value of K, only the catalyzed reaction could proceed in one hour because its reactant molecules had a higher average kinetic energy. B Although the reaction is thermodynamically favorable because ΔG°<0 based on the value of K, only the catalyzed reaction could proceed in one hour because it has a lower activation-energy reaction pathway. C The reaction is not thermodynamically favorable because ΔG°>0 based on the value of K, but the addition of a catalyst improved the orientation of the reactants during collisions, allowing the catalyzed reaction to proceed in one hour. D The reaction is not thermodynamically favorable because ΔG°>0 based on the value of K, but the catalyzed reaction could proceed in one hour because it has a lower ΔH and a higher
A stoichiometric mixture of CO(g) and H2(g) was allowed to react in two different 2.0L rigid containers at a constant temperature of 298K. The reaction is represented by the equation above. Diagram 1 represents the uncatalyzed reaction and diagram 2 represents the catalyzed reaction one hour after the reactants were mixed.
Which of the following correctly explains the experimental results represented in the particle diagrams?
A Although the reaction is
D The reaction is not thermodynamically favorable because ΔG°>0 based on the value of K, but the catalyzed reaction could proceed in one hour because it has a lower ΔH and a higher
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images









