Consider a rectangular pipe with dimensions (Ax, Ay, Az), with insulating sidewalls (located at +Ax/2) and conducting top/bottom walls (located at ±Ay/2). Ionized, conducting plasma flows through the pipe with velocity v= v, î, and a uniform magnetic field is imposed: B = B, î. %D (a) What is the potential between the top and bottom walls of the pipe? (b) If the top and bottom walls are connected by a load resistance R, and the plasma has conductivity o, how much current is driven through the load?
Consider a rectangular pipe with dimensions (Ax, Ay, Az), with insulating sidewalls (located at +Ax/2) and conducting top/bottom walls (located at ±Ay/2). Ionized, conducting plasma flows through the pipe with velocity v= v, î, and a uniform magnetic field is imposed: B = B, î. %D (a) What is the potential between the top and bottom walls of the pipe? (b) If the top and bottom walls are connected by a load resistance R, and the plasma has conductivity o, how much current is driven through the load?
Related questions
Question
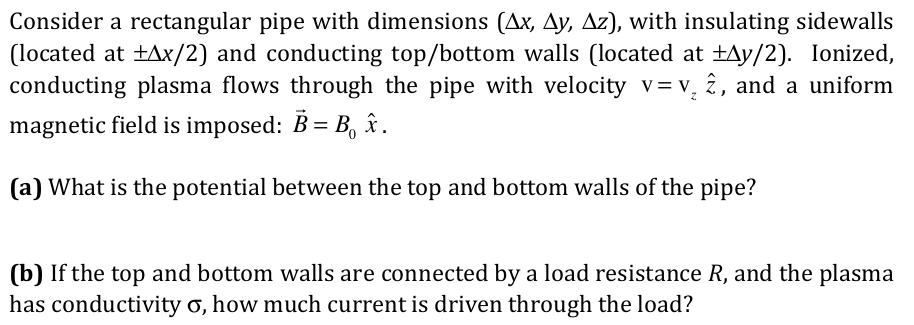
Transcribed Image Text:Consider a rectangular pipe with dimensions (Ax, Ay, Az), with insulating sidewalls
(located at +Ax/2) and conducting top/bottom walls (located at ±Ay/2). Ionized,
conducting plasma flows through the pipe with velocity v= v, î, and a uniform
magnetic field is imposed: B = B, î.
%D
(a) What is the potential between the top and bottom walls of the pipe?
(b) If the top and bottom walls are connected by a load resistance R, and the plasma
has conductivity o, how much current is driven through the load?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 6 images
