EXAMPLE 1 Máňufacturing A factory of the Global Manufacturing Company was manufacturing products with a defect rate of 15% (based on data from the Harvard Business Review). If a customer pur- chases 12 of the products, what is the probability of getting at least one that is defective? SOLUTION
EXAMPLE 1 Máňufacturing A factory of the Global Manufacturing Company was manufacturing products with a defect rate of 15% (based on data from the Harvard Business Review). If a customer pur- chases 12 of the products, what is the probability of getting at least one that is defective? SOLUTION
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition 2012
1st Edition
ISBN:9780547587776
Author:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Chapter11: Data Analysis And Probability
Section11.8: Probabilities Of Disjoint And Overlapping Events
Problem 2C
Related questions
Question
could you please explain me the 0.85, how it was calculated?
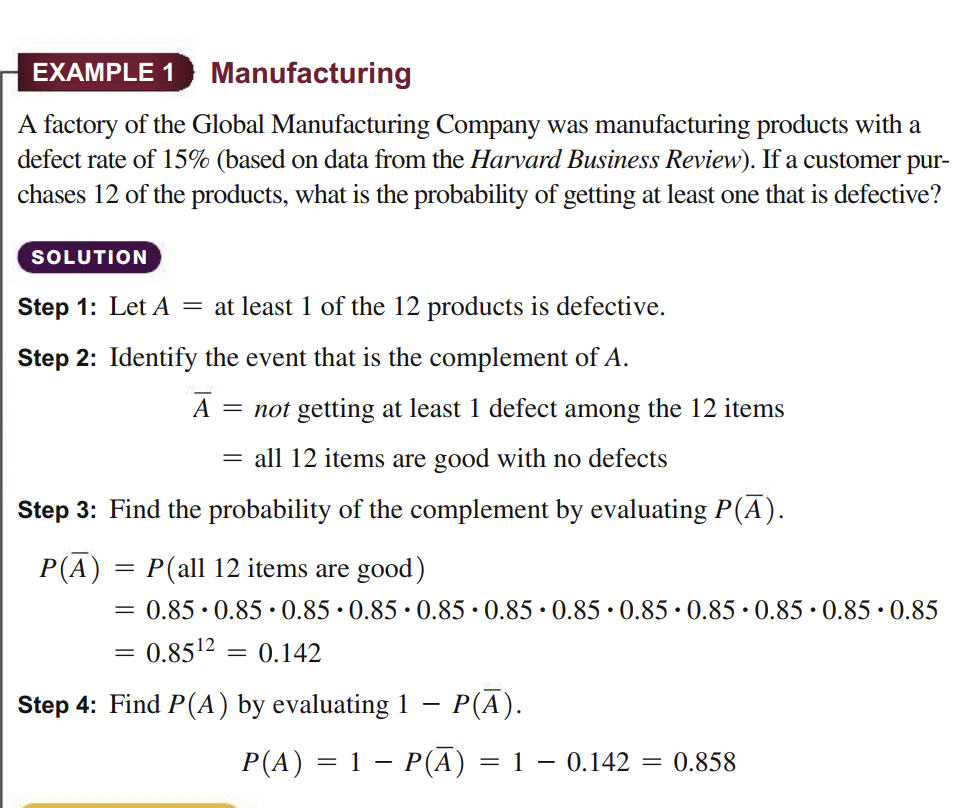
Transcribed Image Text:EXAMPLE 1
Manufacturing
A factory of the Global Manufacturing Company was manufacturing products with a
defect rate of 15% (based on data from the Harvard Business Review). If a customer pur-
chases 12 of the products, what is the probability of getting at least one that is defective?
SOLUTION
Step 1: Let A
= at least 1 of the 12 products is defective.
Step 2: Identify the event that is the complement of A.
A
= not getting at least 1 defect among the 12 items
= all 12 items are good with no defects
Step 3: Find the probability of the complement by evaluating P(A).
P(A) = P(all 12 items are good)
= 0.85 · 0.85•0.85 · 0.85 · 0.85 · 0.85 · 0.85 · 0.85 · 0.85•0.85 · 0.85 •0.85
= 0.8512
0.142
%3D
Step 4: Find P(A) by evaluating 1 – P(A).
P(A) = 1 – P(A) = 1 – 0.142
= 0.858
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL


Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
