EXPERIMENT 2: CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM Molarity of sodium hydroxide solution =_ _1.4679 Average titre Ke (mL) Vial NaOH titre number (mL) Initial Final Net 1 0.16 10.86 NOT 10.86 21.46 APPLICABLE 3 0.05 25.95 0.07 26.17 5 0.03 16.63 6. 16.63 32.26 7 0.09 25.19 0.07 24.95 Remarks for calculations 1. The average volume of NaOH solution from vials 1 and 2 represents the amount of HCl added. This volume has to be subtracted from the average volume of NaOH solution for vials 4,5,6,7, and 8 to get the volume of NaOH that corresponds to the acetic acid alone. 2. The concentration of water is included in the equilibrium calculations 3. The amount of water in each vial is equal to what we added plus the water that came with the HCI. CALCULATIONS
EXPERIMENT 2: CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM Molarity of sodium hydroxide solution =_ _1.4679 Average titre Ke (mL) Vial NaOH titre number (mL) Initial Final Net 1 0.16 10.86 NOT 10.86 21.46 APPLICABLE 3 0.05 25.95 0.07 26.17 5 0.03 16.63 6. 16.63 32.26 7 0.09 25.19 0.07 24.95 Remarks for calculations 1. The average volume of NaOH solution from vials 1 and 2 represents the amount of HCl added. This volume has to be subtracted from the average volume of NaOH solution for vials 4,5,6,7, and 8 to get the volume of NaOH that corresponds to the acetic acid alone. 2. The concentration of water is included in the equilibrium calculations 3. The amount of water in each vial is equal to what we added plus the water that came with the HCI. CALCULATIONS
Principles of Instrumental Analysis
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
ChapterA1: Evaluation Of Analytical Data
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem A1.22QAP
Related questions
Question
Ex2:
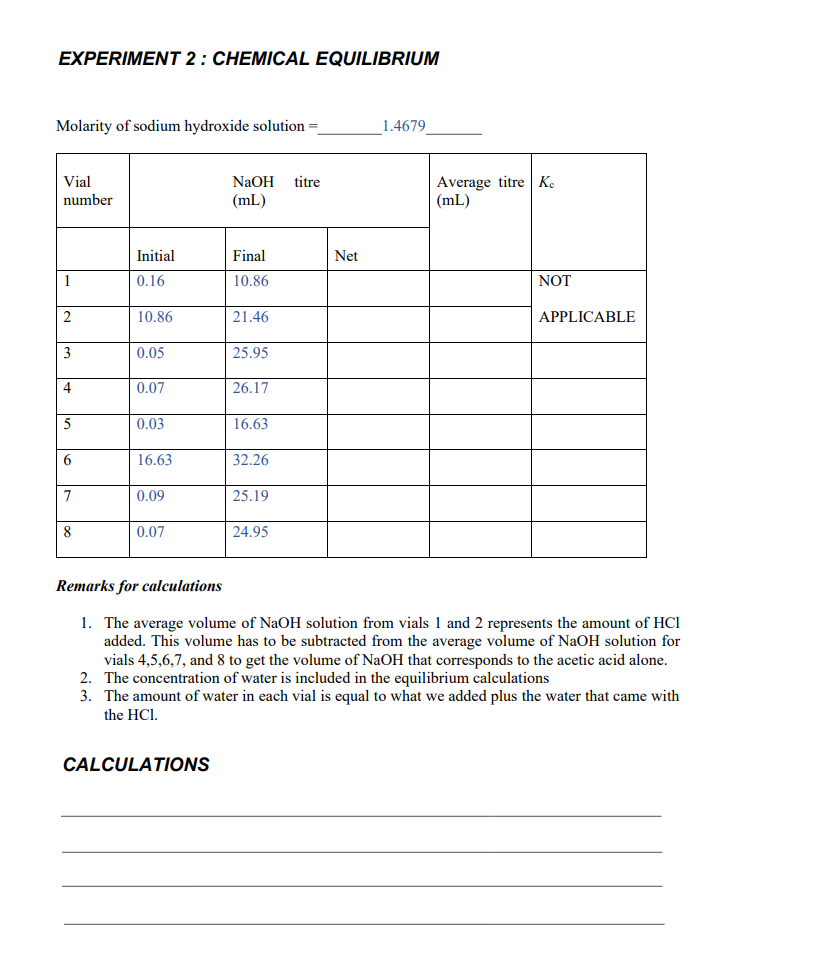
Transcribed Image Text:EXPERIMENT 2: CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM
Molarity of sodium hydroxide solution =_
_1.4679
Average titre Ke
(mL)
Vial
NaOH titre
number
(mL)
Initial
Final
Net
1
0.16
10.86
NOT
10.86
21.46
APPLICABLE
3
0.05
25.95
0.07
26.17
5
0.03
16.63
6.
16.63
32.26
7
0.09
25.19
0.07
24.95
Remarks for calculations
1. The average volume of NaOH solution from vials 1 and 2 represents the amount of HCl
added. This volume has to be subtracted from the average volume of NaOH solution for
vials 4,5,6,7, and 8 to get the volume of NaOH that corresponds to the acetic acid alone.
2. The concentration of water is included in the equilibrium calculations
3. The amount of water in each vial is equal to what we added plus the water that came with
the HCI.
CALCULATIONS
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning