Fish Cannery Hiking Lodge Total Action (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars) No Recycling 3,000 2,000 Recycling 2,200 3,200 Total economic profit is highest when the recycling production method is When the fish cannery uses the recycling method, the hiking lodge earns $3,200 – $2,000 = $1,200 more per week than it does with no recycling. Therefore, the hiking lodge should be willing to pay up to $1,200 per week for the fish cannery to recycle water. However, the recycling method decreases the fish cannery's economic profit by $3,000 – $2,200 = $800 per week. Therefore, the fish cannery should be willing to use the recycling method if it is compensated with at least $800 per week. Suppose the hiking lodge has the property rights to the lake. That is, the hiking lodge has the right to a clean (unpolluted) lake. In this case, assuming the two firms can bargain at no cost, the fish cannery will v the recycling method and will pay the hiking lodge A per week. Now, suppose the fish cannery has the property rights to the lake, including the right to pollute it. In this case, assuming the two firms can bargain at no cost, the fish cannery will ▼ the recycling method, and the hiking lodge will pay the fish cannery per week. The fish cannery will make the most economic profit when True or False: The lake will remain polluted, regardless of who has the property rights. True False
Fish Cannery Hiking Lodge Total Action (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars) No Recycling 3,000 2,000 Recycling 2,200 3,200 Total economic profit is highest when the recycling production method is When the fish cannery uses the recycling method, the hiking lodge earns $3,200 – $2,000 = $1,200 more per week than it does with no recycling. Therefore, the hiking lodge should be willing to pay up to $1,200 per week for the fish cannery to recycle water. However, the recycling method decreases the fish cannery's economic profit by $3,000 – $2,200 = $800 per week. Therefore, the fish cannery should be willing to use the recycling method if it is compensated with at least $800 per week. Suppose the hiking lodge has the property rights to the lake. That is, the hiking lodge has the right to a clean (unpolluted) lake. In this case, assuming the two firms can bargain at no cost, the fish cannery will v the recycling method and will pay the hiking lodge A per week. Now, suppose the fish cannery has the property rights to the lake, including the right to pollute it. In this case, assuming the two firms can bargain at no cost, the fish cannery will ▼ the recycling method, and the hiking lodge will pay the fish cannery per week. The fish cannery will make the most economic profit when True or False: The lake will remain polluted, regardless of who has the property rights. True False
Principles of Economics 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Chapter12: Environmental Protection And Negative Externalities
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10SCQ: Suppose a city releases 16 million gallons of raw sewage into a nearby lake. Table 12.8 shows the...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:The village has a hiking lodge whose visitors use the lake for
recreation. The village also has a fish cannery that dumps
industrial waste into the lake. This pollutes the lake and
makes it a less desirable vacation destination. That is, the
fish cannery's waste decreases the hiking lodge's economic
profit.
Suppose that the fish cannery could use a different production method that involves recycling water. This would reduce the pollution in the lake to
levels safe for recreation, and the hiking lodge would no longer be affected. If the fish cannery uses the recycling method, then the fish cannery's
economic profit is $2,200 per week, and the hiking lodge's economic profit is $3,200 per week. If the fish cannery does not use the recycling method,
then the fish cannery's economic profit is $3,000 per week, and the hiking lodge's economic profit is $2,000 per week. These figures are summarized
in the following table.
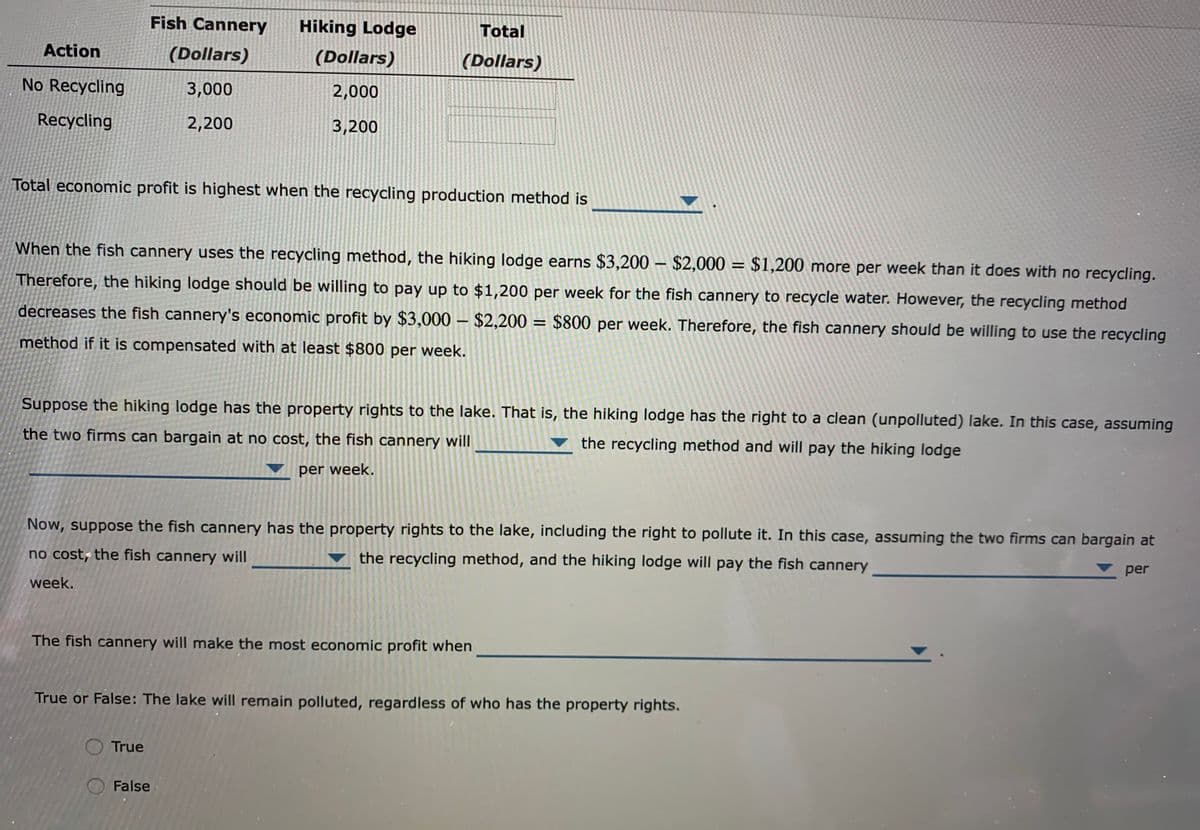
Complete the following table by computing the total profit (the fish cannery's economic profit and the hiking lodge's economic profit combined) with
and without recycling.
Profit
Fish Cannery
Hiking Lodge
Total
Action
(Dollars)
(Dollars)
(Dollars)
No Recycling
3,000
2,000
Recycling
2,200
3,200
Total economic profit is highest when the recycling production method is
Transcribed Image Text:Fish Cannery
Hiking Lodge
Total
Action
(Dollars)
(Dollars)
(Dollars)
No Recycling
3,000
2,000
Recycling
2,200
3,200
Total economic profit is highest when the recycling production method is
When the fish cannery uses the recycling method, the hiking lodge earns $3,200 – $2,000 = $1,200 more per week than it does with no recycling.
%3D
Therefore, the hiking lodge should be willing to pay up to $1,200 per week for the fish cannery to recycle water. However, the recycling method
decreases the fish cannery's economic profit by $3,000 – $2,200 = $800 per week. Therefore, the fish cannery should be willing to use the recycling
%3D
method if it is compensated with at least $800 per week.
Suppose the hiking lodge has the property rights to the lake. That is, the hiking lodge has the right to a clean (unpolluted) lake. In this case, assuming
the two firms can bargain at no cost, the fish cannery will
the recycling method and will pay the hiking lodge
per week.
Now, suppose the fish cannery has the property rights to the lake, including the right to pollute it. In this case, assuming the two firms can bargain at
no cost, the fish cannery will
the recycling method, and the hiking lodge will pay the fish cannery
per
week.
The fish cannery will make the most economic profit when
True or False: The lake will remain polluted, regardless of who has the property rights.
True
False
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:
9781947172364
Author:
Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:
OpenStax

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:
9781305156050
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305971493
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781337091992
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:
9781305585126
Author:
N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
