How can a linear approximation be used to approximate the value of a functionf near a point at which f and f' are easily evaluated? Choose the correct answer below. O A. Iffis differentiable at the point, then near that point, f is approximately linear; so, the function nearly coincides with the tangent line at that point. O B. Iffis differentiable at the point, then near that point, f is nonlinear; so, the function is equal to the tangent line at that point. OC. Iffis differentiable at the point, then near that point, f is approximately linear; so, the function is equal to the tangent line at that point. O D. Iff is differentiable at the point, then near that point, f is approximately linear; so every function value is less than the value of the tangent line at that point.
How can a linear approximation be used to approximate the value of a functionf near a point at which f and f' are easily evaluated? Choose the correct answer below. O A. Iffis differentiable at the point, then near that point, f is approximately linear; so, the function nearly coincides with the tangent line at that point. O B. Iffis differentiable at the point, then near that point, f is nonlinear; so, the function is equal to the tangent line at that point. OC. Iffis differentiable at the point, then near that point, f is approximately linear; so, the function is equal to the tangent line at that point. O D. Iff is differentiable at the point, then near that point, f is approximately linear; so every function value is less than the value of the tangent line at that point.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter7: Analytic Trigonometry
Section7.6: The Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Problem 93E
Related questions
Concept explainers
Rate of Change
The relation between two quantities which displays how much greater one quantity is than another is called ratio.
Slope
The change in the vertical distances is known as the rise and the change in the horizontal distances is known as the run. So, the rise divided by run is nothing but a slope value. It is calculated with simple algebraic equations as:
Question
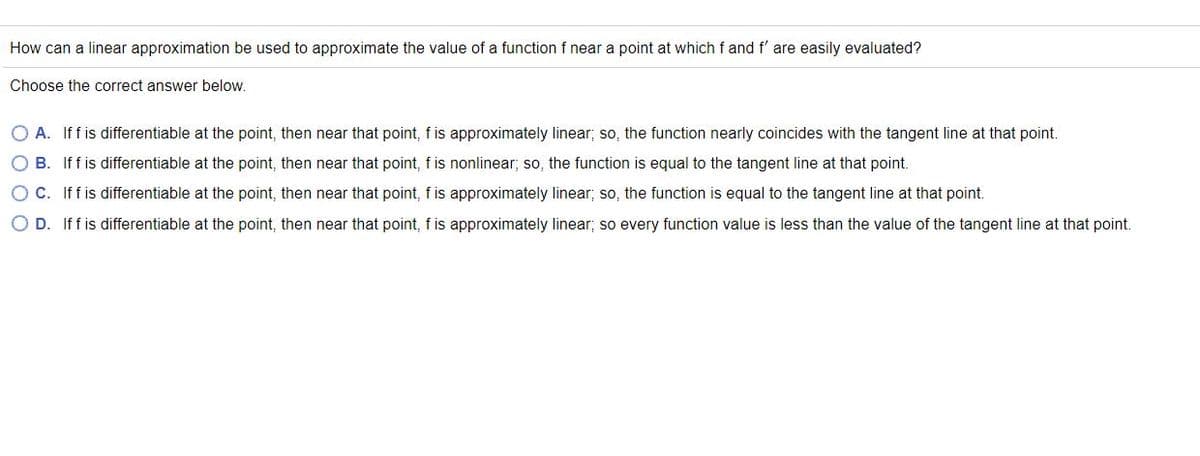
Transcribed Image Text:How can a linear approximation be used to approximate the value of a function f near a point at which f and f' are easily evaluated?
Choose the correct answer below.
O A. If f is differentiable at the point, then near that point, fis approximately linear; so, the function nearly coincides with the tangent line at that point.
O B. If f is differentiable at the point, then near that point, fis nonlinear; so, the function is equal to the tangent line at that point.
O C. Iffis differentiable at the point, then near that point, f is approximately linear; so, the function is equal to the tangent line at that point.
O D. Iff is differentiable at the point, then near that point, f is approximately linear; so every function value is less than the value of the tangent line at that point.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning