I need help with my homework this question is very confusing How long would it take for a solution made by diluting 2.5 ml of #1 with 7.5 ml of H2O to react with 10 ml of #2?
I need help with my homework this question is very confusing How long would it take for a solution made by diluting 2.5 ml of #1 with 7.5 ml of H2O to react with 10 ml of #2?
Basic Clinical Laboratory Techniques 6E
6th Edition
ISBN:9781133893943
Author:ESTRIDGE
Publisher:ESTRIDGE
Chapter6: Basic Clinical Chemistry
Section6.3: Principles Of Chemistry Instrumentation
Problem 1CT
Related questions
Question
I need help with my homework this question is very confusing
How long would it take for a solution made by diluting 2.5 ml of #1 with 7.5 ml of H2O to
react with 10 ml of #2?

Transcribed Image Text:PROCEDURE A: EFFECT OF CONCENTRATION
1.
Fill each buret on the stand with solution that it is marked for.
2.
Deliver exactly 10 ml of solution #1 into a clean dry test tube from buret.
3.
Deliver exactly 10 ml of solution #2 into a separate clean dry test tube.
Get the stopwatch ready, then mix solutions 1 and 2 by pouring back and forth between
the test tubes three times. You should begin timing the reaction as soon as you begin
mixing. Stop timing as soon as the color change occurs. You may need to practice this a
few times before proceeding.
3.
4.
Repeat the above procedure using successive dilutions of solution #1 as per data chart on
the report sheet.
5.
Calculate the reaction rate by using 100/ (time in seconds).
On the graph paper plot a graph of your reaction rates vs. concentration by using
vertical scale or Y-axis representing reaction rate and a horizontal scale or X-axis
representing mls of solution #1(KIO3).
7.
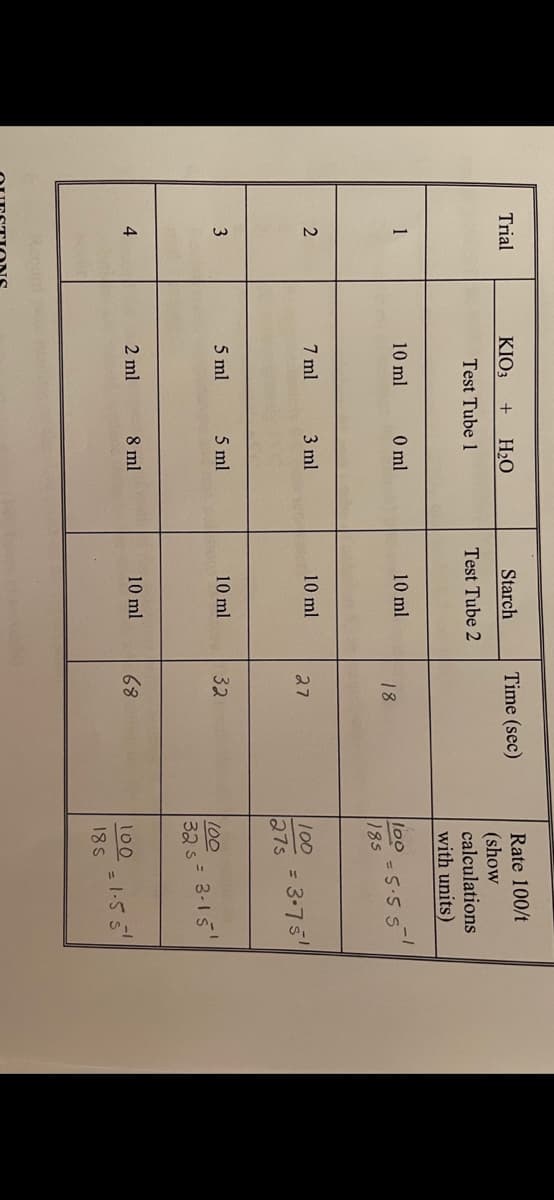
Transcribed Image Text:Rate 100/t
(show
calculations
with units)
Trial
KIO3
H2O
Starch
Time (sec)
Test Tube 1
Test Tube 2
1
10 ml
0 ml
10 ml
l00
= 5.5 S
185
18
2
7 ml
3 ml
10 ml
27
100
= 3-75
27s
3
5 ml
5 ml
10 ml
32
100
32 s= 3-15
4
2 ml
8 ml
10 ml
68
100.155
18S
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

