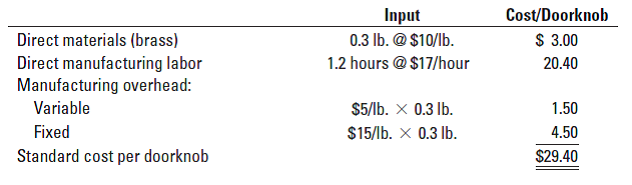
Input 0.3 lb. @ $10/lb. Cost/Doorknob $ 3.00 Direct materials (brass) Direct manufacturing labor Manufacturing overhead: Variable 1.2 hours @ $17/hour 20.40 $5/lb. x 0.3 lb. 1.50 Fixed 4.50 $15/lb. X 0.3 lb. Standard cost per doorknob $29.40 29,000 doorknobs Production 12,400 lb. at $11/lb. Direct materials purchased Direct materials used 8,500 lbs. Direct manufacturing labor Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead 29,200 hours for $671,600 $ 65,100 $158,000 1. For the month of April, compute the following variances, indicating whether each is favorable (F) or unfavorable (U): a. Direct materials price variance (based on purchases) b. Direct materials efficiency variance c. Direct manufacturing labor price variance d. Direct manufacturing labor efficiency variance e. Variable manufacturing overhead spending variance f. Variable manufacturing overhead efficiency variance g. Production-volume variance h. Fixed manufacturing overhead spending variance 2. Can Williams use any of the variances to help explain any of the other variances? Give examples. Required
Variance Analysis
In layman's terms, variance analysis is an analysis of a difference between planned and actual behavior. Variance analysis is mainly used by the companies to maintain a control over a business. After analyzing differences, companies find the reasons for the variance so that the necessary steps should be taken to correct that variance.
Standard Costing
The standard cost system is the expected cost per unit product manufactured and it helps in estimating the deviations and controlling them as well as fixing the selling price of the product. For example, it helps to plan the cost for the coming year on the various expenses.
Flexible-
At the beginning of 2017, DDC budgeted annual production of 420,000 doorknobs and adopted the following standards for each doorknob:

Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 9 steps with 8 images


