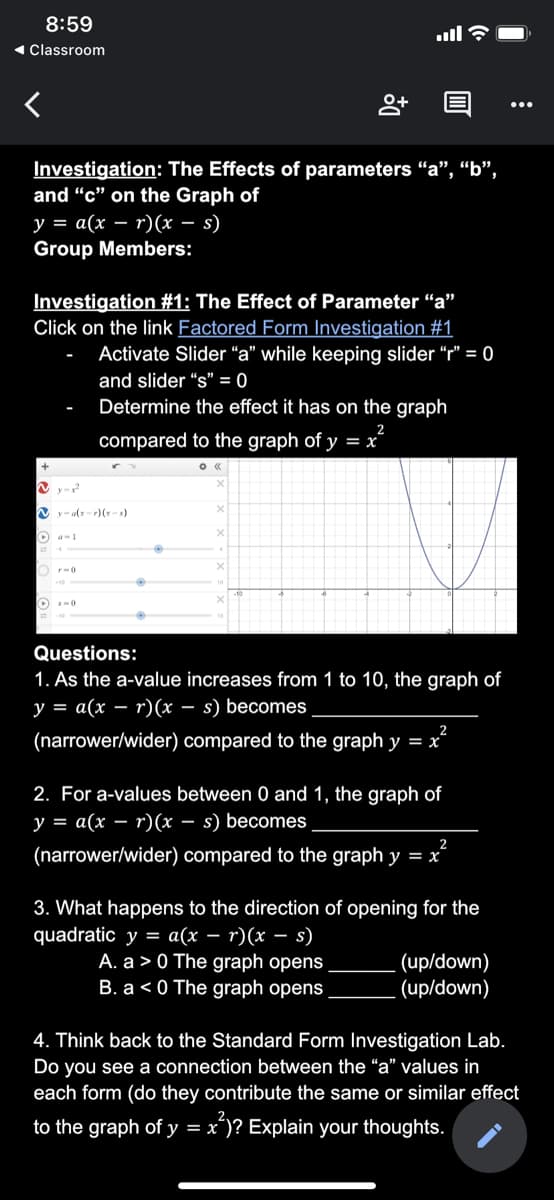
Investigation: The Effects of parameters “a", “b", and "c" on the Graph of y = a(x – r)(x – s) Group Members: Investigation #1: The Effect of Parameter "a" Click on the link Factored Form Investigation #1 Activate Slider "a" while keeping slider "r" = 0 and slider "s" = 0 Determine the effect it has on the graph 2 compared to the graph of y = x 10 Questions: 1. As the a-value increases from 1 to 10, the graph of y = a(x – r)(x – s) becomes %3D - (narrower/wider) compared to the graph y = x 2. For a-values between 0 and 1, the graph of y = a(x – r)(x – s) becomes - - (narrower/wider) compared to the graph y = x = x² 3. What happens to the direction of opening for the quadratic y = a(x – r)(x – s) A. a > 0 The graph opens B. a < 0 The graph opens (up/down) (up/down) e 2 O O O
Investigation: The Effects of parameters “a", “b", and "c" on the Graph of y = a(x – r)(x – s) Group Members: Investigation #1: The Effect of Parameter "a" Click on the link Factored Form Investigation #1 Activate Slider "a" while keeping slider "r" = 0 and slider "s" = 0 Determine the effect it has on the graph 2 compared to the graph of y = x 10 Questions: 1. As the a-value increases from 1 to 10, the graph of y = a(x – r)(x – s) becomes %3D - (narrower/wider) compared to the graph y = x 2. For a-values between 0 and 1, the graph of y = a(x – r)(x – s) becomes - - (narrower/wider) compared to the graph y = x = x² 3. What happens to the direction of opening for the quadratic y = a(x – r)(x – s) A. a > 0 The graph opens B. a < 0 The graph opens (up/down) (up/down) e 2 O O O
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter9: Systems Of Equations And Inequalities
Section9.9: Properties Of Determinants
Problem 46E
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:8:59
ull
1 Classroom
Investigation: The Effects of parameters "a", “b",
and " on the Graph of
y = a(x – r)(x – s)
Group Members:
Investigation #1: The Effect of Parameter “a"
Click on the link Factored Form Investigation #1
Activate Slider "a" while keeping slider "r" = 0
and slider "s" = 0
Determine the effect it has on the graph
compared to the graph of y = x
· =
N y- alx-r)(x-)
O a-1
Questions:
1. As the a-value increases from 1 to 10, the graph of
y = a(x – r)(x – s) becomes
(narrower/wider) compared to the graph y = x
2. For a-values between 0 and 1, the graph of
y = a(x – r)(x – s) becomes
(narrower/wider) compared to the graph y = x
3. What happens to the direction of opening for the
quadratic y = a(x – r)(x – s)
A. a > 0 The graph opens
B. a < 0 The graph opens
(up/down)
(up/down)
4. Think back to the Standard Form Investigation Lab.
Do you see a connection between the “a" values in
each form (do they contribute the same or similar effect
to the graph of y = x')? Explain your thoughts.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 9 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, algebra and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning