Kirtland Corporation uses a periodic inventory system. At the end of the annual accounting period, December 31, the accounting records for the most popular item in inventory showed the following: Unit Cost $4.00 Transactions Units 330 Beginning inventory, January 1 Transactions during the year: Purchase, January 30 230 390 2.70 5.00 a. b. Purchase, May 1 c. Sale ($6 each) Sale ($6 each) (90) (630) d.
Kirtland Corporation uses a periodic inventory system. At the end of the annual accounting period, December 31, the accounting records for the most popular item in inventory showed the following: Unit Cost $4.00 Transactions Units 330 Beginning inventory, January 1 Transactions during the year: Purchase, January 30 230 390 2.70 5.00 a. b. Purchase, May 1 c. Sale ($6 each) Sale ($6 each) (90) (630) d.
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
3rd Edition
ISBN:9781337788281
Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Chapter7: Inventories: Cost Measurement And Flow Assumptions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3RE: Reid Company uses the periodic inventory system. On January 1, it had an inventory balance of...
Related questions
Question
Help

Transcribed Image Text:Kirtland Corporation uses a periodic inventory system. At the end of the annual accounting period, December 31, the accounting
records for the most popular item in inventory showed the following:
Unit Cost
$4.00
Transactions
Units
330
Beginning inventory, January 1
Transactions during the year:
Purchase, January 30
b.
230
390
(90)
(630)
2.70
5.00
a.
c.
d.
Purchase, May 1
Sale ($6 each)
Sale ($6 each)
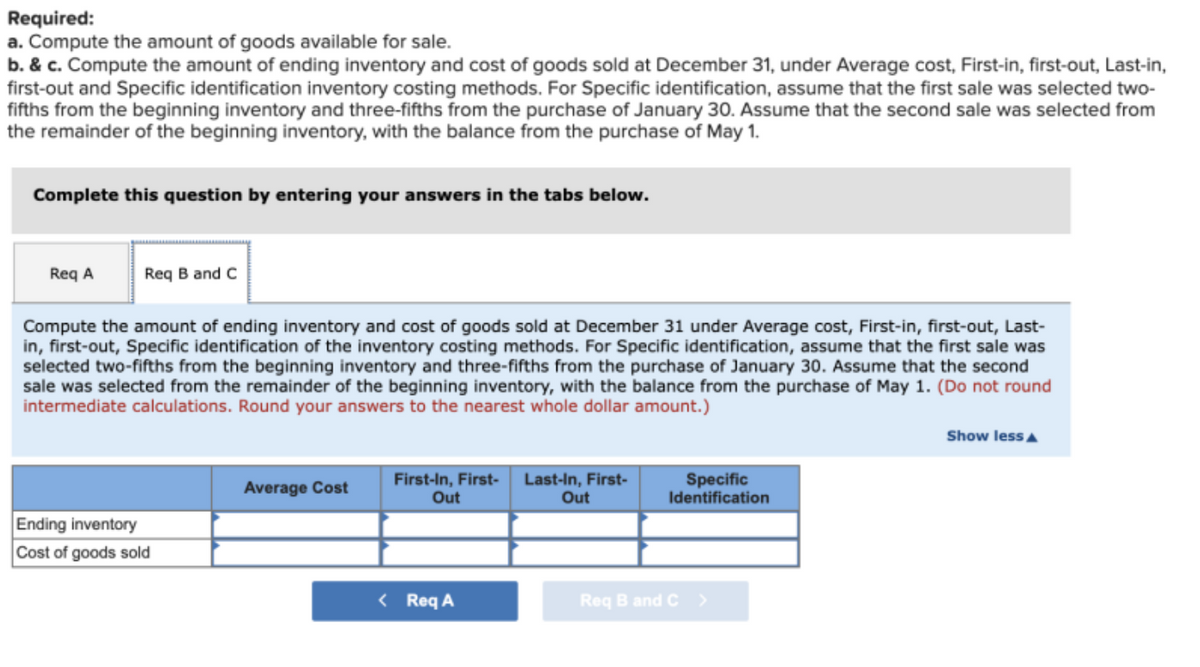
Transcribed Image Text:Required:
a. Compute the amount of goods available for sale.
b. & c. Compute the amount of ending inventory and cost of goods sold at December 31, under Average cost, First-in, first-out, Last-in,
first-out and Specific identification inventory costing methods. For Specific identification, assume that the first sale was selected two-
fifths from the beginning inventory and three-fifths from the purchase of January 30. Assume that the second sale was selected from
the remainder of the beginning inventory, with the balance from the purchase of May 1.
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Req A
Req B and C
Compute the amount of ending inventory and cost of goods sold at December 31 under Average cost, First-in, first-out, Last-
in, first-out, Specific identification of the inventory costing methods. For Specific identification, assume that the first sale was
selected two-fifths from the beginning inventory and three-fifths from the purchase of January 30. Assume that the second
sale was selected from the remainder of the beginning inventory, with the balance from the purchase of May 1. (Do not round
intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar amount.)
Show lessA
Average Cost
First-In, First-
Out
Last-In, First-
Out
Specific
Identification
Ending inventory
Cost of goods sold
< Req A
Req B and C >
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Accounting (Book Only): A Career Approach
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337280570
Author:
Scott, Cathy J.
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Accounting (Book Only): A Career Approach
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337280570
Author:
Scott, Cathy J.
Publisher:
South-Western College Pub

Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337690881
Author:
Jay Rich, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337272124
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337902663
Author:
WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337794756
Author:
HEINTZ, James A.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,