(LO 3) tes the following cost and net realizable value Determine Inventory Categories Cost Net Realizable valuation Data Value Data categories Cameras $12,000 (LO 4) $12,100 9,700 12,800 Camcorders Blu-ray players 9,500 14,000 Compute the lower-of-cost-or-net realizable value for the company's total inventory. BE6-9 At December 31, 2019, the following information was available for A. Kamble Company: ending inventory $40,000, beginning inventory $60,000, cost of goods sold and $270,000, and sales revenue $380,000. Calculate inventory turnover and days in inventory (LO for A. Kamble Company. Com *BE6-10 Gregory Department Store uses a perpetual inventory system. Data for product Ap E2-D2 include the following purchases. Number of Units Unit Price Date $10 13 50 May 7 July 28 30 On June 1, Gregory sold 26 units, and on August 27, 40 more units. Prepare the perpetual inventory schedule for the above transactions using (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, and (c) moving- *BE6-11 At May 31, Suarez Company has net sales of $330,000 and cost of goods available for sale of $230,000. Compute the estimated cost of the ending inventory, assuming th. gross profit rate is 35%. average cost. (Round average cost per unit to nearest cent.)
(LO 3) tes the following cost and net realizable value Determine Inventory Categories Cost Net Realizable valuation Data Value Data categories Cameras $12,000 (LO 4) $12,100 9,700 12,800 Camcorders Blu-ray players 9,500 14,000 Compute the lower-of-cost-or-net realizable value for the company's total inventory. BE6-9 At December 31, 2019, the following information was available for A. Kamble Company: ending inventory $40,000, beginning inventory $60,000, cost of goods sold and $270,000, and sales revenue $380,000. Calculate inventory turnover and days in inventory (LO for A. Kamble Company. Com *BE6-10 Gregory Department Store uses a perpetual inventory system. Data for product Ap E2-D2 include the following purchases. Number of Units Unit Price Date $10 13 50 May 7 July 28 30 On June 1, Gregory sold 26 units, and on August 27, 40 more units. Prepare the perpetual inventory schedule for the above transactions using (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, and (c) moving- *BE6-11 At May 31, Suarez Company has net sales of $330,000 and cost of goods available for sale of $230,000. Compute the estimated cost of the ending inventory, assuming th. gross profit rate is 35%. average cost. (Round average cost per unit to nearest cent.)
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
3rd Edition
ISBN:9781337788281
Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Chapter8: Inventories: Special Valuation Issues
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 2RE: Black Corporation uses the LIFO cost flow assumption. Each unit of its inventory has a net...
Related questions
Question
100%
It's question BE6-10
is a negative going to be the answer?
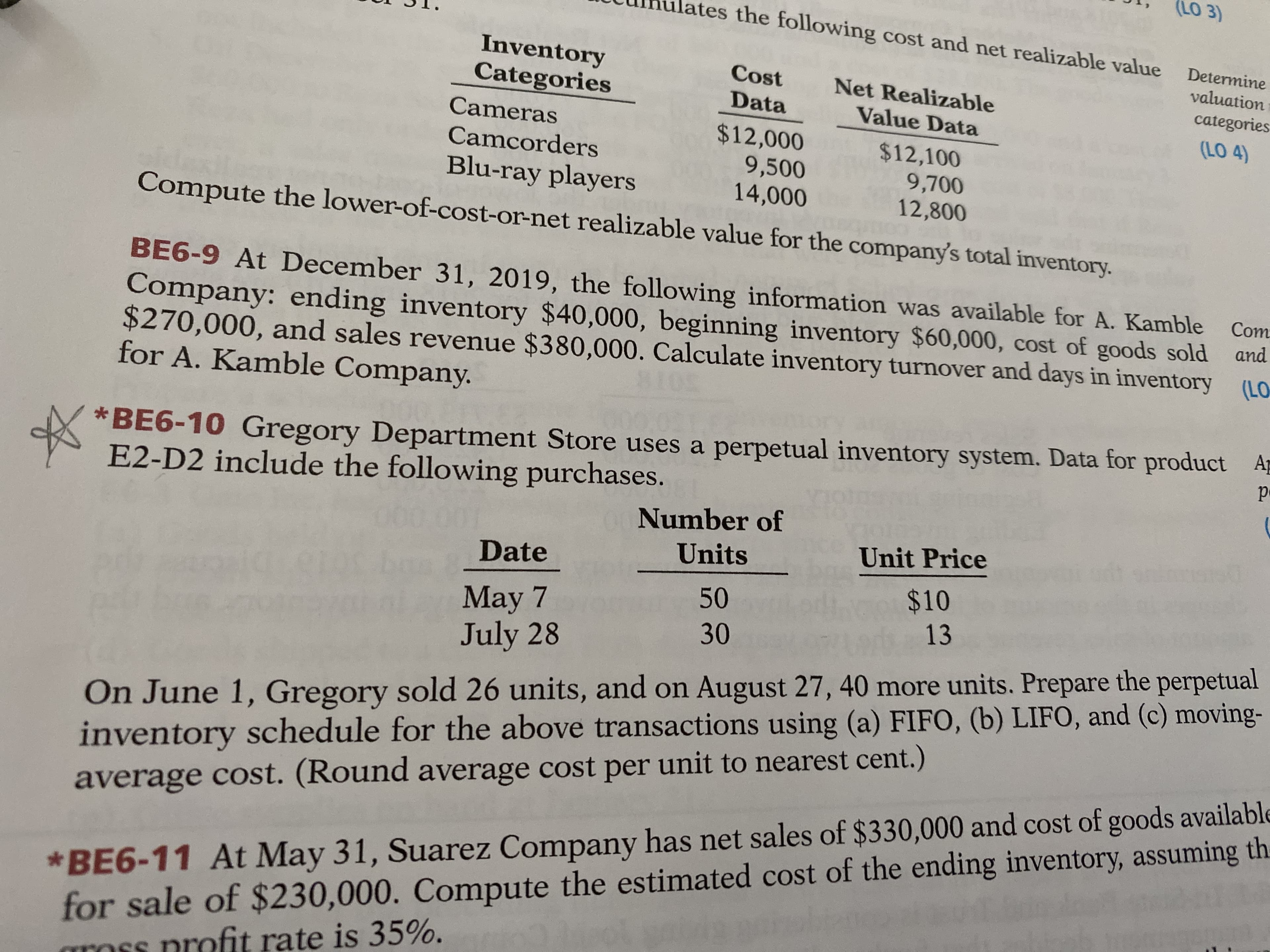
Transcribed Image Text:(LO 3)
tes the following cost and net realizable value
Determine
Inventory
Categories
Cost
Net Realizable
valuation
Data
Value Data
categories
Cameras
$12,000
(LO 4)
$12,100
9,700
12,800
Camcorders
Blu-ray players
9,500
14,000
Compute the lower-of-cost-or-net realizable value for the company's total inventory.
BE6-9 At December 31, 2019, the following information was available for A. Kamble
Company: ending inventory $40,000, beginning inventory $60,000, cost of goods sold and
$270,000, and sales revenue $380,000. Calculate inventory turnover and days in inventory (LO
for A. Kamble Company.
Com
*BE6-10 Gregory Department Store uses a perpetual inventory system. Data for product Ap
E2-D2 include the following purchases.
Number of
Units
Unit Price
Date
$10
13
50
May 7
July 28
30
On June 1, Gregory sold 26 units, and on August 27, 40 more units. Prepare the perpetual
inventory schedule for the above transactions using (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, and (c) moving-
*BE6-11 At May 31, Suarez Company has net sales of $330,000 and cost of goods available
for sale of $230,000. Compute the estimated cost of the ending inventory, assuming th.
gross profit rate is 35%.
average cost. (Round average cost per unit to nearest cent.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337794756
Author:
HEINTZ, James A.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Financial & Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781285866307
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337794756
Author:
HEINTZ, James A.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Financial & Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781285866307
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Corporate Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337398169
Author:
Carl Warren, Jeff Jones
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial & Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337119207
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Corporate Financial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305653535
Author:
Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan Duchac
Publisher:
Cengage Learning