O KINETICS AND EQUILIBRIUM Using an equilibrium constant to predict the direction of spontaneous reaction A chemical engineer is studying the following reaction: H,(9)+Cl,(9) → 2 HC1(g) At the temperature the engineer picks, the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction is 0.72. The engineer charges ("fills") three reaction vessels with hydrogen and chlorine, and lets the reaction begin. He then measures the compe mixture inside each vessel from time to time. His first set of measurements are shown in the table below. Predict the changes in the compositions the engineer should expect next time he measures the compositions. reaction compound pressure expected change in pressure vessel H, 5.79 atm I decrease (no change) increase C1, 4.17 atm ↑ increase I decrease (no change) нсі 4.17 atm f increase I decrease (no change) H, 4.63 atm f increase decrease (no change) Cl, 3.43 atm I decrease (no change) increase 2.40 atm O (no change) нсі ↑ increase Į decrease H, 4.66 atm decrease (no change) increase C1, 3.46 atm ↑ increase I decrease O (no change) HCI 2.34 atm f increase I decrease (no change)
O KINETICS AND EQUILIBRIUM Using an equilibrium constant to predict the direction of spontaneous reaction A chemical engineer is studying the following reaction: H,(9)+Cl,(9) → 2 HC1(g) At the temperature the engineer picks, the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction is 0.72. The engineer charges ("fills") three reaction vessels with hydrogen and chlorine, and lets the reaction begin. He then measures the compe mixture inside each vessel from time to time. His first set of measurements are shown in the table below. Predict the changes in the compositions the engineer should expect next time he measures the compositions. reaction compound pressure expected change in pressure vessel H, 5.79 atm I decrease (no change) increase C1, 4.17 atm ↑ increase I decrease (no change) нсі 4.17 atm f increase I decrease (no change) H, 4.63 atm f increase decrease (no change) Cl, 3.43 atm I decrease (no change) increase 2.40 atm O (no change) нсі ↑ increase Į decrease H, 4.66 atm decrease (no change) increase C1, 3.46 atm ↑ increase I decrease O (no change) HCI 2.34 atm f increase I decrease (no change)
Chemistry for Engineering Students
4th Edition
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Chapter12: Chemical Equilibrium
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 12.108PAE: 12.108 A nuclear engineer is considering the effect of discharging waste heat from a power plant...
Related questions
Question
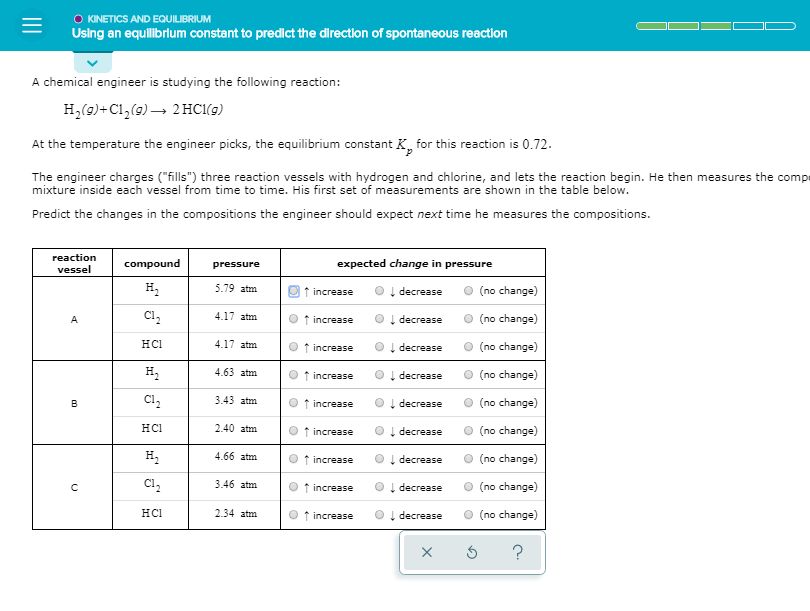
Transcribed Image Text:O KINETICS AND EQUILIBRIUM
Using an equilibrium constant to predict the direction of spontaneous reaction
A chemical engineer is studying the following reaction:
H,(9)+Cl,(9) → 2 HC1(g)
At the temperature the engineer picks, the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction is 0.72.
The engineer charges ("fills") three reaction vessels with hydrogen and chlorine, and lets the reaction begin. He then measures the compe
mixture inside each vessel from time to time. His first set of measurements are shown in the table below.
Predict the changes in the compositions the engineer should expect next time he measures the compositions.
reaction
compound
pressure
expected change in pressure
vessel
H,
5.79 atm
I decrease
(no change)
increase
C1,
4.17 atm
↑ increase
I decrease
(no change)
нсі
4.17 atm
f increase
I decrease
(no change)
H,
4.63 atm
f increase
decrease
(no change)
Cl,
3.43 atm
I decrease
(no change)
increase
2.40 atm
O (no change)
нсі
↑ increase
Į decrease
H,
4.66 atm
decrease
(no change)
increase
C1,
3.46 atm
↑ increase
I decrease
O (no change)
HCI
2.34 atm
f increase
I decrease
(no change)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781337398909
Author:
Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079243
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305580343
Author:
Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; Darrell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781133949640
Author:
John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning