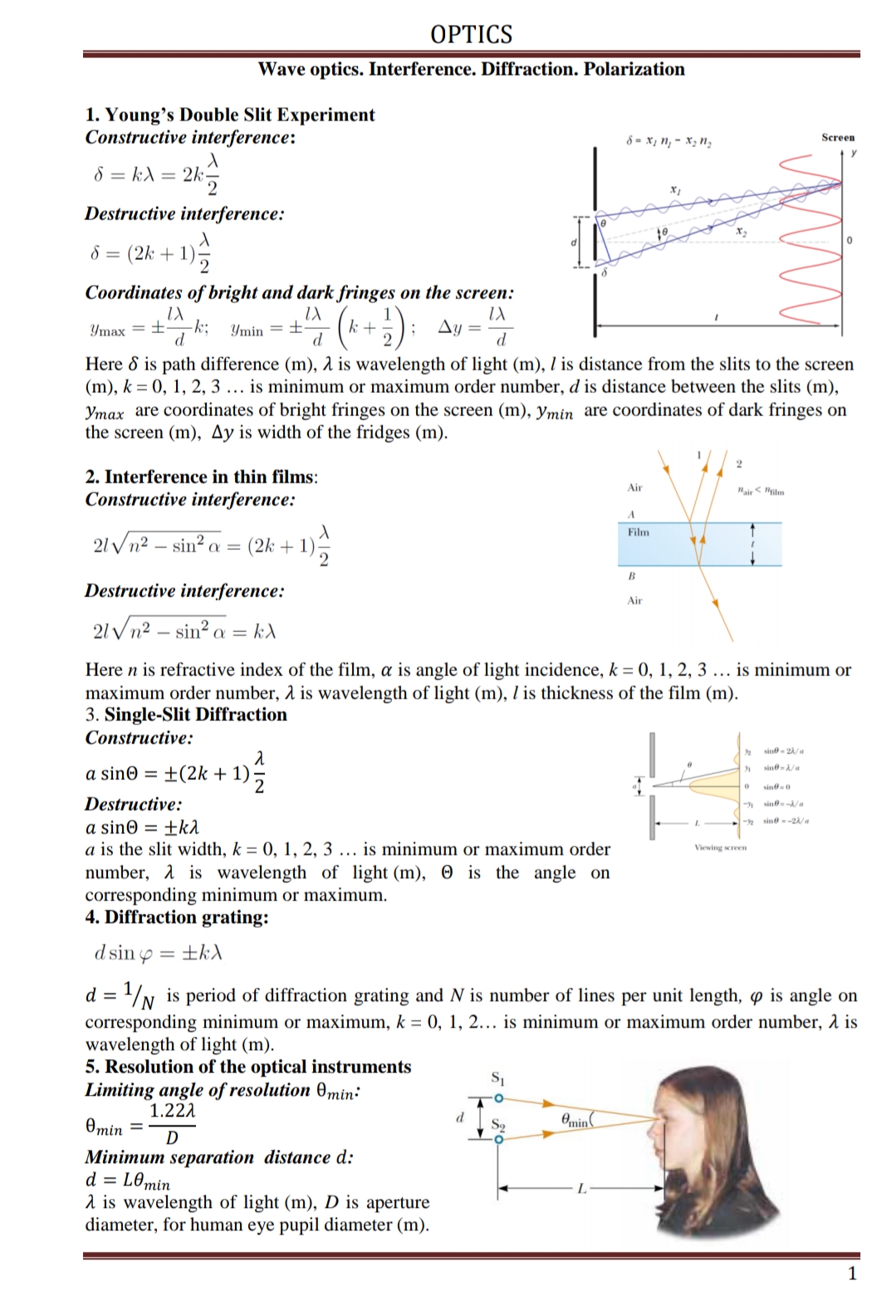
OPTICS Wave optics. Interference. Diffraction. Polarization 1. Young's Double Slit Experiment Constructive interference: Screen 8 = k) = 2k- х, Destructive interference: 8 = (2k + 1) Coordinates of bright and dark fringes on the screen: Ymax =± -k; Ymin =± Here 8 is path difference (m), 1 is wavelength of light (m), l is distance from the slits to the screen (m), k = 0, 1, 2, 3 ... is minimum or maximum order number, d is distance between the slits (m), Ymax are coordinates of bright fringes on the screen (m), ymin are coordinates of dark fringes on the screen (m), Ay is width of the fridges (m). 2. Interference in thin films: Air Constructive interference: Film 21 V n2 – sin? a (2k + 1) 2 Destructive interference: Air 21 Vn² – sin? a = k) Here n is refractive index of the film, a is angle of light incidence, k = 0, 1, 2, 3 ... is minimum or maximum order number, 1 is wavelength of light (m), l is thickness of the film (m). 3. Single-Slit Diffraction Constructive: sine - 2à/a sine -/a a sin© = ±(2k + 1), sine0 Destructive: sine-A/a - sine --2/a a sinº = ±ka a is the slit width, k = 0, 1, 2, 3 ... is minimum or maximum order Viewing screen number, A is wavelength of light (m), 0 is the angle on corresponding minimum or maximum. 4. Diffraction grating: d sin ±kX d = '/N is period of diffraction grating and N is number of lines per unit length, o is angle on corresponding minimum or maximum, k = 0, 1, 2... is minimum or maximum order number, 1 is wavelength of light (m). 5. Resolution of the optical instruments Limiting angle of resolution 0min: S1 1.22A Өmin Omin = D Minimum separation distance d: d = L0min a is wavelength of light (m), D is aperture diameter, for human eye pupil diameter (m). 10. Georges Seurat, a post-impressionist French painter, used a technique of painting with small dots of color placed close together on a canvas. From sufficiently far away, the dots cannot be distinguished and the painting looks normal in appearance. If the dots on the painting are separated by 1.5 mm and the painting is observed under light of 550 nm wavelength with eyes having a pupil diameter of 2 mm, find the minimum distance you must stand from the painting so that the individual dots cannot be resolved.
OPTICS Wave optics. Interference. Diffraction. Polarization 1. Young's Double Slit Experiment Constructive interference: Screen 8 = k) = 2k- х, Destructive interference: 8 = (2k + 1) Coordinates of bright and dark fringes on the screen: Ymax =± -k; Ymin =± Here 8 is path difference (m), 1 is wavelength of light (m), l is distance from the slits to the screen (m), k = 0, 1, 2, 3 ... is minimum or maximum order number, d is distance between the slits (m), Ymax are coordinates of bright fringes on the screen (m), ymin are coordinates of dark fringes on the screen (m), Ay is width of the fridges (m). 2. Interference in thin films: Air Constructive interference: Film 21 V n2 – sin? a (2k + 1) 2 Destructive interference: Air 21 Vn² – sin? a = k) Here n is refractive index of the film, a is angle of light incidence, k = 0, 1, 2, 3 ... is minimum or maximum order number, 1 is wavelength of light (m), l is thickness of the film (m). 3. Single-Slit Diffraction Constructive: sine - 2à/a sine -/a a sin© = ±(2k + 1), sine0 Destructive: sine-A/a - sine --2/a a sinº = ±ka a is the slit width, k = 0, 1, 2, 3 ... is minimum or maximum order Viewing screen number, A is wavelength of light (m), 0 is the angle on corresponding minimum or maximum. 4. Diffraction grating: d sin ±kX d = '/N is period of diffraction grating and N is number of lines per unit length, o is angle on corresponding minimum or maximum, k = 0, 1, 2... is minimum or maximum order number, 1 is wavelength of light (m). 5. Resolution of the optical instruments Limiting angle of resolution 0min: S1 1.22A Өmin Omin = D Minimum separation distance d: d = L0min a is wavelength of light (m), D is aperture diameter, for human eye pupil diameter (m). 10. Georges Seurat, a post-impressionist French painter, used a technique of painting with small dots of color placed close together on a canvas. From sufficiently far away, the dots cannot be distinguished and the painting looks normal in appearance. If the dots on the painting are separated by 1.5 mm and the painting is observed under light of 550 nm wavelength with eyes having a pupil diameter of 2 mm, find the minimum distance you must stand from the painting so that the individual dots cannot be resolved.
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter37: Wave Optics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 37.9OQ: A plane monochromatic light wave is incident on a double slit as illustrated in Figure 37.1. (i) As...
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:OPTICS
Wave optics. Interference. Diffraction. Polarization
1. Young's Double Slit Experiment
Constructive interference:
Screen
8 = k) = 2k-
х,
Destructive interference:
8 = (2k + 1)
Coordinates of bright and dark fringes on the screen:
Ymax =±
-k;
Ymin =±
Here 8 is path difference (m), 1 is wavelength of light (m), l is distance from the slits to the screen
(m), k = 0, 1, 2, 3 ... is minimum or maximum order number, d is distance between the slits (m),
Ymax are coordinates of bright fringes on the screen (m), ymin are coordinates of dark fringes on
the screen (m), Ay is width of the fridges (m).
2. Interference in thin films:
Air
Constructive interference:
Film
21 V n2 – sin? a
(2k + 1)
2
Destructive interference:
Air
21 Vn² – sin? a = k)
Here n is refractive index of the film, a is angle of light incidence, k = 0, 1, 2, 3 ... is minimum or
maximum order number, 1 is wavelength of light (m), l is thickness of the film (m).
3. Single-Slit Diffraction
Constructive:
sine - 2à/a
sine -/a
a sin© = ±(2k + 1),
sine0
Destructive:
sine-A/a
- sine --2/a
a sinº = ±ka
a is the slit width, k = 0, 1, 2, 3 ... is minimum or maximum order
Viewing screen
number, A is wavelength of light (m), 0 is the angle on
corresponding minimum or maximum.
4. Diffraction grating:
d sin
±kX
d = '/N is period of diffraction grating and N is number of lines per unit length, o is angle on
corresponding minimum or maximum, k = 0, 1, 2... is minimum or maximum order number, 1 is
wavelength of light (m).
5. Resolution of the optical instruments
Limiting angle of resolution 0min:
S1
1.22A
Өmin
Omin =
D
Minimum separation distance d:
d = L0min
a is wavelength of light (m), D is aperture
diameter, for human eye pupil diameter (m).

Transcribed Image Text:10. Georges Seurat, a post-impressionist French painter, used a technique of painting with small
dots of color placed close together on a canvas. From sufficiently far away, the dots cannot be
distinguished and the painting looks normal in appearance. If the dots on the painting are separated
by 1.5 mm and the painting is observed under light of 550 nm wavelength with eyes having a pupil
diameter of 2 mm, find the minimum distance you must stand from the painting so that the individual
dots cannot be resolved.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781285737027
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781305952300
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168000
Author:
Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:
OpenStax College