or to pass the pot to the other player. In other words, player 1 chooses between D (Down) and A (Across), where D is pocketing the pot and A is passing the pot to the player 2. Similarly, player 2 chooses between A and D. The payoffs are arranged so that if one passes the pot to one's opponent and the opponent takes the pot on the next round, one receives slightly less than if one had taken the pot on this round. D 1 A 2 D (1,0) (0,2) A 1 A 2 D D (3,1) A 1 A D (2,4) (4,3) (3,5) 1. Find the subgame perfect Nash Equilibrium using backward induction.
or to pass the pot to the other player. In other words, player 1 chooses between D (Down) and A (Across), where D is pocketing the pot and A is passing the pot to the player 2. Similarly, player 2 chooses between A and D. The payoffs are arranged so that if one passes the pot to one's opponent and the opponent takes the pot on the next round, one receives slightly less than if one had taken the pot on this round. D 1 A 2 D (1,0) (0,2) A 1 A 2 D D (3,1) A 1 A D (2,4) (4,3) (3,5) 1. Find the subgame perfect Nash Equilibrium using backward induction.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter10: Sequences, Series, And Probability
Section10.8: Probability
Problem 30E
Related questions
Question
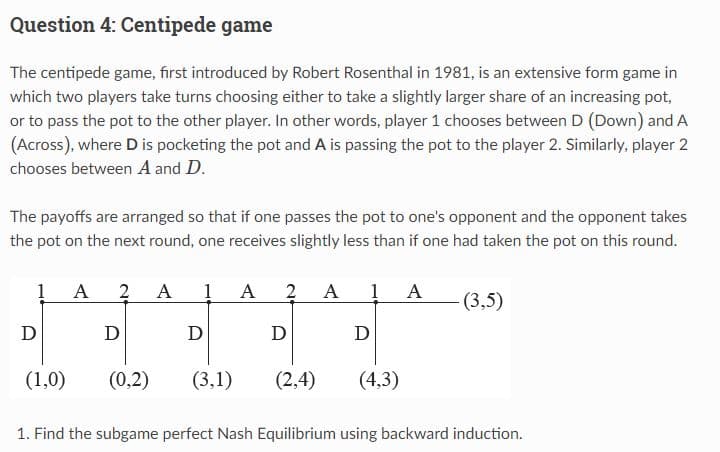
Transcribed Image Text:Question 4: Centipede game
The centipede game, first introduced by Robert Rosenthal in 1981, is an extensive form game in
which two players take turns choosing either to take a slightly larger share of an increasing pot,
or to pass the pot to the other player. In other words, player 1 chooses between D (Down) and A
(Across), where D is pocketing the pot and A is passing the pot to the player 2. Similarly, player 2
chooses between A and D.
The payoffs are arranged so that if one passes the pot to one's opponent and the opponent takes
the pot on the next round, one receives slightly less than if one had taken the pot on this round.
D
1
(1,0)
A 2 A 1 A 2 A 1 A
D
D
(0,2)
(3,1)
D
D
(2,4) (4,3)
- (3,5)
1. Find the subgame perfect Nash Equilibrium using backward induction.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage