Origin of new gene via gene duplication Function A Gene Z ab Gene Z Function B Gene duplication Function A Genes Z, and Z, are initially identical to gene Z. Gene Z, Z, ab Function B Z, Function A ab Gene Z, Function B 2 Subfunctionalization 3 Neofunctionalization Pseudogene Function ab z, z, X z, Gene Z, Gene Z, → Function A ak Z, ab Function A Z, Z, Gene Z, → Function c ab Gene Z, → Function B Inactivating Gene Z, retains the original function of gene Z, while gene Z, acquires a new function. The composite functions of genes Z, and Z, are equivalent to those of gene z. mutations ab z, z, X ab Function A Gene Z, Function B 2015 Pearson Eduoalion, Ino. Majority of new genes Gene duplication Derivation of exons from transposable elements (TE) TE Duplication I Divergence New splice sites evolve within TE Gene duplication by unequal crossover Other TE sequences degenerate Lateral gene transfer Organism A | Transfer Exon shuffling Organism B | Diverge Organism B Gene fission/ fusion Fusion t Fission Reverse transcription | Transcription De novo derivation from noncoding sequence Reverse transcription and insertion © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. 2019 Pearson Education, Inc.
Origin of new gene via gene duplication Function A Gene Z ab Gene Z Function B Gene duplication Function A Genes Z, and Z, are initially identical to gene Z. Gene Z, Z, ab Function B Z, Function A ab Gene Z, Function B 2 Subfunctionalization 3 Neofunctionalization Pseudogene Function ab z, z, X z, Gene Z, Gene Z, → Function A ak Z, ab Function A Z, Z, Gene Z, → Function c ab Gene Z, → Function B Inactivating Gene Z, retains the original function of gene Z, while gene Z, acquires a new function. The composite functions of genes Z, and Z, are equivalent to those of gene z. mutations ab z, z, X ab Function A Gene Z, Function B 2015 Pearson Eduoalion, Ino. Majority of new genes Gene duplication Derivation of exons from transposable elements (TE) TE Duplication I Divergence New splice sites evolve within TE Gene duplication by unequal crossover Other TE sequences degenerate Lateral gene transfer Organism A | Transfer Exon shuffling Organism B | Diverge Organism B Gene fission/ fusion Fusion t Fission Reverse transcription | Transcription De novo derivation from noncoding sequence Reverse transcription and insertion © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc. 2019 Pearson Education, Inc.
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
14th Edition
ISBN:9781305073951
Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Chapter26: Human Evolution
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1DAA: Neanderthal Hair Color The MC1R gene regulates pigmentation in humans (Sections 14.1 and 15.1...
Related questions
Question
How do these 2 diagrams fit within the scope of evolutionary genomics?
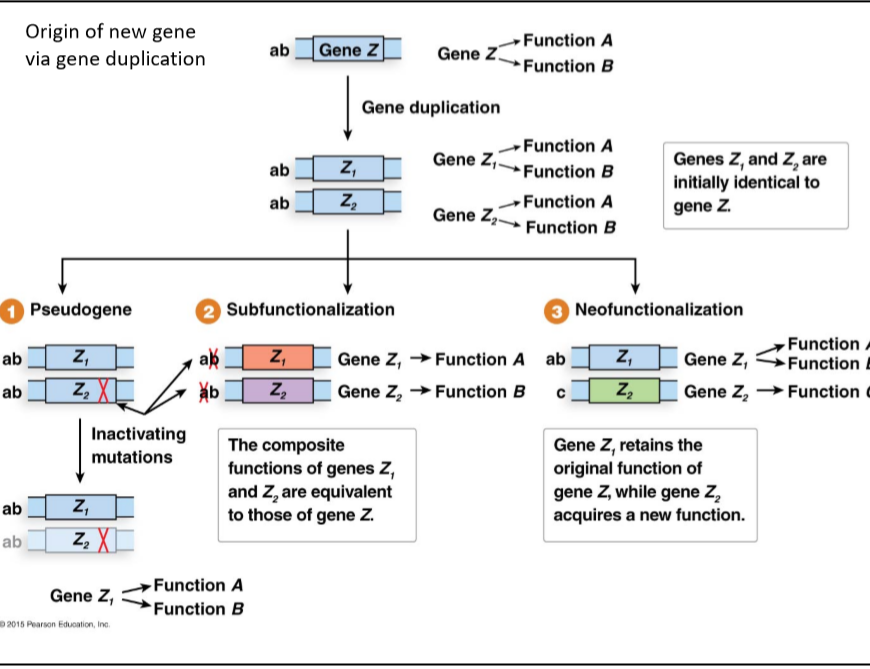
Transcribed Image Text:Origin of new gene
via gene duplication
Function A
Gene Z
ab
Gene Z
Function B
Gene duplication
Function A
Genes Z, and Z, are
initially identical to
gene Z.
Gene Z,
Z,
ab
Function B
Z,
Function A
ab
Gene Z,
Function B
2 Subfunctionalization
3 Neofunctionalization
Pseudogene
Function
ab z,
z, X
z,
Gene Z,
Gene Z, → Function A
ak
Z,
ab
Function A
Z,
Z,
Gene Z, → Function c
ab
Gene Z, → Function B
Inactivating
Gene Z, retains the
original function of
gene Z, while gene Z,
acquires a new function.
The composite
functions of genes Z,
and Z, are equivalent
to those of gene z.
mutations
ab z,
z, X
ab
Function A
Gene Z,
Function B
2015 Pearson Eduoalion, Ino.
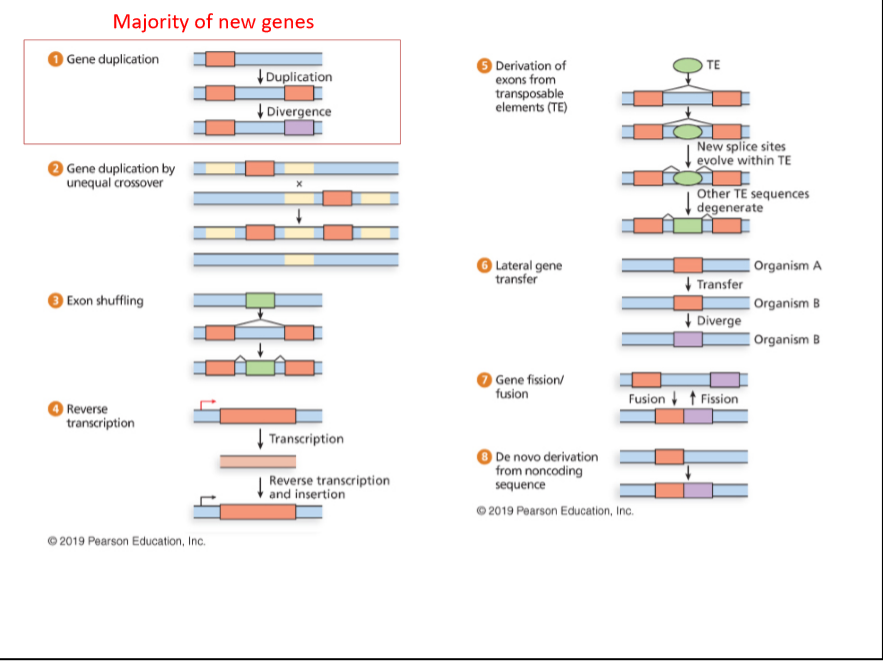
Transcribed Image Text:Majority of new genes
Gene duplication
Derivation of
exons from
transposable
elements (TE)
TE
Duplication
I Divergence
New splice sites
evolve within TE
Gene duplication by
unequal crossover
Other TE sequences
degenerate
Lateral gene
transfer
Organism A
| Transfer
Exon shuffling
Organism B
| Diverge
Organism B
Gene fission/
fusion
Fusion t Fission
Reverse
transcription
| Transcription
De novo derivation
from noncoding
sequence
Reverse transcription
and insertion
© 2019 Pearson Education, Inc.
2019 Pearson Education, Inc.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305073951
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305073951
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305251052
Author:
Michael Cummings
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781337408332
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:
9781305577206
Author:
Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Concepts of Biology
Biology
ISBN:
9781938168116
Author:
Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James Wise
Publisher:
OpenStax College