oson? Data for Question 2: mixture density mole fraction of (g/cm3) molar mass H2O: 18.015 g/mol EtOH 0.99706 molar mass EtOH: 0 46.058 g/mol 0.98820 0.05 0.99706 g/cm3 0.785 g/cm3 0.98055 0.1 pH20: 0.97354 0.15 PETOH: 0.96655 0.2 0.25 0.95905 0.95666 0.3 0.35 0.94158 0.93158 0.4 0.92099 0.45 0.90993 0.5 0.89857 0.55 0.88700 0.6 0.87527 0.65 0.86341 0.7 0.85138 0.75 0.83915 0.8 0.82664 0.85 0.81365 0.9 0.79990 0.95 0.78500 1
oson? Data for Question 2: mixture density mole fraction of (g/cm3) molar mass H2O: 18.015 g/mol EtOH 0.99706 molar mass EtOH: 0 46.058 g/mol 0.98820 0.05 0.99706 g/cm3 0.785 g/cm3 0.98055 0.1 pH20: 0.97354 0.15 PETOH: 0.96655 0.2 0.25 0.95905 0.95666 0.3 0.35 0.94158 0.93158 0.4 0.92099 0.45 0.90993 0.5 0.89857 0.55 0.88700 0.6 0.87527 0.65 0.86341 0.7 0.85138 0.75 0.83915 0.8 0.82664 0.85 0.81365 0.9 0.79990 0.95 0.78500 1
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P
Related questions
Question
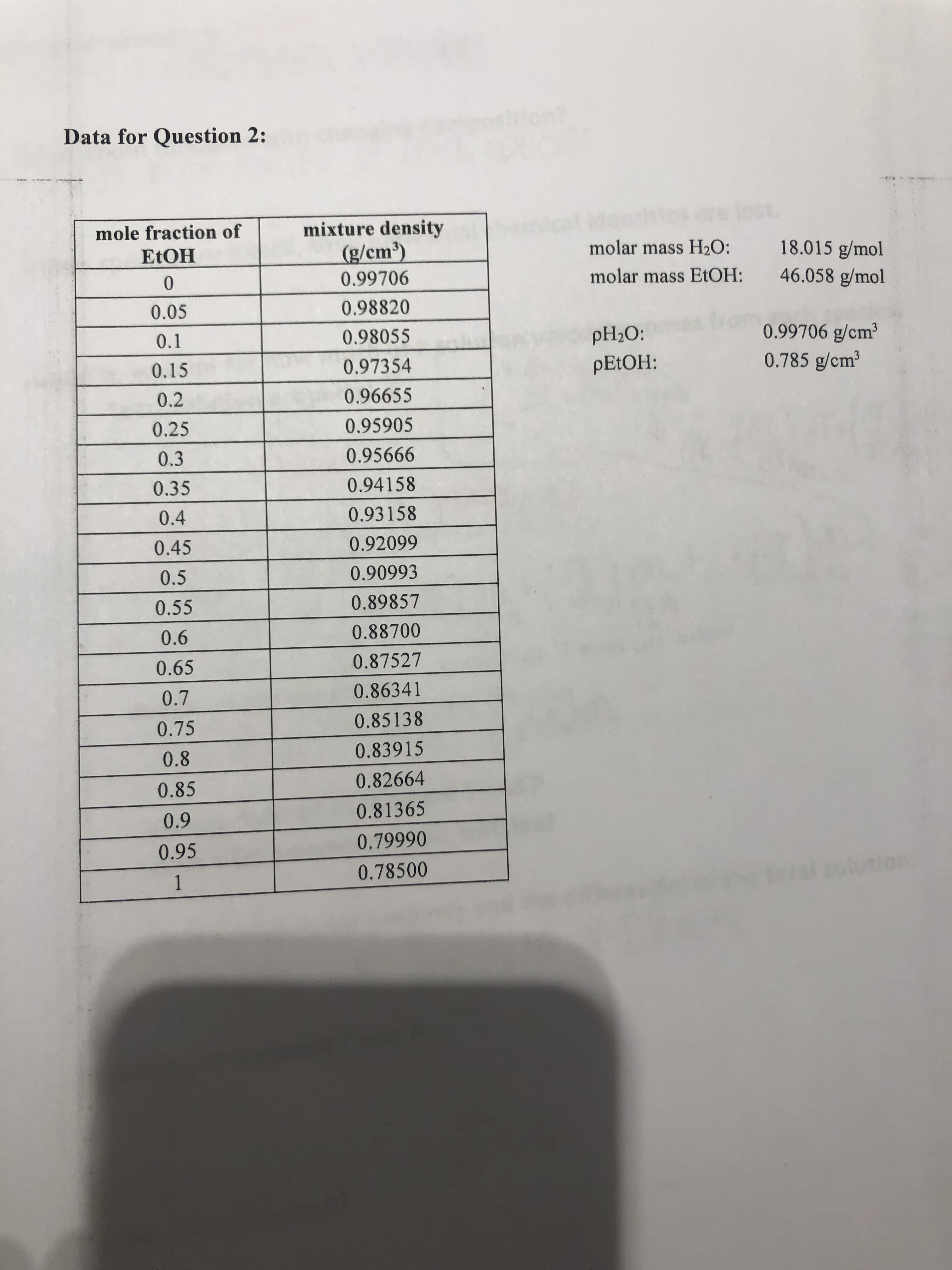
2) Given the data on the next page on the ethanol-water system, determine the following: a) Make a plot of the molar volume of the solution vs. mole fraction of ethanol.
b) On the same plot, graph the molar volume of the solution as a function of mole fraction ethanol if the volumes of pure water and pure ethanol could simply be added.
c) Determine the partial molar volume of both ethanol and water for a solution made from 50 mL of ethanol and 20 mL of water.
d) Using those partial molar volumes, confirm that the total molar volume of a solution of 50 mL ethanol and 20 mL water is not 70 mL.
Transcribed Image Text:oson?
Data for Question 2:
mixture density
mole fraction of
(g/cm3)
molar mass H2O:
18.015 g/mol
EtOH
0.99706
molar mass EtOH:
0
46.058 g/mol
0.98820
0.05
0.99706 g/cm3
0.785 g/cm3
0.98055
0.1
pH20:
0.97354
0.15
PETOH:
0.96655
0.2
0.25
0.95905
0.95666
0.3
0.35
0.94158
0.93158
0.4
0.92099
0.45
0.90993
0.5
0.89857
0.55
0.88700
0.6
0.87527
0.65
0.86341
0.7
0.85138
0.75
0.83915
0.8
0.82664
0.85
0.81365
0.9
0.79990
0.95
0.78500
1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285061238
Author:
Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:
Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780072848236
Author:
Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Companies, The